| Table of Contents |
|---|
Key Points
- provides REST api to NoSQL documents
- supports basic aggregation
- has Fauxton admin browser for Web queries using NoSQL without coding
- does not support JDBC access from other tools directly for easy reporting
- see CAMEL for some data integration options with Java, XML
- CouchDB v4x will use FoundationDB key-value store as the storage engine
- Mango query in Fauxton client is similar to Mongo Query syntax
References
...
Mango Query in Fauxton client or via REST api
supports: CRUD and create-index
...
CouchDb is migrating to FoundationDB in version 4.0
FoundationDB has an old JDBC driver that may still work
...
https://github.com/jcouchdb/jcouchdb-site/blob/master/Tutorial.wiki
...
https://code.google.com/archive/p/jcouchdb/
Google Code Archive - jcouchdb archived - for Java 5 .pdf
mailing list for jcouchdb
...
http://fforw.github.io/svenson/
jcouchdb- parser- lib -Svenson by fforw.pdf
...
Kivik - CouchDB CLI admin tool
https://github.com/go-kivik/xkivik/releases
...
Key Concepts
CouchDb Setup
https://docs.couchdb.org/en/stable/install/index.html
Setup TLS access for CouchDB
haproxy should be as simple as installing the binary on your *NIX platform, then using something similar to our shipped configuration:
Also, I see this walkthrough is referenced elsewhere as working for Let's Encrypt and CouchDB:
https://www.joshmorony.com/creating-a-couchdb-database-on-an-ubuntu-server-digital-ocean/
Basic CouchDb Operations
CouchDB Design Documents
https://docs.couchdb.org/en/stable/ddocs/index.html#
CouchDB supports special documents within databases known as “design documents”. These documents, mostly driven by JavaScript you write, are used to build indexes, validate document updates, format query results, and filter replications.
Note: Previously, the functionality provided by CouchDB’s design documents, in combination with document attachments, was referred to as “CouchApps.” The general principle was that entire web applications could be hosted in CouchDB, without need for an additional application server.
Use of CouchDB as a combined standalone database and application server is no longer recommended. There are significant limitations to a pure CouchDB web server application stack, including but not limited to: fully-fledged fine-grained security, robust templating and scaffolding, complete developer tooling, and most importantly, a thriving ecosystem of developers, modules and frameworks to choose from.
Apache camel data service overview
https://cwiki.apache.org/confluence/display/CAMEL/Index
Apache Camel ™ is a versatile open-source integration framework based on known Enterprise Integration Patterns.
Camel empowers you to define routing and mediation rules in a variety of domain-specific languages, including a Java-based Fluent API, Spring or Blueprint XML Configuration files, and a Scala DSL. This means you get smart completion of routing rules in your IDE, whether in a Java, Scala or XML editor.
Apache Camel uses URIs to work directly with any kind of Transport or messaging model such as HTTP, ActiveMQ, JMS, JBI, SCA, MINA or CXF, as well as pluggable Components and Data Format options. Apache Camel is a small library with minimal dependencies for easy embedding in any Java application. Apache Camel lets you work with the same API regardless which kind of Transport is used - so learn the API once and you can interact with all the Components provided out-of-box.
Apache Camel provides support for Bean Binding and seamless integration with popular frameworks such as CDI, Spring, Blueprint and Guice. Camel also has extensive support for unit testing your routes.
The following projects can leverage Apache Camel as a routing and mediation engine:
- Apache ServiceMix - a popular distributed open source ESB and JBI container
- Apache ActiveMQ - a mature, widely used open source message broker
- Apache CXF - a smart web services suite (JAX-WS and JAX-RS)
- Apache Karaf - a small OSGi based runtime in which applications can be deployed
- Apache MINA - a high-performance NIO-driven networking framework
Postman CRUD tests on CouchDB
https://dzone.com/articles/couchdb-rest-api-for-document-crud-operations-exam
React.js frontend tutorial using nano for CouchDB CRUD services
https://scriptverse.academy/tutorials/reactjs-couchdb.html
couchdb-CRUD-ReactReactJS and CouchDB CRUD Operations w Nano.pdf
Fauxton admin client for CouchDB
Fauxton Visual Guide
https://couchdb.apache.org/fauxton-visual-guide/
fauxton readthedocs
https://docs.couchdb.org/en/master/fauxton/index.html
fauxton setup
https://docs.couchdb.org/en/stable/fauxton/install.html
fauxton github
https://github.com/apache/couchdb-fauxton
Using Fauxton article
Fauxton setup
Go to couchdb.apache.org, and click download
Learn how to install and setup CouchDB from here, then go to http://127.0.0.1:5984/_utils
Fauxton URL
http://<my-server-or-ip>:5984/_utils/index.html
Using Fauxton
https://couchdb.apache.org/fauxton-visual-guide/#_all_dbs
CouchDB Mango Query in Fauxton client or API
https://github.com/apache/couchdb-mango
Mango provides a single HTTP API endpoint that accepts JSON bodies via HTTP POST. These bodies provide a set of instructions that will be handled with the results being returned to the client in the same order as they were specified. The general principle of this API is to be simple to implement on the client side while providing users a more natural conversion to Apache CouchDB than would otherwise exist using the standard RESTful HTTP interface that already exists.
Mango API design
The general API exposes a set of actions that are similar to what MongoDB exposes (although not all of MongoDB's API is supported). These are meant to be loosely and obviously inspired by MongoDB but without too much attention to maintaining the exact behavior.
Each action is specified as a JSON object with a number of keys that affect the behavior. Each action object has at least one field named "action" which must have a string value indicating the action to be performed. For each action there are zero or more fields that will affect behavior. Some of these fields are required and some are optional.
For convenience, the HTTP API will accept a JSON body that is either a single JSON object which specifies a single action or a JSON array that specifies a list of actions that will then be invoked serially. While multiple commands can be batched into a single HTTP request, there are no guarantees about atomicity or isolation for a batch of commands.
Configure Mango on a cluster
Query can be enabled by setting the following config:
...
Mango HTTP API Design
This API adds a single URI endpoint to the existing CouchDB HTTP API. Creating databases, authentication, Map/Reduce views, etc are all still supported exactly as currently document. No existing behavior is changed.
The endpoint added is for the URL pattern /dbname/_query and has the following characteristics:
- The only HTTP method supported is
POST. - The request
Content-Typemust beapplication/json. - The response status code will either be
200,4XX, or5XX - The response
Content-Typewill beapplication/json - The response
Transfer-Encodingwill bechunked. - The response is a single JSON object or array that matches to the single command or list of commands that exist in the request.
This is intended to be a significantly simpler use of HTTP than the current APIs. This is motivated by the fact that this entire API is aimed at customers who are not as savvy at HTTP or non-relational document stores. Once a customer is comfortable using this API we hope to expose any other "power features" through the existing HTTP API and its adherence to HTTP semantics.
Supports CRUD and manage indexes
Mango Query Examples
implicit or explicit and syntax
{"foo": "bar", "baz": true}
{"$and": [{"foo": {"$eq": "bar"}}, {"baz": {"$eq": true}}]}object subfields in a doc
{"location": {"city": "Omaha"}}
{"location.city": "Omaha"}escape char = \ , operator prefix = $
{"age": {"$gt": 21}}The list of combining characters:
- "$and" - array argument
- "$or" - array argument
- "$not" - single argument
- "$nor" - array argument
- "$all" - array argument (special operator for array values)
- "$elemMatch" - single argument (special operator for array values)
- "$allMatch" - single argument (special operator for array values)
Condition Operators
Each of the combining operators take a single argument that is either a condition operator or an array of condition operators.
The list of combining characters:
- "$and" - array argument
- "$or" - array argument
- "$not" - single argument
- "$nor" - array argument
- "$all" - array argument (special operator for array values)
- "$elemMatch" - single argument (special operator for array values)
- "$allMatch" - single argument (special operator for array values)
Condition Operators
Condition operators are specified on a per field basis and apply to the value indexed for that field. For instance, the basic "$eq" operator matches when the indexed field is equal to its argument. There is currently support for the basic equality and inequality operators as well as a number of meta operators. Some of these operators will accept any JSON argument while some require a specific JSON formatted argument. Each is noted below.
The list of conditional arguments:
(In)equality operators
- "$lt" - any JSON
- "$lte" - any JSON
- "$eq" - any JSON
- "$ne" - any JSON
- "$gte" - any JSON
- "$gt" - any JSON
Object related operators
- "$exists" - boolean, check whether the field exists or not regardless of its value
- "$type" - string, check the document field's type
Array related operators
- "$in" - array of JSON values, the document field must exist in the list provided
- "$nin" - array of JSON values, the document field must not exist in the list provided
- "$size" - integer, special condition to match the length of an array field in a document. Non-array fields cannot match this condition.
Misc related operators
- "$mod" - [Divisor, Remainder], where Divisor and Remainder are both positive integers (ie, greater than 0). Matches documents where (field % Divisor == Remainder) is true. This is false for any non-integer field
- "$regex" - string, a regular expression pattern to match against the document field. Only matches when the field is a string value and matches the supplied matches
Sort
The sort syntax is a basic array of field name and direction pairs. It looks like such:
[{field1: dir1} | ...]
Where field1 can be any field (dotted notation is available for sub-document fields) and dir1 can be "asc" or "desc".
Fields
Unlike MongoDB only the fields specified are included, there is no automatic inclusion of the "_id" or other metadata fields when a field list is included.
A trivial example:
["foo", "bar", "baz"]
More Mango Query Examples - regex, lists, starting date
...
CouchDB migration to FoundationDB
https://forums.foundationdb.org/t/update-couchdb-4-0-on-foundationdb/1690
FoundationDB JDBC driver notes
https://javalibs.com/artifact/com.foundationdb/fdb-sql-layer-jdbc
IDEA - implement JDBC driver for Mango client to connect BI tools
support defined JDBC type 4 client interfaces ..
Driver
Connection
Request
Response
Error protocols
Potential Value Opportunities
Potential Challenges
Engineering CouchDB Networks
...
Issue - Using a JDBC driver to connect ot CouchDB
https://lists.apache.org/list.html?user@couchdb.apache.org
Issue - CouchDB connection when server certs expired
...
| Table of Contents |
|---|
Key Points
- provides REST api to NoSQL documents
- supports basic aggregation
- has Fauxton admin browser for Web queries using NoSQL without coding
- does not support JDBC access from other tools directly for easy reporting
- see CAMEL for some data integration options with Java, XML
- CouchDB v4x will use FoundationDB key-value store as the storage engine
- Mango query in Fauxton client is similar to Mongo Query syntax
- Berlin couchdb meetup site - jm0 for jem1
References
Key Concepts
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/top-10-open-source-nosql-databases-in-2020/
Apache CouchDB is an open-source project and a single node database that allows you to easily store your data and access it when you need it. Couch DB can also scale up for more demanding projects into a cluster of nodes with multiple servers. It supports the HTTP protocol along with the JSON data format and also integrates with HTTP proxy servers. Apache CouchDB is designed for reliability with a crash-resistant structure that supports “Offline First” applications and a system that saves data redundantly so that it is never lost and available in a state of emergency.
CouchDb Setup
https://docs.couchdb.org/en/stable/install/index.html
Setup TLS access for CouchDB
haproxy should be as simple as installing the binary on your *NIX platform, then using something similar to our shipped configuration:
Also, I see this walkthrough is referenced elsewhere as working for Let's Encrypt and CouchDB:
https://www.joshmorony.com/creating-a-couchdb-database-on-an-ubuntu-server-digital-ocean/
Basic CouchDb Operations
CouchDB Design Documents
https://docs.couchdb.org/en/stable/ddocs/index.html#
CouchDB supports special documents within databases known as “design documents”. These documents, mostly driven by JavaScript you write, are used to build indexes, validate document updates, format query results, and filter replications.
Note: Previously, the functionality provided by CouchDB’s design documents, in combination with document attachments, was referred to as “CouchApps.” The general principle was that entire web applications could be hosted in CouchDB, without need for an additional application server.
Use of CouchDB as a combined standalone database and application server is no longer recommended. There are significant limitations to a pure CouchDB web server application stack, including but not limited to: fully-fledged fine-grained security, robust templating and scaffolding, complete developer tooling, and most importantly, a thriving ecosystem of developers, modules and frameworks to choose from.
Apache camel data service overview
https://cwiki.apache.org/confluence/display/CAMEL/Index
Apache Camel ™ is a versatile open-source integration framework based on known Enterprise Integration Patterns.
Camel empowers you to define routing and mediation rules in a variety of domain-specific languages, including a Java-based Fluent API, Spring or Blueprint XML Configuration files, and a Scala DSL. This means you get smart completion of routing rules in your IDE, whether in a Java, Scala or XML editor.
Apache Camel uses URIs to work directly with any kind of Transport or messaging model such as HTTP, ActiveMQ, JMS, JBI, SCA, MINA or CXF, as well as pluggable Components and Data Format options. Apache Camel is a small library with minimal dependencies for easy embedding in any Java application. Apache Camel lets you work with the same API regardless which kind of Transport is used - so learn the API once and you can interact with all the Components provided out-of-box.
Apache Camel provides support for Bean Binding and seamless integration with popular frameworks such as CDI, Spring, Blueprint and Guice. Camel also has extensive support for unit testing your routes.
The following projects can leverage Apache Camel as a routing and mediation engine:
- Apache ServiceMix - a popular distributed open source ESB and JBI container
- Apache ActiveMQ - a mature, widely used open source message broker
- Apache CXF - a smart web services suite (JAX-WS and JAX-RS)
- Apache Karaf - a small OSGi based runtime in which applications can be deployed
- Apache MINA - a high-performance NIO-driven networking framework
Postman CRUD tests on CouchDB
https://dzone.com/articles/couchdb-rest-api-for-document-crud-operations-exam
React.js frontend tutorial using nano for CouchDB CRUD services
https://scriptverse.academy/tutorials/reactjs-couchdb.html
couchdb-CRUD-ReactReactJS and CouchDB CRUD Operations w Nano.pdf
Fauxton admin client for CouchDB
Fauxton Visual Guide
https://couchdb.apache.org/fauxton-visual-guide/
fauxton readthedocs
https://docs.couchdb.org/en/master/fauxton/index.html
fauxton setup
https://docs.couchdb.org/en/stable/fauxton/install.html
fauxton github
https://github.com/apache/couchdb-fauxton
Using Fauxton article
Fauxton setup
Go to couchdb.apache.org, and click download
Learn how to install and setup CouchDB from here, then go to http://127.0.0.1:5984/_utils
Fauxton URL
http://<my-server-or-ip>:5984/_utils/index.html
Using Fauxton
https://couchdb.apache.org/fauxton-visual-guide/#_all_dbs
CouchDB Mango Query in Fauxton client or API
https://github.com/apache/couchdb-mango
Mango provides a single HTTP API endpoint that accepts JSON bodies via HTTP POST. These bodies provide a set of instructions that will be handled with the results being returned to the client in the same order as they were specified. The general principle of this API is to be simple to implement on the client side while providing users a more natural conversion to Apache CouchDB than would otherwise exist using the standard RESTful HTTP interface that already exists.
Mango API design
The general API exposes a set of actions that are similar to what MongoDB exposes (although not all of MongoDB's API is supported). These are meant to be loosely and obviously inspired by MongoDB but without too much attention to maintaining the exact behavior.
Each action is specified as a JSON object with a number of keys that affect the behavior. Each action object has at least one field named "action" which must have a string value indicating the action to be performed. For each action there are zero or more fields that will affect behavior. Some of these fields are required and some are optional.
For convenience, the HTTP API will accept a JSON body that is either a single JSON object which specifies a single action or a JSON array that specifies a list of actions that will then be invoked serially. While multiple commands can be batched into a single HTTP request, there are no guarantees about atomicity or isolation for a batch of commands.
Configure Mango on a cluster
Query can be enabled by setting the following config:
rpc:multicall(config, set, ["native_query_servers", "query", "{mango_native_proc, start_link, []}"]).
Mango HTTP API Design
This API adds a single URI endpoint to the existing CouchDB HTTP API. Creating databases, authentication, Map/Reduce views, etc are all still supported exactly as currently document. No existing behavior is changed.
The endpoint added is for the URL pattern /dbname/_query and has the following characteristics:
- The only HTTP method supported is
POST. - The request
Content-Typemust beapplication/json. - The response status code will either be
200,4XX, or5XX - The response
Content-Typewill beapplication/json - The response
Transfer-Encodingwill bechunked. - The response is a single JSON object or array that matches to the single command or list of commands that exist in the request.
This is intended to be a significantly simpler use of HTTP than the current APIs. This is motivated by the fact that this entire API is aimed at customers who are not as savvy at HTTP or non-relational document stores. Once a customer is comfortable using this API we hope to expose any other "power features" through the existing HTTP API and its adherence to HTTP semantics.
Supports CRUD and manage indexes
Mango Query Examples
implicit or explicit and syntax
{"foo": "bar", "baz": true}
{"$and": [{"foo": {"$eq": "bar"}}, {"baz": {"$eq": true}}]}object subfields in a doc
{"location": {"city": "Omaha"}}
{"location.city": "Omaha"}escape char = \ , operator prefix = $
{"age": {"$gt": 21}}The list of combining characters:
- "$and" - array argument
- "$or" - array argument
- "$not" - single argument
- "$nor" - array argument
- "$all" - array argument (special operator for array values)
- "$elemMatch" - single argument (special operator for array values)
- "$allMatch" - single argument (special operator for array values)
Condition Operators
Each of the combining operators take a single argument that is either a condition operator or an array of condition operators.
The list of combining characters:
- "$and" - array argument
- "$or" - array argument
- "$not" - single argument
- "$nor" - array argument
- "$all" - array argument (special operator for array values)
- "$elemMatch" - single argument (special operator for array values)
- "$allMatch" - single argument (special operator for array values)
Condition Operators
Condition operators are specified on a per field basis and apply to the value indexed for that field. For instance, the basic "$eq" operator matches when the indexed field is equal to its argument. There is currently support for the basic equality and inequality operators as well as a number of meta operators. Some of these operators will accept any JSON argument while some require a specific JSON formatted argument. Each is noted below.
The list of conditional arguments:
(In)equality operators
- "$lt" - any JSON
- "$lte" - any JSON
- "$eq" - any JSON
- "$ne" - any JSON
- "$gte" - any JSON
- "$gt" - any JSON
Object related operators
- "$exists" - boolean, check whether the field exists or not regardless of its value
- "$type" - string, check the document field's type
Array related operators
- "$in" - array of JSON values, the document field must exist in the list provided
- "$nin" - array of JSON values, the document field must not exist in the list provided
- "$size" - integer, special condition to match the length of an array field in a document. Non-array fields cannot match this condition.
Misc related operators
- "$mod" - [Divisor, Remainder], where Divisor and Remainder are both positive integers (ie, greater than 0). Matches documents where (field % Divisor == Remainder) is true. This is false for any non-integer field
- "$regex" - string, a regular expression pattern to match against the document field. Only matches when the field is a string value and matches the supplied matches
Sort
The sort syntax is a basic array of field name and direction pairs. It looks like such:
[{field1: dir1} | ...]
Where field1 can be any field (dotted notation is available for sub-document fields) and dir1 can be "asc" or "desc".
Fields
Unlike MongoDB only the fields specified are included, there is no automatic inclusion of the "_id" or other metadata fields when a field list is included.
A trivial example:
["foo", "bar", "baz"]
More Mango Query Examples - regex, lists, starting date
{
"selector": {
"offerKWH": {
"$gte": 80 },
"startTS": {
"$gte": "2021-01-27"}
} }
{
"selector": {
"objectType": {
"$in": [
"device",
"bid",
"offer",
"trade"
] },
"Timestamp": {
"$gte": "2021-02-22"
} } }
{
"selector": {
"name": {
"$regex": "^Test acc"
} } }
CouchDB migration to FoundationDB
https://forums.foundationdb.org/t/update-couchdb-4-0-on-foundationdb/1690
FoundationDB JDBC driver notes
https://javalibs.com/artifact/com.foundationdb/fdb-sql-layer-jdbc
IDEA - implement JDBC driver for Mango client to connect BI tools
support defined JDBC type 4 client interfaces ..
Driver
Connection
Request
Response
Error protocols
PSCouchDB, a complete and Object Oriented cli for CouchDB
Matteo Guadrini <matteo.guadrini@hotmail.it>
Mon, Jun 27 at 4:39 AM
Hello everybody,
I wanted to announce the new version of PSCouchDB, a complete and Object Oriented cli for CouchDB, written in powershell (running on any operating system).
Find the release notes here: https://github.com/MatteoGuadrini/PSCouchDB/releases/tag/2.5.0
Other useful links
Installation: https://github.com/MatteoGuadrini/PSCouchDB#installation-and-simple-usage
Full docs: https://pscouchdb.readthedocs.io/en/latest/
PowershellGallery: https://www.powershellgallery.com/packages/PSCouchDB/2.5.0
Site: https://matteoguadrini.github.io/PSCouchDB
Thanks to everyone!
Matteo Guadrini
CouchDB JWT authentication and Identity Provider’s JWKS URLs ( beta feature )
Potential Value Opportunities
Potential Challenges
Engineering CouchDB Networks
mesh-like architecture which uses CouchDB replication protocol to
distribute/aggregate data is perfectly viable. As well as other members of
the ML I also have several projects employing this approach. And like
others I also can not disclose any details, even qty of nodes involved; you
better be ready to see this attitude for any mesh-related project, because
they often involve processing sensitive personal, industry or
infrastructure data in vast amounts.
However, I have a lot of observations, main are:
- whenever possible use CouchDB, not Pouch, because failure rate of
Pouch instances on whatever platform is much higher overall
- CouchDB is able to run for years without getting down, Pouch is not so
sturdy, there exist a bunch of ways to knock down Pouch node with a single
request
- on mobile devices you better avoid constantly growing DBs, you may
loose data and DB integrity eventually
- a single doc rejected by Couch during upstream replication from Pouch
can block entire process of replication, you can easily get the situation
when sync just can’t restart – so carefully check what you store in Pouch,
especially attachments size
- get ready to spend a lot of time debugging Pouch—Couch routes having
enormous latencies (like sync through satellites or 14400 GPRS connections)
- mesh CouchDB networks tend to have very fast growing logs, reason is
the number of repeated connections from different peers, so take care of it
- do not distribute mesh topology across nodes using CouchDB
replication, this approach looks inviting but brings a lot of risks.
Best regards.
ermouth
Issue - Using a JDBC driver to connect ot CouchDB
https://lists.apache.org/list.html?user@couchdb.apache.org
Issue - CouchDB connection when server certs expired
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/20082893/unable-to-verify-leaf-signature
setting NODE_TLS_REJECT_UNAUTHORIZED might fix your problem.
If you don't have access to the code, you can set a shell variable and
restart Node:
export NODE_TLS_REJECT_UNAUTHORIZED=0
CAUTION: This should only be used as a TEMPORARY fix until you can get your
certs updated. It opens you up to attacks.
Cheers,
- Bill
On Mon, Oct 18, 2021 at 3:44 PM Rick Jarvis <rick@magicmail.mooo.com> wrote:
> Can anyone tell me (urgently lol) how to ignore invalid certificates with
> nano?
>
> My backups haven’t been running and I’m desperate.
>
> I’ll then need to figure out why, despite having updated all the routes
> etc (due to R3 expiry) it’s still not working!
Candidate Solutions
CouchDb v3.4 updates
CouchDB 3.4.0 and 3.4.1
full text search for couchdb
add embedded QuickJS engine
release 3.4.0 problems
avoid breaking changes and support CouchDB version rollback now in 3.4.1
new hashing methods
QuickJS
Spider Monkey from Firefox still the default js engine in CouchDB
or change config in design doc for flex
test engine
Compare CouchDB v4x with FoundationDB to LevelDB
...
- Create a view that provides all the documents that contain an email address and have a type of ‘userProfile’.
- Query that view for the email address of the user whose profile you want to retrieve.
Couchbase has SDKs for development and a JDBC driver
Couchbase Server has several SDKs that are developed and supported by Couchbase Inc. These provide idiomatic access to the full range of Couchbase Server features, including N1QL, views and key-value access. Official SDKs are available for:
- an email address and have a type of ‘userProfile’.
- Query that view for the email address of the user whose profile you want to retrieve.
Couchbase has SDKs for development and a JDBC driver
Couchbase Server has several SDKs that are developed and supported by Couchbase Inc. These provide idiomatic access to the full range of Couchbase Server features, including N1QL, views and key-value access. Official SDKs are available for:
Couchbase open-source JDBC driver
https://github.com/couchbaselabs/couchbase-jdbc-driver
SQL Select ONLY - no CRUD
This project contains the source code for the Couchbase JDBC Driver which supports the Analytics Service (not Query!). Its main purpose is to provide the low-level glue to facilitate integration with high level BI-Tools like Tableau.
Couchbase connection via Apache Drill
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/48826163/connecting-couchbase-with-apache-drill
Couchbase uses mem-cache to store key-value tables
...
For your working set, most key-value requests are sub-millisecond.
Adding a Validator Function to a CouchDB view to validate documents
FoundationDB features ( CouchDB v4x )
...
Programming language bindingsFoundationDB supports language bindings for Python, Go, Ruby, Node.js, Java, PHP, and C, all of which are made available with the product.[13]
Design limitations[edit]
The design of FoundationDB results in several limitations:
...
https://apple.github.io/foundationdb/performance.html
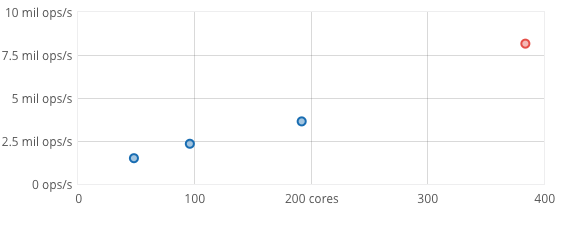
FoundationDB uses commodity hardware to provide high throughputs and low latencies to your application at a variety of scales
FoundationDB scales linearly with the number of cores in a cluster over a wide range of sizes.
Here, a cluster of commodity hardware scales to 8.2 million operations/sec doing a 90% read and 10% write workload with 16 byte keys and values between 8 and 100 bytes.
...