Key Points
- services management has defined goals, models for delivery, operations, support, maintenance, retirement
- services delivery process defined
- services operations standards defined as operations service tiers normally
- services measured at runtime based on execution with results captured summarized by tools like Promtheus, Grafana
- services maturity models exist for referemce
- services catalog can be reviewed to assess current maturity levels vs planned service strategies to identify opportunities
References
| Reference_description_with_linked_URLs_______________________ | Notes______________________________________________________________ |
|---|---|
Architecture Themes
ascrum definitions
Concepts on Service Maturity
https://docs.splunk.com/Documentation/Splunk/latest/RESTREF/RESTmetrics
https://spiresearch.com/psmaturitymodel/service-maturity-levels.html
https://plextrac.com/capability-maturity-model-cmm/
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/cmmi/cmmi-maturity-levels.htm
https://www.megatronicstech.com/maturity-level-of-technology/
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Capability_Maturity_Model
Key Concepts
Key Concepts for Service Maturity
- Correctness: The microservice does what it is intended to do without causing errors.
- Reliability: The microservice can perform its intended function consistently over time.
- Efficiency: The microservice provides value for the resources it consumes (like memory, CPU time, etc.).
- Resilience: The microservice can handle failures gracefully, both within itself and when other services fail.
- Scalability: The microservice can handle increased load by either scaling up (using more resources on a single node) or scaling out (distributing the load across multiple nodes).
- Manageability: The ease with which the microservice can be monitored, managed, and updated.
- Operability: The degree to which the microservice supports the tasks that operators need to do, like deploying new versions, scaling, diagnosing problems, etc.
Reference: The Maturity of Microservices
Importance of Measuring Service Maturity
Measuring service maturity is crucial for several reasons:
- Quality Assurance: Helps to ensure that all microservices meet the organization's standards for performance and reliability.
- Risk Mitigation: Identifies potential issues before they become larger problems.
- Resource Allocation: Informs decisions about where to invest time and resources for improvement.
- Performance Benchmarking: Provides a means of tracking improvement over time.
- Return on Investment: Mature services provide more value for the resources consumed, increasing the return on investment.
Reference: Microservices Maturity Assessment
Ideas for Measuring Service Maturity
- Establish Metrics: Define what constitutes maturity for your microservices, considering aspects like reliability, scalability, resilience, etc.
- Automated Testing and Monitoring: Use automated tools to continuously monitor and test your microservices, providing real-time feedback on their performance and maturity.
- Service-Level Objectives (SLOs) and Service-Level Indicators (SLIs): SLOs define the level of service you aim to provide, and SLIs are the metrics that measure your actual performance against these objectives.
- Incident Response and Postmortem Analysis: When something goes wrong, have a plan to fix it quickly and then conduct a postmortem analysis to learn from it and improve the maturity of the service.
- Regular Reviews: Regularly review the maturity of your services to identify trends, pinpoint areas for improvement, and track progress over time.
Potential Value Opportunities
Potential Challenges
ITSM and Service Maturity Assessments
Service Maturity Concepts
Resources
https://itsmacademy.com/content/WHATIS_The_ITIL_Maturity_Model.pdf
https://about.gitlab.com/handbook/engineering/infrastructure/service-maturity-model/
ITSM
ITSM levels
https://www.infopulse.com/blog/itsm-maturity-assessment-checklist
https://www.infotech.com/research/service-management-maturity-assessment-tool
W3school on api / capabilities
Oai
Api design patterns
Api design practices
ETE
Functional, NFR, linting for patterns / reuse
E2M2 for higher reuse
Smarter apps, services using interfaces in xucs to find / gen / apply ABC parts
https://www.ibm.com/garage/method/practices/code/tool_lint/
Topics
Background
ITSM, ITSM levels,
Service criticality
Service SLA, SLOs, SLIs
Environment policies
SDP life cycle
Maturity Dimenions
Management models
Service Dimensions and related Policies
Functional
NFR
Economic
Governance
Operations
Support
Capability Mapping
Service maturity is a general conceptual framework to measure service maturity
If the solution and the environment are measuring KPIs, SLOs, incidents by severity level, automated operations management etc then service maturity isn’t a desk exercise with limited validity but a sustainable reflection of the quality of the managed environment covering the SDP for clients and operators of the environment.
CMM levels applied to Service Maturity
Modes
Definition, delivery, operation, support, improvement
Each mode has operational features / attributes
ascrum NFR can be applied by use case to each mode
Service Assessment Audit
Service 5WH
Definition
Clients
Client survey results
ITSM - SLA, SLO, SLI, incidents, root cause summary
Alignment with IT Strategy, Operations
Environments
Audit Areas > VCRS for each Dimension
Findings
Recommendations by area
Improvement Priorities
Budgeted Projects
Candidate Solutions
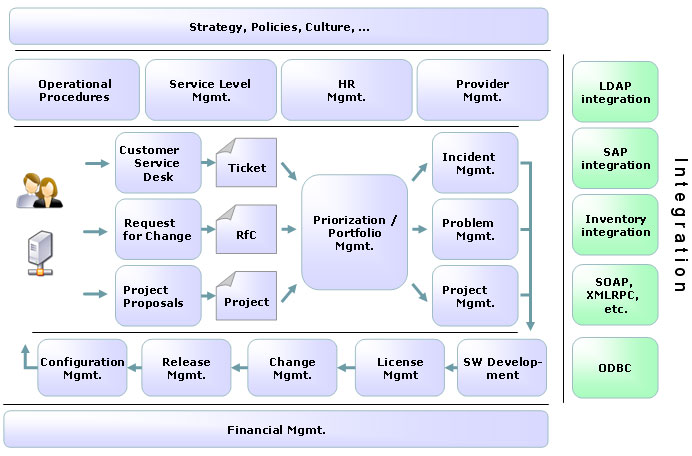
http://www.project-open.com/en/module-itsm
Covers
- Incident Management
- Problem Management
- Change Management
- Configuration Management
- Release Management
- Service Level Management
- Defect Management
- SLA Management
- Configuration Management
http://www.project-open.com/en/process-itsm-service-level-management
Step-by-step guide for Example
sample code block