| Table of Contents |
|---|
Key Points
References
...
| Table of Contents |
|---|
Key Points
References
| Reference_description_with_linked_URLs_______________________ | Notes_________________________________________________________________ |
|---|---|
https://medium.com/javascript-scene/the-forgotten-history-of-oop-88d71b9b2d9f | Roots of OOP - Alan Kay Smalltalk keys encapsulation, abstraction, delegation, dynamic associations, collaboration via messages, events, listeners, promises benefits - decoupling to reduce complexity, avoiding shared state, adaptability to change ( CIC policy nbr ) |
| Ward Cunningham - Portland Pattern Repository | |
| Gang of Four Design Patterns | |
| https://www.tutorialspoint.com/design_pattern/factory_pattern.htm | G4 Pattern summary tutorials point |
| https://springframework.guru/gang-of-four-design-patterns/ | G4 Pattern summary Spring - 1 page |
| JEE Enterprise Services Patterns | |
| Enterprise Integration Patterns | |
| https://microservices.io/patterns/index.html | Microservices Design Patterns |
| https://microservices.io/patterns/monolithic.html | Monolithic Architecture pattern |
| https://microservices.io/patterns/microservices.html | Microservices Architecture pattern |
| Microservices orchestration vs choreography | |
| https://sites.google.com/a/mammatustech.com/ mammatusmain/reactive-microservices | Reactive microservices pattern |
...
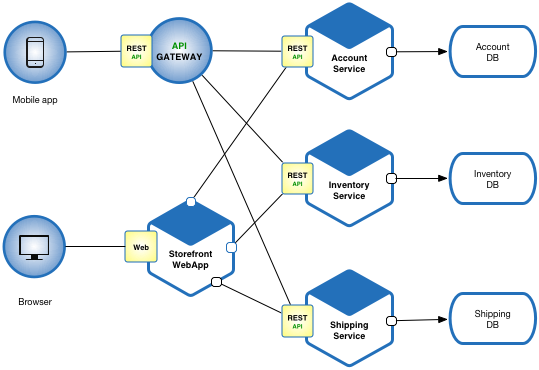
Microservices Application Pattern
Please see the example applications developed by Chris Richardson. These examples on Github illustrate various aspects of the microservice architecture.
Resulting Context
Benefits
...
P2P Escrow Transaction Pattern
goals
- 2 parties complete an atomic swap of asset 1 for asset 2 without risk
- contract config defines terms of the swap
- if swap can't meet completion criteria, swap transaction is reversed for all parties returning initial states for each
- optionally, a 3rd party notary service may need to approve the transaction
- optionally, a 3rd party observer service may record the transaction
- optionally, the 2 parties may be on different networks
...
specific validators only for that transaction type and parties are active
- multi-party contract with roles where config defines terms of the swap
- each party is identified and claims a role ( eg buyer, seller etc )
- define multi-step transaction types
- create transaction instance using the shared transaction manager with workflow from the contract config for that transaction type
- each transaction has a unique ID
- set the parties who validate the transaction on each ledger
- contract takes control over both assets from each party using locks and confirms locks ( if funds or asset limited, policy may allow partial transactions )
- obligation set for each asset in the contract locking a portion of the assets for a time period
- after lock done, the lock status for all assets in the contract is shared
- if all assets in the contract locked, next step executes ( normally the trade )
- funds transferred to new party, assets transferred to new party
- after delivery completed, obligations removed
- after each step, the contract instance is updated for both parties and confirmed
- signatures and consents required by all parties for each step
- state changes are validated as complete on each ledger for the current step before moving to next step - 100% endorsement of each update by relevant parties
- if completion criteria for a step not fulfilled by X time, the transaction is cancelled and all parties are restored to initial states
- completion messages recorded and events published on success or failure of the transaction
context
assume 2 different orgs on 2 different blockchains on 2 different platforms want to execute a sale using an order (any type of asset )
a blockchain with 2 parties as nodes each running a ledger copy and a contract
assume direct payment ( no margin loan ) on purchase transaction
blockchains implement escrow transaction interface services in a smart contract
...
step 5 - any dependent actors are notified of the completion of the purchase which may trigger additional transactions ( eg start an automatic purchase warranty etc )
Hashed Timelock Contract | Hashed Timelock Agreement
https://www.investopedia.com/terms/h/hashed-timelock-contract.asp
https://academy.binance.com/en/glossary/hashed-timelock-contract
Hash Time Locked Contracts (HTLCs) Explained
https://medium.com/liquality/hash-time-locked-contracts-htlcs-explained-e88aa99cc824
Refund scenario for HTLC
leverage HTLCs in Atomic Swaps, but also lead industry-wide efforts to standardize their implementation across different applications and blockchains.
Bitcoin UXTO model
https://river.com/learn/bitcoins-utxo-model/
- Bitcoin does not have accounts with balances. Instead, individual coins are owned by Bitcoin users.
- An Unspent Transaction Output (UTXO) is a discrete piece of bitcoin. UTXOs are used as the inputs of every Bitcoin transaction.
- The UTXO model makes Bitcoin more auditable, transparent, and efficient than traditional financial systems, which rely on accounts, balances, and third parties.
Potential Value Opportunities
...