...
gcp services match apache open-source projects
References
| Reference_description_with_linked_URLs___________________________ | Notes_____________________________________________________________ |
|---|---|
| https://cloud.google.com/solutions/#smart-business-analytics-ai | GCP pricing page for services |
| https://cloudonair.withgoogle.com/cloud101?utm_source=linkedin&utm_medium=sponsoredupdates&utm_content=fundamentals&utm_ campaign=FY19-Q4-NORTHAM-onair-displaypaidsocial-er-GC_None_OnAir_Northam &dclid=CMSy9-bxveYCFURjwQod4ucHuQ | Online GCP training webinars |
| Google Cloud Platform in Action 1st edition ebook | |
| https://www.infoq.com/news/2020/11/eventarc-google-cloud-run/ | Eventarc notifications for Google Cloud Run serverless functions for automation |
Key Concepts
Potential Value Opportunities
...
Any thoughts?
@piotr.s.brainhub haven’t we had these changes running for a week already without issue? That’s what confusing if this is actually related to the issue i’m describing above. (edited)
Candidate Solutions
CloudEvents standard
https://github.com/cloudevents/spec/blob/master/primer.md
The source generates a message where the event is encapsulated in a protocol. The event arrives to a destination, triggering an action which is provided with the event data.
A source is a specific instance of a source-type which allows for staging and test instances. Open source software of a specific source-type may be deployed by multiple companies or providers.
Events can be delivered through various industry standard protocols (e.g. HTTP, AMQP, MQTT, SMTP), open-source protocols (e.g. Kafka, NATS), or platform/vendor specific protocols (AWS Kinesis, Azure Event Grid).
An action processes an event defining a behavior or effect which was triggered by a specific occurrence from a specific source. While outside of the scope of the specification, the purpose of generating an event is typically to allow other systems to easily react to changes in a source that they do not control. The source and action are typically built by different developers. Often the source is a managed service and the action is custom code in a serverless Function (such as AWS Lambda or Google Cloud Functions).
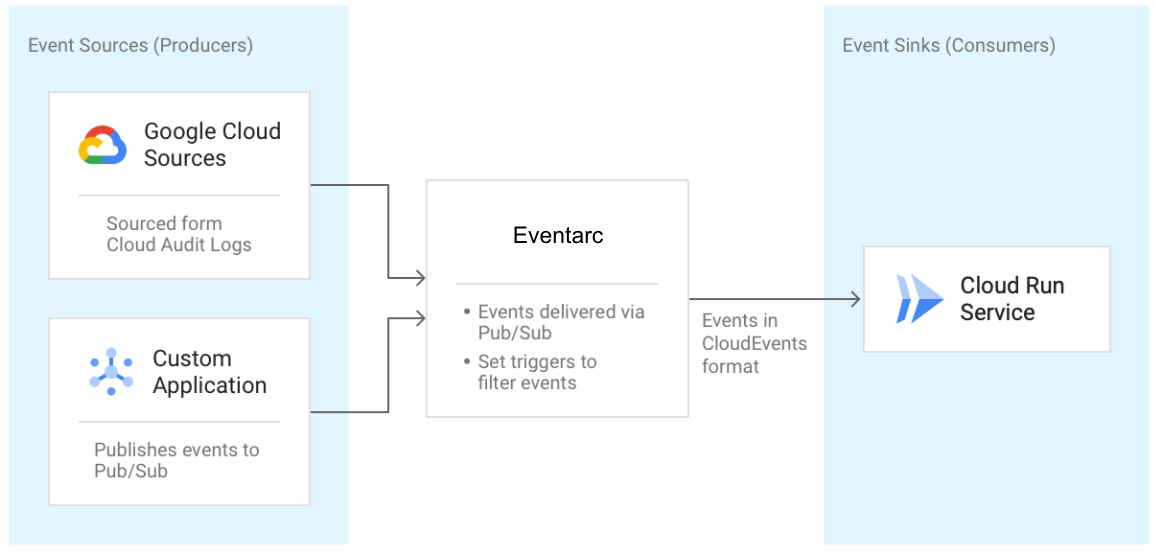
Eventarc notifications for Google Cloud Run serverless functions for automation
https://www.infoq.com/news/2020/11/eventarc-google-cloud-run/
customers can use Eventarc to address use cases such as video analysis, file conversion, new user signup, application monitoring, and hundreds of others by acting on events that originate from Cloud Storage, BigQuery, Firestore, and more than 60 other Google Cloud sources. Eventarc supports:
- Receiving events from 60+ Google Cloud sources (via Cloud Audit logs)
- Receiving events from custom sources by publishing to Pub/Sub – customer's code can send events to signal between microservices
- Adhere to the CloudEvents standard for all events, regardless of source, to ensure a consistent developer experience
- On-demand scalability and no minimum fees
The underlying delivery mechanism in Eventarc is Pub/Sub, and topics and subscriptions. Event sources produce events and publish them on the Pub/Sub topic in any format. Subsequently, the events are delivered to the Google Run sinks. Developers can use Eventarc for applications running on Cloud Run to use a Cloud Storage event (via Cloud Audit Logs) to trigger a data processing pipeline or an event from custom sources (publishing to Cloud Pub/Sub) to signal between microservices.
Source: https://codelabs.developers.google.com/codelabs/cloud-run-events#2
Step-by-step guide for Example
...