| Table of Contents |
|---|
Key Points
- services management has defined goals, models for delivery, operations, support, maintenance, retirement
- services delivery process defined
- services operations standards defined as operations service tiers normally
- services measured at runtime based on execution with results captured summarized by tools like Promtheus, Grafana
- services maturity models exist for referemce
- services catalog can be reviewed to assess current maturity levels vs planned service strategies to identify opportunities
References
| Reference_description_with_linked_URLs_______________________ | Notes______________________________________________________________ |
|---|---|
...
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Capability_Maturity_Model
Key Concepts
Key Concepts for Service Maturity
...
- Establish Metrics: Define what constitutes maturity for your microservices, considering aspects like reliability, scalability, resilience, etc.
- Automated Testing and Monitoring: Use automated tools to continuously monitor and test your microservices, providing real-time feedback on their performance and maturity.
- Service-Level Objectives (SLOs) and Service-Level Indicators (SLIs): SLOs define the level of service you aim to provide, and SLIs are the metrics that measure your actual performance against these objectives.
- Incident Response and Postmortem Analysis: When something goes wrong, have a plan to fix it quickly and then conduct a postmortem analysis to learn from it and improve the maturity of the service.
- Regular Reviews: Regularly review the maturity of your services to identify trends, pinpoint areas for improvement, and track progress over time.
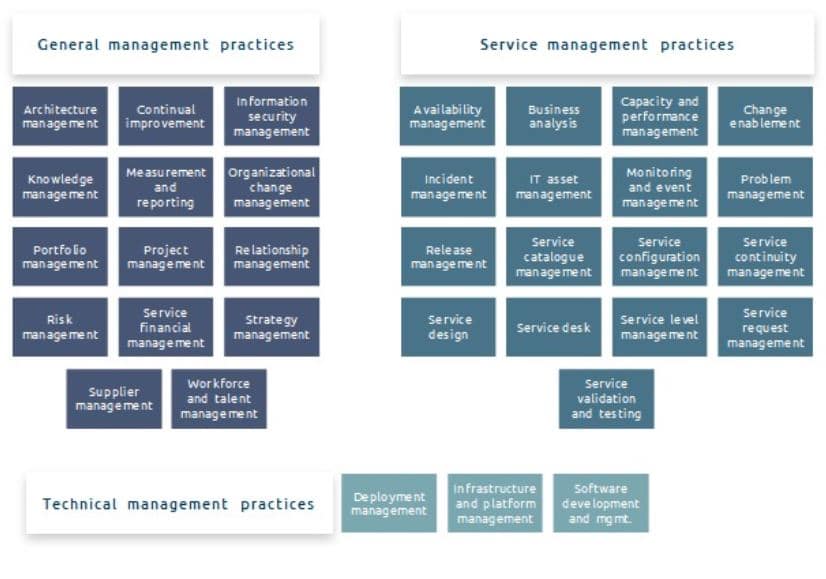
ITIL SVS - Service Value System - Foundation for Service Management
https://www.owlpoint.com/itil-4/itil-service-value-system/
Principles
The guiding principles helps an organization’s decision making by ensuring there is a shared understanding and common approach to service management across the organization. Each of the guiding principles can be used to evaluate whether an approach or decision meets the fundamentals of the organizations goals and helps sets the organization’s behaviors and culture.
Governance
Governance ensures that the actions of the organization are aligned properly with the strategic direction and goals established by the sponsor groups or governing bodies. It is governance that ensures that value is actually achieved, not just talked about as a target.
Service Value Chain
The Service Value Chain is an operating model for the creation, delivery, and continual improvement of services. The service value chain represents a set of key activities that leverage various practices to form different value streams. These value streams can be adapted for different types of organizations, including those that have distributed IT versus a centralized IT.
Practices
Practices are the evolution of processes and functions from previous versions of ITIL. They are a set of organizational resources, based on the elements of the four dimensions of service management, designed for performing work or accomplishing an objective.
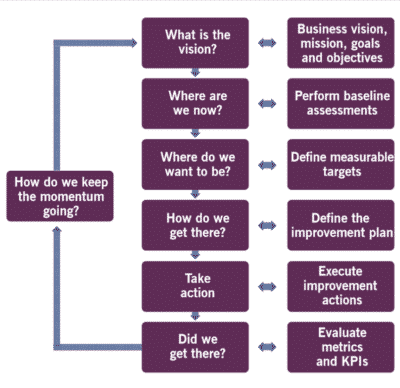
Continual Improvement
Continual Improvement is an ongoing set of organizational activities at all levels that ensure that the organization’s performance continues to meet the evolving objectives of its key stakeholders.
ITIL Maturity Assessments
https://www.owlpoint.com/itil-maturity-model-and-itil-assessment-qa/
Maturity Model vs Maturity Assessment
The ITIL Maturity Model establishes the criteria to achieve each level of maturity of the Service Value System and the capability of each of the 34 ITIL 4 Practices. The ITIL Assessment is a process of evaluating an organization against a specific set of practices and usually the organization’s adoption of a Service Value System using the criteria established by the ITIL Maturity Model.
3 types of Assessments
There are 3 types of assessments that have been defined by AXELOS. They are:
- Comprehensive Assessment – The evaluation of 7 or more practices as well as the components of the ITIL Service Value System
- Capability Assessment – The assessment of selected practices but does not include the SVS components
- Maturity Assessment – The review of the SVS components and up to 6 practices
Capability Maturity Model
CMM Level 1 — Initial
Organizations in the Initial level of the CMM are getting real work done, but often are finishing this work on a delayed timeframe and over their allotted budget
Goal > track work to budget
CMM Level 2 — Managed
Organizational process in the Managed level of the CMM is being managed at least on the project level. This is a huge area of improvement, as the work of the collective is able to be planned, performed, measured, and controlled.
Goal > move to proactive vs reactive projects and solutions
CMM Level 3 — Defined
Organizations in the Defined level of the CMM are on their way to a healthy composition and structure. Processes in level 3 are well characterized and understood, and often are described with standards, procedures, tools, and methods. What really makes the Defined level stand out from the Managed level is the scope of the standards, process descriptions, and overall procedures.
Goal > more usage monitoring and opportunity to expand quantification in all activities along with automation
CMM Level 4 — Quantitatively Managed
Organizations in the Quantitatively Managed level of the CMM are realizing most of their full potential. The big drive in organizations and teams working at level 4 is the inclusions of data and other quantitative information in their processes. The improvement objectives for these individuals are predictable, and all align to meet the expectations of both internal and external stakeholders. These objectives are made based on the needs of the customer, end users, organization, and process implementers.
Goal > automation of service capabilities to fit demand patterns based on quantitative inputs
CMM Level 5 — Optimizing
The ultimate level of maturity for organizations and teams is level 5, Optimizing. The Optimizing level is focused on continuous improvement, and is built to pivot and respond to opportunity and change as it presents itself. This agility is based on the level of stability that the organization has built up over time. This stability allows a baseline of processes that can then be tweaked to better serve the needs of the organization at that present moment. To speak simply: This is an organization firing on all cylinders
Goal > continue optimization and adaptivity as organization grows, changes
CIP - Continuous Improvement Process
BWC defined in. 1985
The purpose of Continual Improvement is to ensure service and products align – and remain aligned – to the Business continuously.
Potential Value Opportunities
Potential Challenges
ITSM and Service Maturity Assessments
Service Maturity Concepts
Resources
https://itsmacademy.com/content/WHATIS_The_ITIL_Maturity_Model.pdf
...
https://www.ibm.com/garage/method/practices/code/tool_lint/
Topics
Background
ITSM, ITSM levels,
...
ascrum NFR can be applied by use case to each mode
Service Assessment Audit
Service 5WH
Definition
Clients
...
Improvement Priorities
Budgeted Projects
Candidate Solutions
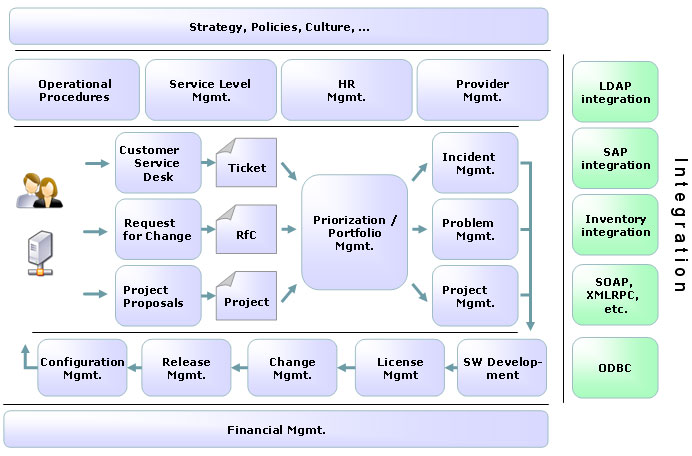
http://www.project-open.com/en/module-itsm
Covers
- Incident Management
- Problem Management
- Change Management
- Configuration Management
- Release Management
- Service Level Management
- Defect Management
- SLA Management
- Configuration Management
http://www.project-open.com/en/process-itsm-service-level-management
Step-by-step guide for Example
| Info |
|---|
sample code block
| Code Block | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||
Recommended Next Steps
Related articles
| Page Properties | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
|
...