| Table of Contents |
|---|
...
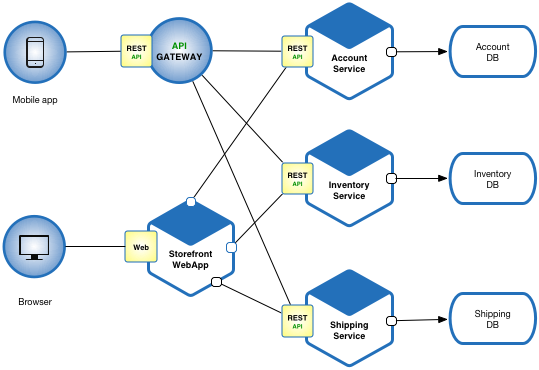
Microservices Application Pattern
Please see the example applications developed by Chris Richardson. These examples on Github illustrate various aspects of the microservice architecture.
Resulting Context
Benefits
...
Interoperable Blockchain ACID transaction pattern
blockchain interoperability on atomic transactions using escrow transactions for DvP
context
assume 2 different orgs on 2 different blockchains on 2 different platforms want to execute a sale using an order (any type of asset )
...
how to ensure only authorized parties participate in the transactiontransactions for settlement of a trade agreement
how to ensure both parties will execute their transaction once and only once to complete the purchase transaction
how to ensure that the purchase is cancelled if either party fails to complete their part of the purchase transaction within the designated time limit
how to prevent either party from failing to deliver or accept delivery of assets or funds per the terms of the trade agreement
pre-requisites
network connectivity and interoperability across all related networks
blockchain directory services and access
...
each party implements the escrow transaction interfaces as buyer, seller and their agents
each party communicates using one of the supported protocols: gRPC or REST api or ?
each party digital certificates to sign and execute transactions identifying the authorized party
gateway nodes connect 2 different logical blockchain networks directly or indirectly ( blockchain networks normally not physical but virtual overlay networks across multiple provider networks )
solution
use an escrow transction transaction with smart contracts that
...
step 5 - any dependent actors are notified of the completion of the purchase which may trigger additional transactions ( eg start an automatic purchase warranty etc )
P2P Escrow Transaction Pattern
goals
- 2 parties complete an atomic swap of asset 1 for asset 2 without risk
- if swap can't meet completion criteria, swap transaction is reversed for all parties returning initial states for each
- optionally, a 3rd party notary service may need to approve the transaction
- optionally, a 3rd party observer service may record the transaction
- optionally, the 2 parties may be on different networks
model
issues with simple saga pattern above - why escrow manager adds value
IF the trade settlement is executed simple on 1 network, real-time using a synchronous model it may work well using simple HTLC
AND both parties fulfill all their obligations to deliver and accept delivery of assets and funds
OTHERWISE 1 or both parties may fail to deliver or accept delivery of the assets or funds for settlement after the trade agreement is set
P2P Escrow Transaction Pattern
goals
- 2 parties complete an atomic swap of asset 1 for asset 2 without risk
- if swap can't meet completion criteria, swap transaction is reversed for all parties returning initial states for each
- optionally, a 3rd party notary service may need to approve the transaction
- optionally, a 3rd party observer service may record the transaction
- optionally, the 2 parties may be on different networks
model
a chain manager ( on a chain ) for other chain transactions ?? ( or a configurable chain model ? )
...
how to ensure both parties will execute their transaction once and only once to complete the purchase transaction
how to ensure each party will accept delivery of assets and funds
how to ensure that the purchase is cancelled if either party fails to complete their part of the purchase transaction within the designated time limit
...
gateway nodes connect 2 different logical blockchain networks directly or indirectly ( blockchain networks normally not physical but virtual overlay networks across multiple provider networks )
solution
use an escrow transction transaction with smart contracts that
...
https://medium.com/liquality/hash-time-locked-contracts-htlcs-explained-e88aa99cc824
Refund scenario for HTLC
leverage HTLCs in Atomic Swaps, but also lead industry-wide efforts to standardize their implementation across different applications and blockchains.
Bitcoin UXTO model
...
https://www.ecb.europa.eu/pub/pdf/other/stella_project_report_march_2018.pdf
Simple DvP Trade Settlement Context, Goals, Landscape
2 parties ( buyer and seller ) each have a custody bank and a settlement bank
assumes security trade place in US markets subject to US rules for settlement
goals include:
- automated, atomic trade settlement of both asset delivery and payment delivery
- minimization of settlement risks for all parties during settlement based on trade agreement, delivery and acceptance of assets and funds
- support full and partial trade settlements based on availability of securities ( assets ) and funds for settlement based on buyer and seller account policies
- regulatory compliance in the jurisdictions the trade and settlement are subject to
- efficient, low-cost trade settlement that scales across multiple networks
The DvP operating landscape is a logical network of independently managed and governed networks
Many payment networks and CBDC networks are independently defined and operated
Many asset networks and CBDC networks are independently defined and operated
Secure, Scalable Interoperability with Operational Governance and Standards across networks is required to execute DvP settlement for any trade between parties
A conceptual diagram showing a logical network for networks
Key Questions to Answer for the DvP Settlement Use Case
- What is the use case?
- What are the parties, roles and goals for each?
- What is the use case context for trade settlement?
- What are the key assumptions in the model?
- What are the key dependencies in the model?
- What are the scenarios for the use case?
- What is the economic model and incentives for parties for the use case and scenarios?
- What is the governance model for parties for the use case and scenarios?
- What are the jurisdictions in effect for regulation and taxation?
- What is the process model and related contracts between parties for each scenario?
- What is the security model for each scenario given the process and parties?
- What is the privacy model for each scenario given the process and parties?
- What is the trust model for each scenario given the process and parties?
- What is the decision model for each scenario?
- What is the public and private data model for each scenario?
Simple DvP Settlement Using HTLC controls
a relevant HTLC process flow for DvP on security trade settlement
it depends on ...
wallets
tokenized assets
tokenized currencies
RTGS
UXTO
parties that fulfill their obligations in the process for all scenarios
challenges ...
needs sync model
needs trusted parties to fulfill their roles regardless of state changes
by scale
by multi-network processing
wallet risks
has execution risks on some scenarios
has regulatory issues to manage not accounted for in simple HTLC
doesn't support partial trades on securities, funds correctly
Escrow DvP Settlement using Orchestration
a relevant Escrow Orchestration process flow for DvP on security trade settlement
it depends on ...
wallets
tokenized assets
tokenized currencies
near-RTGS
account management
netting optimizations
parties that fulfill their obligations in the process for all scenarios
challenges
wallet risks
account risks
supports async model with N-RTGS
with escrow, needs lower trusts by trusted parties to fulfill their roles
scales better with async ( throughput vs transaction latency, nettings optimizations )
by multi-network processing for centralized orchestration
has lower execution risks on some scenarios
has regulatory support accounted for in DSM.O
supports partial trades on securities, funds correctly
Escrow DvP Settlement using Choreography
a relevant Escrow Choreography process flow for DvP on security trade settlement
it depends on ...
wallets
tokenized assets
tokenized currencies
near-RTGS
account management
netting optimizations
parties that fulfill their obligations in the process for all scenarios
challenges
wallet risks
account risks
supports async model with N-RTGS
with escrow, needs lower trusts by trusted parties to fulfill their roles
scales better with async ( throughput vs transaction latency, nettings optimizations )
by multi-network processing for decentralized choreography
has lower execution risks on some scenarios
has regulatory support accounted for in DSM.C
supports partial trades on securities, funds correctly
sequencediagram.io
Potential Value Opportunities
...