| Table of Contents |
|---|
...
Microservices Application Pattern
Please see the example applications developed by Chris Richardson. These examples on Github illustrate various aspects of the microservice architecture.
Resulting Context
Benefits
This solution has a number of benefits:
- Enables the continuous delivery and deployment of large, complex applications.
- Improved maintainability - each service is relatively small and so is easier to understand and change
- Better testability - services are smaller and faster to test
- Better deployability - services can be deployed independently
- It enables you to organize the development effort around multiple, autonomous teams. Each (so called two pizza) team owns and is responsible for one or more services. Each team can develop, test, deploy and scale their services independently of all of the other teams.
- Each microservice is relatively small:
- Easier for a developer to understand
- The IDE is faster making developers more productive
- The application starts faster, which makes developers more productive, and speeds up deployments
- Improved fault isolation. For example, if there is a memory leak in one service then only that service will be affected. The other services will continue to handle requests. In comparison, one misbehaving component of a monolithic architecture can bring down the entire system.
- Eliminates any long-term commitment to a technology stack. When developing a new service you can pick a new technology stack. Similarly, when making major changes to an existing service you can rewrite it using a new technology stack.
Drawbacks
This solution has a number of drawbacks:
- Developers must deal with the additional complexity of creating a distributed system:
- Developers must implement the inter-service communication mechanism and deal with partial failure
- Implementing requests that span multiple services is more difficult
- Testing the interactions between services is more difficult
- Implementing requests that span multiple services requires careful coordination between the teams
- Developer tools/IDEs are oriented on building monolithic applications and don’t provide explicit support for developing distributed applications.
- Deployment complexity. In production, there is also the operational complexity of deploying and managing a system comprised of many different services.
- Increased memory consumption. The microservice architecture replaces N monolithic application instances with NxM services instances. If each service runs in its own JVM (or equivalent), which is usually necessary to isolate the instances, then there is the overhead of M times as many JVM runtimes. Moreover, if each service runs on its own VM (e.g. EC2 instance), as is the case at Netflix, the overhead is even higher.
Issues
There are many issues that you must address.
When to use the microservice architecture?
One challenge with using this approach is deciding when it makes sense to use it. When developing the first version of an application, you often do not have the problems that this approach solves. Moreover, using an elaborate, distributed architecture will slow down development. This can be a major problem for startups whose biggest challenge is often how to rapidly evolve the business model and accompanying application. Using Y-axis splits might make it much more difficult to iterate rapidly. Later on, however, when the challenge is how to scale and you need to use functional decomposition, the tangled dependencies might make it difficult to decompose your monolithic application into a set of services.
How to decompose the application into services?
Another challenge is deciding how to partition the system into microservices. This is very much an art, but there are a number of strategies that can help:
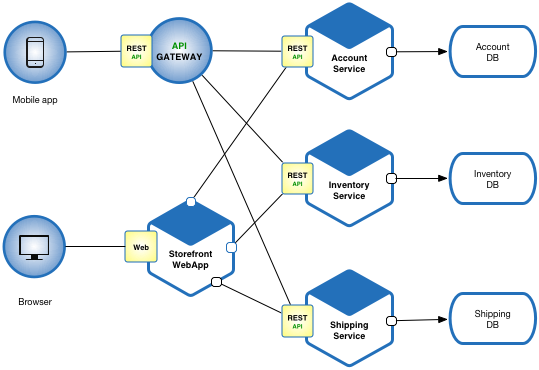
- Decompose by business capability and define services corresponding to business capabilities.
- Decompose by domain-driven design subdomain.
- Decompose by verb or use case and define services that are responsible for particular actions. e.g. a
Shipping Servicethat’s responsible for shipping complete orders. - Decompose by by nouns or resources by defining a service that is responsible for all operations on entities/resources of a given type. e.g. an
Account Servicethat is responsible for managing user accounts.
Ideally, each service should have only a small set of responsibilities. (Uncle) Bob Martin talks about designing classes using the Single Responsibility Principle (SRP). The SRP defines a responsibility of a class as a reason to change, and states that a class should only have one reason to change. It make sense to apply the SRP to service design as well.
Another analogy that helps with service design is the design of Unix utilities. Unix provides a large number of utilities such as grep, cat and find. Each utility does exactly one thing, often exceptionally well, and can be combined with other utilities using a shell script to perform complex tasks.
How to maintain data consistency?
In order to ensure loose coupling, each service has its own database. Maintaining data consistency between services is a challenge because 2 phase-commit/distributed transactions is not an option for many applications. An application must instead use the Saga pattern. A service publishes an event when its data changes. Other services consume that event and update their data. There are several ways of reliably updating data and publishing events including Event Sourcing and Transaction Log Tailing.
How to implement queries?
Another challenge is implementing queries that need to retrieve data owned by multiple services.
- The API Composition and Command Query Responsibility Segregation (CQRS) patterns.
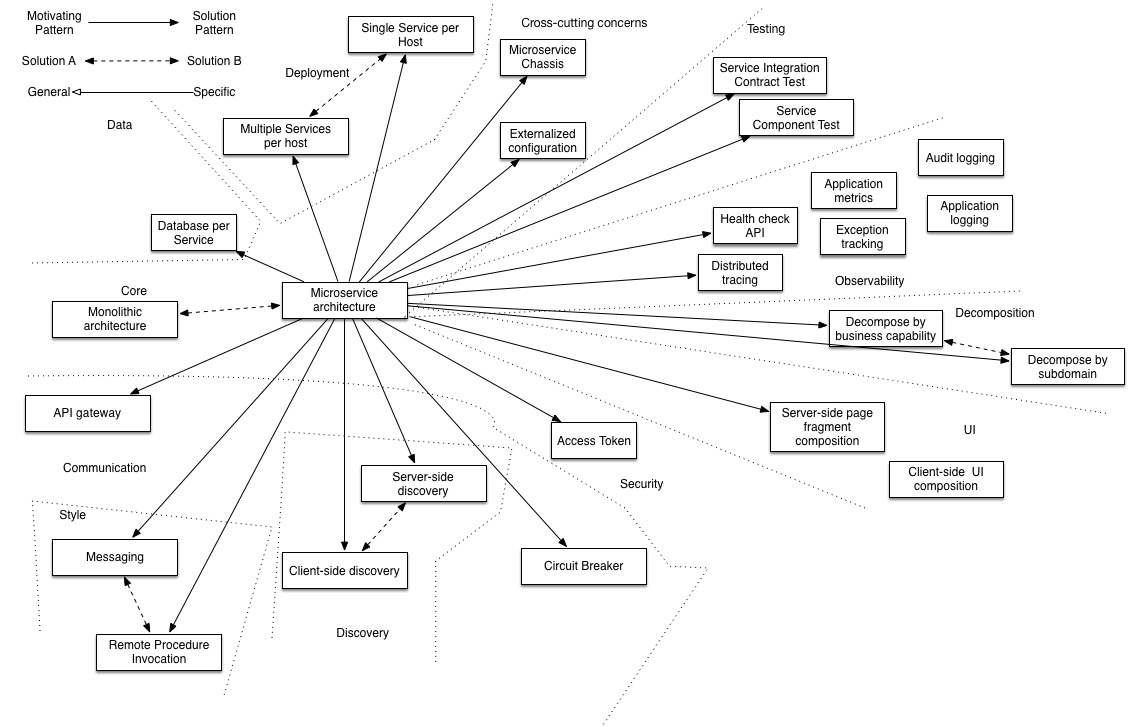
Related patterns for Microservices
There are many patterns related to the microservices pattern. The Monolithic architecture is an alternative to the microservice architecture. The other patterns address issues that you will encounter when applying the microservice architecture.
- Decomposition patterns
- The Database per Service pattern describes how each service has its own database in order to ensure loose coupling.
- The API Gateway pattern defines how clients access the services in a microservice architecture.
- The Client-side Discovery and Server-side Discovery patterns are used to route requests for a client to an available service instance in a microservice architecture.
- The Messaging and Remote Procedure Invocation patterns are two different ways that services can communicate.
- The Single Service per Host and Multiple Services per Host patterns are two different deployment strategies.
- Cross-cutting concerns patterns: Microservice chassis pattern and Externalized configuration
- Testing patterns: Service Component Test and Service Integration Contract Test
- Circuit Breaker
- Access Token
- Observability patterns:
- UI patterns:
Interoperable Blockchain ACID transaction pattern
blockchain interoperability on atomic transactions using escrow transactions
context
blockchains implement escrow transaction interface services in a smart contract
2 independent chains A and B can send messages using a common protocol ( gRPC or ??? )
party A wants to buy X from party B for Y currency amount
problems
how to ensure only authorized parties participate in the transaction
how to ensure both parties will execute their transaction once and only once to complete the purchase transaction
how to ensure that the purchase is cancelled if either party fails to complete their part of the purchase transaction within the designated time limit
pre-requisites
network connectivity
blockchain directory services and access
identity, registration and access management services for all parties in a transaction
each party implements the escrow transaction interfaces
each party communicates using one of the supported protocols: gRPC or ?
each party digital certificates to sign and execute transactions identifying the authorized party
solution
use an escrow transction with smart contracts that
records each parties performance of the obligation
This follows a saga pattern to implement the escrow transaction (eg a purchase ) as a set of linked transactions in smart contracts
Singe Use Tokens are used to guarantee that only this single reservation transaction can be executed once by the designated party
step 0 - party A agrees to buy X from party B for Y currency amount
step 1 - reservation for payment from A to B with a token, reservation for delivery from B to A with a token
step 2 - when both reservations complete, the reservations are executable as smart contracts by each party
each party executes their reservation transaction via smart contract using the supplied token
A executes B's reservation using the token from B
B executes A's reservation using the token from A
alternate scenarios
both reservations are not completed within the agreed time limit, all reservations and tokens are cancelled and resources revert to current owner control
step 3 - if both reservations are not executed as transactions within an agreed time limit, each party is notified to manage the purchase based on agreed policy
step 4 - when both reservations have been executed by each party, all parties are notified of the completion of the escrow transaction
step 5 - any dependent actors are notified of the completion of the purchase which may trigger additional transactions ( eg start an automatic purchase warranty etc )
Potential Value Opportunities
...