| Table of Contents |
|---|
Key Points
- Python or R for analytics? creating models or building models in apps?
References
...
python-4-java-medium.com-Python for JAVA Developers Basics.pdf
https://drive.google.com/open?id=13_28SJ-HBeKR-6-atV4yFOHnOf2Qx0K_
...
Python for Java Developers - quick start
...
https://lobster1234.github.io/2017/05/25/python-java-primer/
https://drive.google.com/open?id=1bSt5RuW8VAGmpE9vYa5x-d02i7TnEyrD
python-4-java-io-lobster1234.github.io-Python Primer for Java Developers.pdf
...
https://realpython.com/oop-in-python-vs-java/
python-4-java-realpython.com-Object-Oriented Programming in Python vs Java.pdf
...
| Table of Contents |
|---|
Key Points
- Python or R for analytics? creating models or building models in apps?
References
...
| Reference_description_with_linked_URLs_______________________ | Notes______________________________________________________________ | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Python basic setup tutorial - Datacamp | Python install, setup, basic tutorial ** | ||||
| https://www.python.org/ | Python.org | ||||
| https://docs.python.org/3/ | Python 3.x docs | ||||
| https://wiki.python.org/moin/ | Python wiki | ||||
| https://github.com/bcafferky/shared | Bryan Cafferky's Python Spark repos ** | ||||
| Bryan Cafferky on youtube | Bryan Python, Spark videos ** | ||||
| https://blog.hubspot.com/website/python-ai-libraries | |||||
| https://wiki.python.org/moin/MovingToPythonFromOtherLanguages | Moving to Python from other languages | ||||
| file/d/1kV1wy4-RJbGXecetFMgab_iOyI4UEFoo/view?usp=sharingPython Anaconda - miniconda distributions and key commands | Python for Java Developers - quick start | ||||
https://thevalleyofcode.com/python/ online python-handbook.pdf file | python handbook | Python Programming for Beginners.pdf. link Python Programming for Beginners.pdf filelobster1234.github.io/2017/05/25/python-java-primer/ https://drive.google.com/open?id=1bSt5RuW8VAGmpE9vYa5x-d02i7TnEyrD python-4-java-io-lobster1234.github.io-Python Primer for Java Developers.pdf | Python for Java Developers - includes file , http io | ||
| Python tutorials ** | |||||
| https://scikit-learn.org/stable/ | Scikit-Learn - | ||||
| https://jupyter.org/ | • Jupyter Notebook - python-4-java-realpython.com-Object-Oriented Programming in Python vs Java.pdf | Python for Java Developers - OO concepts - blog - realpython | |||
| http://anh.cs.luc.edu/170/mynotes/userdefinedjavaobjects.html | Python to Java exercises - convert Python code to Java examples | ||||
| anacondaorg/• Anaconda - com/13-conda-commands-for-data-scientists-e443d275eb89 wwwkaggle | • Kaggle - | Analytics with Python or R | Python Anaconda - miniconda distributions and key commands | ||
https://www.datacampthevalleyofcode.com/community/tutorials/r-or-python-for-data-analysis?fbclid= | Python or R for analytics ? comparison from DataCamp | Billable courses on Python | https://www.udemy.com/course/python-for-data-science-and-machine-learning-bootcamp/ | ML and Python basics - RECOMMENDED first course python/ online python-handbook.pdf file | python handbook |
| https://realpython.com/ | Python tutorials ** | ||||
| https://scikit-learn.org/stable/ | Scikit-Learn - | ||||
| https://jupyter.org/ | • Jupyter Notebook - | ||||
| https://anaconda.org/ | • Anaconda - | ||||
| https://www.udemykaggle.com/course/math-with-python/learn Python and Math | • Kaggle - | ||||
| Analytics with Python or R | |||||
| udemycourse/pytorch-for-deep-learning-with-python-bootcamp/Pytorch intermediate | Python or R for analytics ? comparison from DataCamp | ||||
| Billable courses on Python | |||||
| https://moriohwww.udemy.com/p/n0aRySfEzqFf?f=5c21fb01c16e2556b555ab32&fbclid=IwAR3_QQT4 yej5ns4LXwQQVrT4kH7Gkp44Gx7QvWP4ubxRT-LsvIUXmaHl4Nk | Python and MySQL Tutorial | Django - python scrudcourse/python-for-data-science-and-machine-learning-bootcamp/ | ML and Python basics - RECOMMENDED first course | ||
| https://www.djangoprojectudemy.com/Django homecourse/math-with-python/ | learn Python and Math | ||||
| https://www.djangoprojectudemy.com/start/ | Django getting started | ||||
| https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/3.0/ | Django docs |
Key Concepts
| course/pytorch-for-deep-learning-with-python-bootcamp/ | Pytorch intermediate |
| https://morioh.com/p/n0aRySfEzqFf?f=5c21fb01c16e2556b555ab32&fbclid=IwAR3_QQT4 yej5ns4LXwQQVrT4kH7Gkp44Gx7QvWP4ubxRT-LsvIUXmaHl4Nk | Python and MySQL Tutorial |
| Django - python scrud | |
| https:// |
...
...
| Django home | |
| https://www.djangoproject.com/start/ | Django getting started |
| https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/3.0/ | Django docs |
Key Concepts
Python for Java Developers Quickstart
https://medium.com/nestedif/cheatsheet-python-for-java-developers-98f75c94a1a
...
Python indexes and slices for a six-element list.
Indexes enumerate the elements, slices enumerate the spaces between the elements.
Index from rear: -6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 a=[0,1,2,3,4,5] a[1:]==[1,2,3,4,5]
Index from front: 0 1 2 3 4 5 len(a)==6 a[:5]==[0,1,2,3,4]
+---+---+---+---+---+---+ a[0]==0 a[:-2]==[0,1,2,3]
| a | b | c | d | e | f | a[5]==5 a[1:2]==[1]
+---+---+---+---+---+---+ a[-1]==5 a[1:-1]==[1,2,3,4]
Slice from front: : 1 2 3 4 5 : a[-2]==4
Slice from rear: : -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 :
b=a[:]
b==[0,1,2,3,4,5] (shallow copy of a)- Lose the braces, as you know them, and most of the semicolons, obviously.
- Backslash can be used to allow continuing the program line past a carriage-return, but you almost never have to use it. Python is smart enough to do the right thing when it sees an open bracket, a comma separated list, and a carriage-return.
- Strings are immutable. Whenever you think you have changed a string, remember that you really created a new string.
Where you would use <vector T>, use lists, or tuples, that is [] or (). Where you would use <map T1, T2>, use dictionaries, that is {} .
The semantics of iterators is available, but most of the syntax goes away. for item in alist: iterates over all the items in alist, one by one .. where alist is a sequence, i.e. a list, tuple, or string. To iterate over a sublist, use slices: for item in alist[1:-1]: does as above, but omits the first and last items.
- For trickier iterations, read and re-read the Library doc on the topic of general-purpose functions. There are some functions that apply to sequences: map, filter, reduce, zip. that can work wonders. Hidden somewhere under the documentation for sequences there is a description of string methods that you'll want to read.
Hidden under the docs for 'Other Types' are the descriptions of all the file methods. There are no iostreams per se, but the class method str can get some of the effect for your own classes, and there are surely other angles I haven't thought of.
Forget overloading. You can define a function, and call it with anything you want, but if it has to behave differently for different type operands, you have to use the run-time type identification type function explicitly within the single definition of the function. Default arguments to functions are just as powerful a tool as in C++. Actually polymorphism does work as expected, it just doesn't require deriving from a base class as in C++ or Java.
In class definitions the equivalents of operator methods are covered in a chapter in the Python Language Reference. (Look for the double-underscore methods like __cmp__, __str__, __add__, etc.)
- In C, the gotcha for new users is probably about pointers; they're tricky and they can't be avoided. The gotchas in Python are situations when you use different references to a single object, thinking you are using different objects. I believe the difference between mutable and immutable objects comes into play. I have no clear answers here .. I still get caught once in a while .. keep your eyes open.
- Read the Tutorial once, skim the Library Reference .. at least the table of contents, then skim the Language Reference and you will probably have encountered everything you need.
For reference the excellent Python Quick Reference and the Module Index of the Python docs are generally sufficient.
Python PEP 8: Style Guide for Python Code
Sample Python Projects
Basic Python projects
Python and MySQL Tutorial
sample code
https://github.com/hnasr/python_playground/tree/master/mysqldemopython
| Code Block | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||
import mysql.connector
#connecting to a database
con = mysql.connector.connect(
host = "husseinmac",
user = "root",
password = "password",
database = "husseindb",
port = 3306
)
print("Hey, I think I'm connected")
#cursor
cur = con.cursor()
#insert a new row
for i in range(100):
cur.execute("INSERT INTO employees (ID, NAME) VALUES (%s, %s)", (i+10, f'Mark{i}' ))
#execute the query
cur.execute("SELECT ID,NAME FROM employees")
#cur.execute("SELECT ID,NAME FROM employees where NAME = %s", ("Yara",))
rows = cur.fetchall()
for r in rows:
print(f" ID = {r[0]} NAME = {r[1]}")
#commit the transaction
con.commit()
#close the cursor
cur.close()
#close the connection
con.close() |
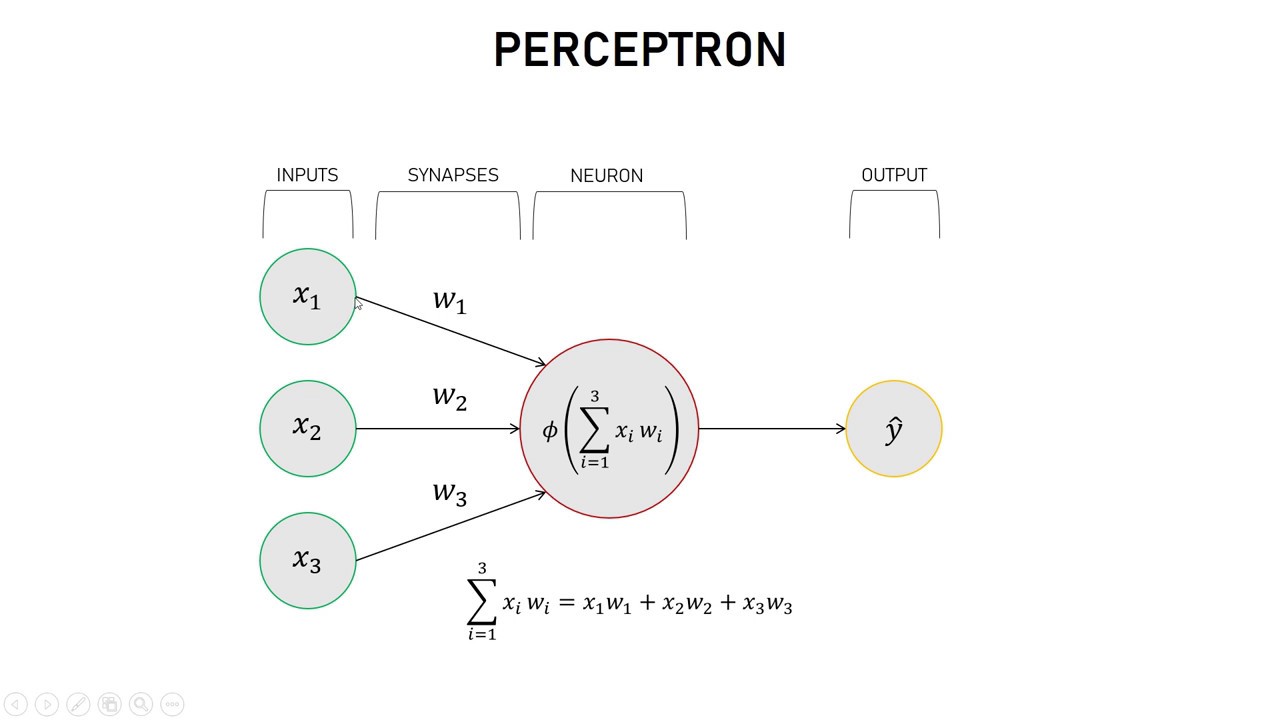
Simplest Neural Network in Python - Perceptron
In this video I'll show you how an artificial neural network works, and how to make one yourself in Python. In the next video we'll make one that is usable, but if you want, that code can already be found on github. I recommend watching at 1.5x speed, unless you're coding along.
video
| Widget Connector | ||
|---|---|---|
|
video 2
| Widget Connector | ||
|---|---|---|
|
https://morioh.com/p/512d41219fda
Github code
https://github.com/jonasbostoen/simple-neural-network
reating a simple neural network in Python with one input layer (3 inputs) and one output neuron. A neural network with no hidden layers is called a perceptron. In the training_version.py I train the neural network in the clearest way possible, but it's not really useable. The outputs of the training can be found in outputs.txt . neural_network.py is an object and can be used by giving in different inputs.
Thanks to Milo Spencer-Harber for this: https://medium.com/technology-invention-and-more/how-to-build-a-simple-neural-network-in-9-lines-of-python-code-cc8f23647ca1
And to Andrew Trask for this: https://iamtrask.github.io/2015/07/12/basic-python-network/
What does it do?
The neural_net.py tries to predict the output given 3 binary inputs. If the first input is 1, the output should be one. Otherwise the output should be 0.
...
| language | py |
|---|---|
| title | simple neural network - perceptron |
| collapse | true |
Build Amazon Price Checker with Python, Selenium
In this FREE LIVE training, Qazi and Jakob will show you how to build an AMAZON Price Tracker with Python and Selenium 🚀
Github Repo 👉 https://github.com/jakobowsky/AmazonPriceTracker
| Widget Connector | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Screen Scrape to create Web dataset with Python, SOAP library
...
Web Scraping with Beautiful Soap
Beautiful Soap is a Library in Python which will provide you some flexible tools to for Web Scraping. Now let’s import some necessary libraries to get started with with our task:
Logistic Regression Using Python
Python Programming for Beginners - Bryan Cafferky
series
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCEdMzQ0m9WcZQepgizrHpMw
p1 -get started
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iL1DJSpRxaM&t=7s
p2 - syntax
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Y69OtFzeY-Y&t=32s
p3 - variables
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oLYJIBOLfGI&t=2s
Python and SQL series - Bryan Cafferky
Python + SQL: Part 1 - The Easiest Way
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xY54Emo8rQM
Why use SQLite ?
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=E7aY1XJX1og&t=147s
Using SQLite Studio
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dugUk893gxQ
Python and Postgres Video Series
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=u-c6rhd8MJc
https://github.com/bcafferky/shared/tree/master/PythonPostgreSQLUpsert
...
...
Potential Value Opportunities
Potential Challenges
...
b=a[:]
b==[0,1,2,3,4,5] (shallow copy of a)- Lose the braces, as you know them, and most of the semicolons, obviously.
- Backslash can be used to allow continuing the program line past a carriage-return, but you almost never have to use it. Python is smart enough to do the right thing when it sees an open bracket, a comma separated list, and a carriage-return.
- Strings are immutable. Whenever you think you have changed a string, remember that you really created a new string.
Where you would use <vector T>, use lists, or tuples, that is [] or (). Where you would use <map T1, T2>, use dictionaries, that is {} .
The semantics of iterators is available, but most of the syntax goes away. for item in alist: iterates over all the items in alist, one by one .. where alist is a sequence, i.e. a list, tuple, or string. To iterate over a sublist, use slices: for item in alist[1:-1]: does as above, but omits the first and last items.
- For trickier iterations, read and re-read the Library doc on the topic of general-purpose functions. There are some functions that apply to sequences: map, filter, reduce, zip. that can work wonders. Hidden somewhere under the documentation for sequences there is a description of string methods that you'll want to read.
Hidden under the docs for 'Other Types' are the descriptions of all the file methods. There are no iostreams per se, but the class method str can get some of the effect for your own classes, and there are surely other angles I haven't thought of.
Forget overloading. You can define a function, and call it with anything you want, but if it has to behave differently for different type operands, you have to use the run-time type identification type function explicitly within the single definition of the function. Default arguments to functions are just as powerful a tool as in C++. Actually polymorphism does work as expected, it just doesn't require deriving from a base class as in C++ or Java.
In class definitions the equivalents of operator methods are covered in a chapter in the Python Language Reference. (Look for the double-underscore methods like __cmp__, __str__, __add__, etc.)
- In C, the gotcha for new users is probably about pointers; they're tricky and they can't be avoided. The gotchas in Python are situations when you use different references to a single object, thinking you are using different objects. I believe the difference between mutable and immutable objects comes into play. I have no clear answers here .. I still get caught once in a while .. keep your eyes open.
- Read the Tutorial once, skim the Library Reference .. at least the table of contents, then skim the Language Reference and you will probably have encountered everything you need.
For reference the excellent Python Quick Reference and the Module Index of the Python docs are generally sufficient.
Python PEP 8: Style Guide for Python Code
Sample Python Projects
Basic Python projects
Python and MySQL Tutorial
sample code
https://github.com/hnasr/python_playground/tree/master/mysqldemopython
| Code Block | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||
import mysql.connector
#connecting to a database
con = mysql.connector.connect(
host = "husseinmac",
user = "root",
password = "password",
database = "husseindb",
port = 3306
)
print("Hey, I think I'm connected")
#cursor
cur = con.cursor()
#insert a new row
for i in range(100):
cur.execute("INSERT INTO employees (ID, NAME) VALUES (%s, %s)", (i+10, f'Mark{i}' ))
#execute the query
cur.execute("SELECT ID,NAME FROM employees")
#cur.execute("SELECT ID,NAME FROM employees where NAME = %s", ("Yara",))
rows = cur.fetchall()
for r in rows:
print(f" ID = {r[0]} NAME = {r[1]}")
#commit the transaction
con.commit()
#close the cursor
cur.close()
#close the connection
con.close() |
Simplest Neural Network in Python - Perceptron
In this video I'll show you how an artificial neural network works, and how to make one yourself in Python. In the next video we'll make one that is usable, but if you want, that code can already be found on github. I recommend watching at 1.5x speed, unless you're coding along.
video
| Widget Connector | ||
|---|---|---|
|
video 2
| Widget Connector | ||
|---|---|---|
|
https://morioh.com/p/512d41219fda
Github code
https://github.com/jonasbostoen/simple-neural-network
reating a simple neural network in Python with one input layer (3 inputs) and one output neuron. A neural network with no hidden layers is called a perceptron. In the training_version.py I train the neural network in the clearest way possible, but it's not really useable. The outputs of the training can be found in outputs.txt . neural_network.py is an object and can be used by giving in different inputs.
Thanks to Milo Spencer-Harber for this: https://medium.com/technology-invention-and-more/how-to-build-a-simple-neural-network-in-9-lines-of-python-code-cc8f23647ca1
And to Andrew Trask for this: https://iamtrask.github.io/2015/07/12/basic-python-network/
What does it do?
The neural_net.py tries to predict the output given 3 binary inputs. If the first input is 1, the output should be one. Otherwise the output should be 0.
| Code Block | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||
Build Amazon Price Checker with Python, Selenium
In this FREE LIVE training, Qazi and Jakob will show you how to build an AMAZON Price Tracker with Python and Selenium 🚀
Github Repo 👉 https://github.com/jakobowsky/AmazonPriceTracker
| Widget Connector | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Screen Scrape to create Web dataset with Python, SOAP library
Web Scraping using Python To Create a Dataset | Data Science | Machine Learning | Python
In this article I will show you how you can create your own dataset by Web Scraping using Python. Web Scraping means to extract a set of data from web. If you are a programmer, a Data Scientist, Engineer or anyone who works by manipulating the data, the skills of Web Scrapping will help you in your career. Suppose you are working on a project where no data is available, then how you are going to collect the data. In this situation Web Scraping skills will help you.
Web Scraping with Beautiful Soap
Beautiful Soap is a Library in Python which will provide you some flexible tools to for Web Scraping. Now let’s import some necessary libraries to get started with with our task:
Logistic Regression Using Python
Python Libraries
https://blog.hubspot.com/website/python-ai-libraries
Introduction-To-Python.pdf. link
Python Programming for Beginners - Bryan Cafferky
series
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCEdMzQ0m9WcZQepgizrHpMw
p1 -get started
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iL1DJSpRxaM&t=7s
p2 - syntax
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Y69OtFzeY-Y&t=32s
p3 - variables
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oLYJIBOLfGI&t=2s
Python and SQL series - Bryan Cafferky
Python + SQL: Part 1 - The Easiest Way
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xY54Emo8rQM
Why use SQLite ?
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=E7aY1XJX1og&t=147s
Using SQLite Studio
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dugUk893gxQ
Python and Postgres Video Series
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=u-c6rhd8MJc
https://github.com/bcafferky/shared/tree/master/PythonPostgreSQLUpsert
Potential Value Opportunities
Potential Challenges
Candidate Solutions
The Quick Python Book, Fourth Edition“ by Naomi Ceder - review
Dunja Nikitovic <duni@manning.com>
Please let me know if you would like to take part in the review and I will share review instructions.
Thank you for joining us in this review, your support means a lot to us.
Chapters 1-17 from "The Quick Python Book, Fourth Edition" by Naomi Ceder are ready for the second review. More information about the book and its full table of contents is available here.
The due date for submitting the feedback is August 26th 2024.
If you see that you won’t be able to provide feedback, or that you could use more time to review, let me know as soon as you can!
The manuscript is available on the following link. You need to sign in with your Manning account to access it:
https://livebook.manning.com/book/ceder5/chapter-1/r-2
You leave comments in the manuscript by selecting a word, sentence, or a paragraph and choosing the "Annotate" icon. Also, you can rate individual figures, listings, code snippets or sections by clicking "like", "don't like" or "neutral" icons below them and leaving the comment.
While you read, or at the end of the review, you should fill the manuscript review questionnaire available at any moment on the following link:
By accessing the manuscript you agree that you will not duplicate it or use the material to create a similar book nor discuss its contents with potential authors of similar books until this book is published or canceled.
We are making all reviews anonymous to obtain more constructive comments. Your review will be made anonymous prior to submitting to the author.
We -- that is the publisher and the author -- appreciate your assistance in making this book as useful as possible to its readers.
Thank you and kind regards,
--
Step-by-step guide for Example
...