| Table of Contents |
|---|
Key Points
- Spring saves work but adds work - need to fit to use cases
JHipster is a development platform to generate, develop and deploy Spring Boot + Angular / React / Vue Web applications and Spring microservices.
JHipster is open-source
References
...
https://s3.amazonaws.com/baeldung.com/Persistence+with+Spring.pdf?__s=dks6vftyyy
n6rnaspucsspring-Persistence+with+Spring.pdf
...
Spring Persistence Overview
...
https://s3.amazonaws.com/baeldung.com/Building+a+REST+API+with+Spring.pdf?
__s=dks6vftyyyn6rnaspucs
...
spring-REST-Building+a+REST+API+with+Spring.pdf
...
Build Spring REST services
...
...
Spring Cookbook
...
Simple Aspects using Annotations in Grails _ Man Builds Website.pdf
...
Grails and Spring Aspect
...
spring-6-.io-A Java 17 and Jakarta EE 9 baseline for Spring Framework 6.pdf
spring-6-.io-A Java 17 and Jakarta EE 9 baseline for Spring Framework 6
...
https://stackify.com/spring-boot-level-up/
https://drive.google.com/open?id=1_NfWcLnIABOD0KQ8khcktS3qn_rfblHM
...
https://www.baeldung.com/spring-vs-spring-boot
https://drive.google.com/open?id=1dGQuibfgkwxlKoGkXUYLfGldLF_HLiyO
...
https://www.springboottutorial.com/spring-boot-vs-spring-mvc-vs-spring
https://drive.google.com/open?id=1T1BODw5dkSWlfpZnmRlN6YyCQzn_kXhM
...
https://developer.okta.com/blog/2021/05/12/spring-boot-r2dbc
R2DBC and Spring for Non-Blocking Database Access pdf
...
Master Microservices with Spring Boot and Spring Cloud
...
https://speakerdeck.com/mraible/front-end-development-for-back-end-java-
developers-jfokus-2020
Front_End_Development_for_Back_End_Java_Developers_-_Jfokus_2020.pdf
...
https://res.cloudinary.com/snyk/image/upload/v1534422834/blog/
Spring_Boot_Security_Cheat_Sheet.pdf
Spring_Boot_Security_Cheat_Sheet.pdf
...
https://developer.okta.com/blog/2020/04/15/spring-cloud-stream
spring-cloud-stream-for-messaging-developer.okta.com-A
Quick Guide to Spring Cloud Stream.pdf
...
https://www.slideshare.net/JesusPerezFranco/spring-security-5?from_action=save
springsecurity-v5-181008152249.pdf
...
https://docs.spring.io/spring-security/site/docs/5.2.2.BUILD-SNAPSHOT/reference/htmlsingle/
https://docs.spring.io/spring-security/site/docs/current/reference/htmlsingle/
...
https://howtodoinjava.com/spring-webflux/spring-webflux-tutorial/
spring-webflux-tutorial-howtodoinjava.com-Spring WebFlux Tutorial.pdf
...
| Table of Contents |
|---|
Key Points
- Spring saves work but adds work - need to fit to use cases
JHipster is a development platform to generate, develop and deploy Spring Boot + Angular / React / Vue Web applications and Spring microservices.
JHipster is open-source
References
Key Concepts
Spring Training resources
...
...
com/course/microservices-with-spring-boot-and-spring-cloud/learn/lecture/8004660#overview
Spring Concepts
...
...
Spring Framework
- Spring 5 Tutorials
- Spring Core Tutorials
- Spring Boot Tutorials
- Spring Batch Tutorials
- Spring Cloud Tutorials
- Spring AOP Tutorials
- Spring MVC Tutorials
- Spring Security Tutorials
- Spring ORM Tutorials
- Spring REST Tutorials
- Spring WebFlux Tutorials
Spring Core
Dependency Injection, AOP, beans
- Spring Bean Java Config Example
- Spring Bean XML Config Example
- Spring Bean Eager vs Lazy Initialization
- Spring bean scopes
Spring Boot
...
...
...
JHipster - oss
...
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/JHipster
...
| Widget Connector | ||
|---|---|---|
|
...
https://developer.okta.com/blog/2019/04/04/java-11-java-12-jhipster-oidc
...
JHipster 6 and Java 12 overview
has: Openid and CRUD features
...
https://www.infoq.com/minibooks/jhipster-mini-book-5
https://drive.google.com/file/d/1hRMArtWHBOFXYRWpKSXacxuyzwaoZa5c/
view?usp=sharing
...
JHipster mini book
...
https://developer.okta.com/blog/2018/11/26/spring-boot-2-dot-1-oidc-
oauth2-reactive-apis
...
SpringBoot oid, oauth2 support
...
https://www.jhipster.tech/#/learn
...
Learn JHipster
...
https://www.jhipster.tech/#/learn
...
Great set of modules and blueprints:
docker, swagger, ionic etc
...
https://developer.okta.com/blog/2019/05/15/spring-boot-login-options
...
Spring Boot authentication options
?? is this all ?? oauth2 no okta ??
...
https://developer.okta.com/blog/2019/05/13/angular-8-spring-boot-2
...
Basic CRUD app with Java, Spring and Angular 8
...
https://drive.google.com/open?id=1RjS0Lxazvix68o2tdMWIjWoV-L0ugODt
...
java-Front_End_Development_for_Back_End_Java_Developers_-_NYJavaSIG_2019.pdf
...
Build Mobile Apps with Angular, Ionic 4, and Spring Boot
...
Spring RDBC - Reactive Database Connector Framework
synch vs asynch like GORM
...
Key Concepts
...
https://spring.io/blog/2013/08/06/spring-boot-simplifying-spring-for-everyone
We are pleased to announce the first milestone release of a new project called Spring Boot.
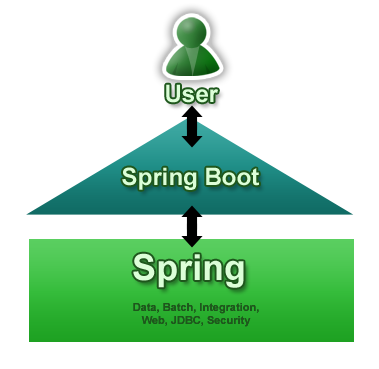
Spring Boot aims to make it easy to create Spring-powered, production-grade applications and services with minimum fuss. It takes an opinionated view of the Spring platform so that new and existing users can quickly get to the bits they need. You can use it to create stand-alone Java applications that can be started using ‘java -jar’ or more traditional WAR deployments. We also provide a command line tool that runs ‘spring scripts’.
The diagram below shows Spring Boot as a point of focus on the larger Spring ecosystem. It presents a small surface area for users to approach and extract value from the rest of Spring:
The primary goals of Spring Boot are:
- To provide a radically faster and widely accessible ‘getting started’ experience for all Spring development
- To be opinionated out of the box, but get out of the way quickly as requirements start to diverge from the defaults
- To provide a range of non-functional features that are common to large classes of projects (e.g. embedded servers, security, metrics, health checks, externalized configuration)
Spring Boot does not generate code and there is absolutely no requirement for XML configuration.
Spring Scripts
Spring Boot ships with a small command line application that can be used to run ‘spring scripts’. Spring scripts are written in Groovy, which means that you have a familiar Java-like syntax, without so much boilerplate code. We are able to deduce a lot of information simply by looking at the way you have written your script. For example, here is a simple web application:
@Controller
class ThisWillActuallyRun {
@RequestMapping("/")
@ResponseBody
String home() {
return "Hello World!"
}
}When you run this application using ‘spring run webapp.groovy’ a number things are happening:
- Your script is enhanced with common
‘import’statements to save you typing them - We recognize the
@ResponseBodyannotation and download appropriate Spring JARs - We automatically create the Spring
@Configurationthat you would otherwise need to write - We start up an embedded servlet container and handle incoming requests on port 8080
The command line tool recognizes a number of different types of Spring Applications, including Web, Batch and Integration. There are a number of samples available in the GitHub repository.
Spring Boot with Java
You don’t need use the command line tool or write Groovy code to get the benefits of Spring Boot. We also have first class Java support. For example, here is the same application written in Java:
import org.springframework.boot.*;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.*;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
@Controller
@EnableAutoConfiguration
public class SampleController {
@RequestMapping("/")
@ResponseBody
String home() {
return "Hello World!";
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
SpringApplication.run(SampleController.class, args);
}
}Other than import statements, the main difference between this example and the earlier Groovy script is the main() method that calls SpringApplication and the @EnableAutoConfiguration annotation.
Obviously with Java you also need a build system to compile and package your code. We provide a number of convenient ‘starter’ POMs that you can use with Maven, Gradle or Ant+Ivy to
Getting Started with Spring Boot and Spring Cloud
https://www.udemy.com/course/microservices-with-spring-boot-and-spring-cloud
...
JUST - new CLI for Spring Boot
https://howtodoinjava.com/
Spring Framework
- Spring 5 Tutorials
- Spring Core Tutorials
- Spring Boot Tutorials
- Spring Batch Tutorials
- Spring Cloud Tutorials
- Spring AOP Tutorials
- Spring MVC Tutorials
- Spring Security Tutorials
- Spring ORM Tutorials
- Spring REST Tutorials
- Spring WebFlux Tutorials
Spring Core
Dependency Injection, AOP, beans
- Spring Bean Java Config Example
- Spring Bean XML Config Example
- Spring Bean Eager vs Lazy Initialization
- Spring bean scopes
Spring Boot
https://howtodoinjava.com/spring-5-tutorial/www.infoq.com/news/2023/01/just-spring-boot-cli/
JUST getting started docs
https://springjust.maciejwalkowiak.iocom/blog/2013/08/06/spring-boot-simplifying-spring-for-everyone
We are pleased to announce the first milestone release of a new project called Spring Boot.
Spring Boot aims to make it easy to create Spring-powered, production-grade applications and services with minimum fuss. It takes an opinionated view of the Spring platform so that new and existing users can quickly get to the bits they need. You can use it to create stand-alone Java applications that can be started using ‘java -jar’ or more traditional WAR deployments. We also provide a command line tool that runs ‘spring scripts’.
The diagram below shows Spring Boot as a point of focus on the larger Spring ecosystem. It presents a small surface area for users to approach and extract value from the rest of Spring:
The primary goals of Spring Boot are:
- To provide a radically faster and widely accessible ‘getting started’ experience for all Spring development
- To be opinionated out of the box, but get out of the way quickly as requirements start to diverge from the defaults
- To provide a range of non-functional features that are common to large classes of projects (e.g. embedded servers, security, metrics, health checks, externalized configuration)
Spring Boot does not generate code and there is absolutely no requirement for XML configuration.
Spring Scripts
Spring Boot ships with a small command line application that can be used to run ‘spring scripts’. Spring scripts are written in Groovy, which means that you have a familiar Java-like syntax, without so much boilerplate code. We are able to deduce a lot of information simply by looking at the way you have written your script. For example, here is a simple web application:
@Controller
class ThisWillActuallyRun {
@RequestMapping("/")
@ResponseBody
String home() {
return "Hello World!"
}
}When you run this application using ‘spring run webapp.groovy’ a number things are happening:
- Your script is enhanced with common
‘import’statements to save you typing them - We recognize the
@ResponseBodyannotation and download appropriate Spring JARs - We automatically create the Spring
@Configurationthat you would otherwise need to write - We start up an embedded servlet container and handle incoming requests on port 8080
The command line tool recognizes a number of different types of Spring Applications, including Web, Batch and Integration. There are a number of samples available in the GitHub repository.
Spring Boot with Java
You don’t need use the command line tool or write Groovy code to get the benefits of Spring Boot. We also have first class Java support. For example, here is the same application written in Java:
import org.springframework.boot.*;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.*;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
@Controller
@EnableAutoConfiguration
public class SampleController {
@RequestMapping("/")
@ResponseBody
String home() {
return "Hello World!";
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
SpringApplication.run(SampleController.class, args);
}
}Other than import statements, the main difference between this example and the earlier Groovy script is the main() method that calls SpringApplication and the @EnableAutoConfiguration annotation.
Obviously with Java you also need a build system to compile and package your code. We provide a number of convenient ‘starter’ POMs that you can use with Maven, Gradle or Ant+Ivy to
Getting Started with Spring Boot and Spring Cloud
https://www.udemy.com/course/microservices-with-spring-boot-and-spring-clouddocs/getting-started/
Just, a command line tool requiring zero configuration, increases the Java development experience while building Spring Boot applications. Just automatically reloads the application when there is a change in source code, build files or Docker compose files. The project also supports the creation of (native) applications and (native) Docker images.
Maciej Walkowiak, Freelance Architect & Developer, released Just exactly eleven months after the first commit. Just itself is a Spring Boot application compiled to a native binary which uses: picocli to create a rich command line application; Testcontainers to run containers in JUnit tests; Sentry for error monitoring; and JReleaser to release the project.
Just uses Spring Boot Devtools which reloads the application after the source code is changed and a build is triggered. On top of Spring Boot Devtools, Just automatically detects source code changes and compiles those changes. Furthermore, whenever the pom.xml or build.gradle change, the application is stopped, the build file refreshed and the application is started again. Unlike Spring Boot Devtools, Just also starts infrastructure services such as databases and services defined via Docker Compose whenever the run sub-command is executed. Just automatically detects the applications build configuration and uses it whenever a just command is executed. It supports Maven and Gradle, but also their respective wrappers and the Maven Daemon. Just execute the run sub-command once and it takes care of the changes in the application.
Comparable to the run sub-command, the build sub-command is translated to the proper Maven or Gradle command with the correct build goal:
just build [--quick] [--skip-test] <buildTarget>The quick option skips tests, document generation and checks such as formatting and static analysis. Just offers several buildTarget options to create a (native) application or a (native) Docker image: jar, native, image and native-image.
Based on the project's configuration, the format sub-command formats the codebase following the rules of the default settings, Spring Java Format or Spotless configuration.
A running process may be killed with the kill sub-command. By default, the process running on port 8080 is killed. Optionally, a port may be specified with the -p argument and the kill sub-command may be forced by supplying the -9 argument.
Just can be run from the command line or from IntelliJ IDEA by adding a run configuration by executing the init idea sub-command. Alternatively, the run configuration may be added manually by opening the configuration via the Run menu option and clicking on Edit Configurations. Now add a Shell Script and specify the name. The Execute option should be set to Shell Script and the Script Text to just run. After unchecking the Execute in the terminal option, the configuration can be applied. Now the Run menu option shows the name of the new shell script which can be used to start Just.
Just may be installed on MacOs with Homebrew:
brew install maciejwalkowiak/brew/justOr on Windows with Scoop:
scoop bucket add maciejwalkowiak https://github.com/maciejwalkowiak/scoop-just.git
scoop install justAlternatively, the application may be installed manually on macOS, Windows or Linux, for example via the Linux command:
curl -Lo just.zip https://github.com/maciejwalkowiak/just/releases/latest/download/just-0.12.0-linux-x86_64.zip && unzip just.zip && chmod +x just && sudo mv just /usr/local/bin/just && just helpThe help sub-command may be used to verify the installation.
Just is not an open source project. The GitHub repository contains the binaries, release notes and issue tracker, but not the source code. Currently, the project is still in alpha status and available for free. Each release has a built-in expiration date, after which the application may be purchased or the latest release may be installed.
Spring Getting Started Guides - go here for specific framework tutorials
...
Configuration using lambdas
@EnableWebSecurity
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.authorizeRequests(authorizeRequests ->
authorizeRequests
.antMatchers("/blog/**").permitAll()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
)
.formLogin(formLogin ->
formLogin
.loginPage("/login")
.permitAll()
)
.rememberMe(withDefaults());
}
}Equivalent configuration without using lambdas
@EnableWebSecurity
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/blog/**").permitAll()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.formLogin()
.loginPage("/login")
.permitAll()
.and()
.rememberMe();
}
}Lambda DSL configuration tips
...
You may also configure WebFlux security using lambdas in a similar manner.
Below is an example configuration using lambdas.
@EnableWebFluxSecurity
public class SecurityConfig {
@Bean
SecurityWebFilterChain springSecurityFilterChain(ServerHttpSecurity http) {
http
.authorizeExchange(exchanges ->
exchanges
.pathMatchers("/blog/**").permitAll()
.anyExchange().authenticated()
)
.httpBasic(withDefaults())
.formLogin(formLogin ->
formLogin
.loginPage("/login")
);
return http.build();
}
}Goals of the Lambda DSL
The Lambda DSL was created to accomplish to following goals:
...
What makes something RESTful?
So far, you have a web-based service that handles the core operations involving employee data. But that’s not enough to make things "RESTful".
Pretty URLs like /employees/3 aren’t REST.
Merely using
GET,POST, etc. aren’t REST.Having all the CRUD operations laid out aren’t REST.
In fact, what we have built so far is better described as RPC (Remote Procedure Call). That’s because there is no way to know how to interact with this service. If you published this today, you’d also have to write a document or host a developer’s portal somewhere with all the details.
This statement of Roy Fielding may further lend a clue to the difference between REST and RPC:
I am getting frustrated by the number of people calling any HTTP-based interface a REST API. Today’s example is the SocialSite REST API. That is RPC. It screams RPC. There is so much coupling on display that it should be given an X rating.
What needs to be done to make the REST architectural style clear on the notion that hypertext is a constraint? In other words, if the engine of application state (and hence the API) is not being driven by hypertext, then it cannot be RESTful and cannot be a REST API. Period. Is there some broken manual somewhere that needs to be fixed?The side effect of NOT including hypermedia in our representations is that clients MUST hard code URIs to navigate the API. This leads to the same brittle nature that predated the rise of e-commerce on the web. It’s a signal that our JSON output needs a little help.
Introducing Spring HATEOAS, a Spring project aimed at helping you write hypermedia-driven outputs. To upgrade your service to being RESTful, add this to your build:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-hateoas</artifactId>
</dependency>This tiny library will give us the constructs to define a RESTful service and then render it in an acceptible format for client consumption.
A critical ingredient to any RESTful service is adding links to relevant operations. To make your controller more RESTful, add links like this:
@GetMapping("/employees/{id}")
Resource<Employee> one(@PathVariable Long id) {
Employee employee = repository.findById(id)
.orElseThrow(() -> new EmployeeNotFoundException(id));
return new Resource<>(employee,
linkTo(methodOn(EmployeeController.class).one(id)).withSelfRel(),
linkTo(methodOn(EmployeeController.class).all()).withRel("employees"));
}This is very similar to what we had before, but a few things have changed:
The return type of the method has changed from
EmployeetoResource<Employee>.Resource<T>is a generic container from Spring HATEOAS that includes not only the data but a collection of links.linkTo(methodOn(EmployeeController.class).one(id)).withSelfRel()asks that Spring HATEOAS build a link to theEmployeeController'sone()method, and flag it as a self link.linkTo(methodOn(EmployeeController.class).all()).withRel("employees")asks Spring HATEOAS to build a link to the aggregate root,all(), and call it "employees".
What do we mean by "build a link"? One of Spring HATEOAS’s core types is Link. It includes a URI and a rel (relation). Links are what empower the web. Before the World Wide Web, other document systems would render information or links, but it was the linking of documents WITH data that stitched the web together.
Roy Fielding encourages building APIs with the same techniques that made the web successful, and links are one of them.
If you restart the application and query the employee record of Bilbo, you’ll get a slightly different response than earlier:
{
"id": 1,
"name": "Bilbo Baggins",
"role": "burglar",
"_links": {
"self": {
"href": "http://localhost:8080/employees/1"
},
"employees": {
"href": "http://localhost:8080/employees"
}
}
}This decompressed output shows not only the data elements you saw earlier (id, name and role), but also a _links entry containing two URIs. This entire document is formatted using HAL.
HAL is a lightweight mediatype that allows encoding not just data but also hypermedia controls, alerting consumers to other parts of the API they can navigate toward. In this case, there is a "self" link (kind of like a this statement in code) along with a link back to the aggregate root.
To make the aggregate root ALSO more RESTful, you want to include top level links while ALSO including any RESTful components within:
@GetMapping("/employees")
Resources<Resource<Employee>> all() {
List<Resource<Employee>> employees = repository.findAll().stream()
.map(employee -> new Resource<>(employee,
linkTo(methodOn(EmployeeController.class).one(employee.getId())).withSelfRel(),
linkTo(methodOn(EmployeeController.class).all()).withRel("employees")))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
return new Resources<>(employees,
linkTo(methodOn(EmployeeController.class).all()).withSelfRel());
}Wow! That method, which used to just be repository.findAll() has grown big! Let’s unpack it.
Resources<> is another Spring HATEOAS container aimed at encapsulating collections. It, too, also lets you include links. Don’t let that first statement slip by. When does "encapsulating collections" mean? Collections of employees?
Not quite.
...
no way to know how to interact with this service. If you published this today, you’d also have to write a document or host a developer’s portal somewhere with all the details.
This statement of Roy Fielding may further lend a clue to the difference between REST and RPC:
I am getting frustrated by the number of people calling any HTTP-based interface a REST API. Today’s example is the SocialSite REST API. That is RPC. It screams RPC. There is so much coupling on display that it should be given an X rating.
What needs to be done to make the REST architectural style clear on the notion that hypertext is a constraint? In other words, if the engine of application state (and hence the API) is not being driven by hypertext, then it cannot be RESTful and cannot be a REST API. Period. Is there some broken manual somewhere that needs to be fixed?The side effect of NOT including hypermedia in our representations is that clients MUST hard code URIs to navigate the API. This leads to the same brittle nature that predated the rise of e-commerce on the web. It’s a signal that our JSON output needs a little help.
Introducing Spring HATEOAS, a Spring project aimed at helping you write hypermedia-driven outputs. To upgrade your service to being RESTful, add this to your build:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-hateoas</artifactId>
</dependency>This tiny library will give us the constructs to define a RESTful service and then render it in an acceptible format for client consumption.
A critical ingredient to any RESTful service is adding links to relevant operations. To make your controller more RESTful, add links like this:
@GetMapping("/employees/{id}")
Resource<Employee> one(@PathVariable Long id) {
Employee employee = repository.findById(id)
.orElseThrow(() -> new EmployeeNotFoundException(id));
return new Resource<>(employee,
linkTo(methodOn(EmployeeController.class).one(id)).withSelfRel(),
linkTo(methodOn(EmployeeController.class).all()).withRel("employees"));
}This is very similar to what we had before, but a few things have changed:
The return type of the method has changed from
EmployeetoResource<Employee>.Resource<T>is a generic container from Spring HATEOAS that includes not only the data but a collection of links.linkTo(methodOn(EmployeeController.class).one(id)).withSelfRel()asks that Spring HATEOAS build a link to theEmployeeController'sone()method, and flag it as a self link.linkTo(methodOn(EmployeeController.class).all()).withRel("employees")asks Spring HATEOAS to build a link to the aggregate root,all(), and call it "employees".
What do we mean by "build a link"? One of Spring HATEOAS’s core types is Link. It includes a URI and a rel (relation). Links are what empower the web. Before the World Wide Web, other document systems would render information or links, but it was the linking of documents WITH data that stitched the web together.
Roy Fielding encourages building APIs with the same techniques that made the web successful, and links are one of them.
If you restart the application and query the employee record of Bilbo, you’ll get a slightly different response than earlier:
{
"id": 1,
"name": "Bilbo Baggins",
"role": "burglar",
"_links": {
"self": {
"href": "http://localhost:8080/employees/1"
},
"employees": {
"href": "http://localhost:8080/employees"
}
}
}This decompressed output shows not only the data elements you saw earlier (id, name and role), but also a _links entry containing two URIs. This entire document is formatted using HAL.
HAL is a lightweight mediatype that allows encoding not just data but also hypermedia controls, alerting consumers to other parts of the API they can navigate toward. In this case, there is a "self" link (kind of like a this statement in code) along with a link back to the aggregate root.
To make the aggregate root ALSO more RESTful, you want to include top level links while ALSO including any RESTful components within:
@GetMapping("/employees")
Resources<Resource<Employee>> all() {
List<Resource<Employee>> employees = repository.findAll().stream()
.map(employee -> new Resource<>(employee,
linkTo(methodOn(EmployeeController.class).one(employee.getId())).withSelfRel(),
linkTo(methodOn(EmployeeController.class).all()).withRel("employees")))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
return new Resources<>(employees,
linkTo(methodOn(EmployeeController.class).all()).withSelfRel());
}Wow! That method, which used to just be repository.findAll() has grown big! Let’s unpack it.
Resources<> is another Spring HATEOAS container aimed at encapsulating collections. It, too, also lets you include links. Don’t let that first statement slip by. When does "encapsulating collections" mean? Collections of employees?
Not quite.
Tutorial - Spring Boot CRUD with Angular 9
https://developer.okta.com/blog/2020/01/06/crud-angular-9-spring-boot-2
Angular 9’s most prominent new feature is Ivy. Ivy is Angular’s new compiler and renderer. The renderer is the engine that takes your components and templates and translates them into instructions that manipulate the DOM. Ivy is an internal component, so you don’t interact with it directly. However, it can have a significant impact on your code, yielding much smaller JavaScript bundles and increasing performance.
Spring Boot 2.2 was released in September 2019 and focuses on performance improvements and reduced memory usage. It adds Java 13 support, RSocket support, and the ability to group health indicators. Grouping indicators can be useful if you’re deploying to Kubernetes and want different groups for "liveness" and "readiness" probes.
In this post, I’ll show you how to build a CRUD application with Angular 9 and Spring Boot 2.2. Along the way, I’ll do my best to weave in security tips and how to make your apps more secure.
Prerequisites:
- What’s New In Angular 9?
- What’s New in Spring Boot 2.2?
- Create an Angular 9 App
- Add Angular Authentication using OpenID Connect
- Create a Spring Boot 2.2 App
- Add a Notes REST API with Spring Data REST
- Add a Notes CRUD Feature in Angular
- Lock Down Spring Boot with Recommended Security Practices
- Learn More about Angular, Spring Boot, and Kotlin
Angular 9 Spring Boot 2.2 Video Tutorial
| Widget Connector | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Tutorial - Simple CRUD services with React, Spring Boot and JHipster
https://developer.okta.com/blog/20202022/0106/0617/simple-crud-angularreact-9and-spring-boot-2spring-boot-crud-angular-raible-
jhipster-crud-developer.oktacom-Use React and Spring Boot to Build a Simple CRUD App.pdf link
Angular 9’s most prominent new feature is Ivy. Ivy is Angular’s new compiler and renderer. The renderer is the engine that takes your components and templates and translates them into instructions that manipulate the DOM. Ivy is an internal component, so you don’t interact with it directly. However, it can have a significant impact on your code, yielding much smaller JavaScript bundles and increasing performance.
Spring Boot 2.2 was released in September 2019 and focuses on performance improvements and reduced memory usage. It adds Java 13 support, RSocket support, and the ability to group health indicators. Grouping indicators can be useful if you’re deploying to Kubernetes and want different groups for "liveness" and "readiness" probes.
In this post, I’ll show you how to build a CRUD application with Angular 9 and Spring Boot 2.2. Along the way, I’ll do my best to weave in security tips and how to make your apps more secure.
Prerequisites:
- What’s New In Angular 9?
- What’s New in Spring Boot 2.2?
- Create an Angular 9 App
- Add Angular Authentication using OpenID Connect
- Create a Spring Boot 2.2 App
- Add a Notes REST API with Spring Data REST
- Add a Notes CRUD Feature in Angular
- Lock Down Spring Boot with Recommended Security Practices
- Learn More about Angular, Spring Boot, and Kotlin
Angular 9 Spring Boot 2.2 Video Tutorial
| Widget Connector | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Tutorial - Simple CRUD services with React, Spring Boot and JHipster
https://developer.okta.com/blog/2022/06/17/simple-crud-react-and-spring-boot
jhipster-crud-developer.oktacom-Use React and Spring Boot to Build a Simple CRUD App.pdf link
jhipster-crud-developer.okta.com-Use React and Spring Boot to Build a Simple CRUD App.pdf file
React was designed to make it painless to create interactive UIs. Its state management is efficient and only updates components when your data changes. Component logic is written in JavaScript, meaning you can keep state out of the DOM and create encapsulated components.
Developers like CRUD (create, read, update, and delete) apps because they show a lot of the base functionality you need when creating an app. Once you have the basics of CRUD completed in an app, most of the client-server plumbing is finished, and you can move on to implementing the necessary business logic.
Today, I’ll show you how to create a basic CRUD app with Spring Boot and React. In this tutorial, I’ll use the OAuth 2.0 Authorization Code flow and package the React app in the Spring Boot app for production. At the same time, I’ll show you how to keep React’s productive workflow for developing locally.
You will need Java 17 and Node 16 installed to complete this tutorial.
...
...
...
file
React was designed to make it painless to create interactive UIs. Its state management is efficient and only updates components when your data changes. Component logic is written in JavaScript, meaning you can keep state out of the DOM and create encapsulated components.
Developers like CRUD (create, read, update, and delete) apps because they show a lot of the base functionality you need when creating an app. Once you have the basics of CRUD completed in an app, most of the client-server plumbing is finished, and you can move on to implementing the necessary business logic.
Today, I’ll show you how to create a basic CRUD app with Spring Boot and React. In this tutorial, I’ll use the OAuth 2.0 Authorization Code flow and package the React app in the Spring Boot app for production. At the same time, I’ll show you how to keep React’s productive workflow for developing locally.
You will need Java 17 and Node 16 installed to complete this tutorial.
- Create an API app with Spring Boot
- Create a React UI with Create React App
- Call your Spring Boot API and display the results
- Build a React
GroupListcomponent - Add a React
GroupEditcomponent - Add authentication with Okta
- Configure Spring Security for React and user identity
- Modify React to handle CSRF and be identity-aware
- Configure Maven to build and package React with Spring Boot
- Learn more about Spring Boot and React
Building Microservices Architectural Applications using Spring Boot.pdf on Spring Cloud link
help you to understand the theoretical concepts of Microservices and how it practically used for spring boot. The following points will consider in this article — Part 01 ->
Testing Spring Boot Applications: Best Practices and Frameworks.. medium
medium.com-Testing Spring Boot Applications Best Practices.pdf. link
medium.com-Testing Spring Boot Applications Best Practices.pdf. file
Testing is an integral part of software development. It ensures that your Spring Boot applications work as expected and continue to do so as they evolve. In this article, we’ll explore how to test Spring Boot applications using best practices and tools.
Why Testing Matters
Testing is crucial for several reasons:
- Reliability: It ensures your application performs correctly and reliably.
- Bug Detection: It helps identify and fix issues early in development.
- Refactoring: It allows for code refactoring with confidence so existing functionality won’t break.
- Documentation: Well-written tests serve as living documentation for your code.
Types of Testing
Spring Boot applications can be tested at various levels, including:
- Unit Testing: Testing individual components, such as classes or methods, in isolation.
- Integration Testing: Verifying that different components or services work correctly together.
- Functional Testing: Testing the application’s functionality from the user’s perspective.
- End-to-End Testing: Testing the entire application, including its external dependencies, in a production-like environment.
Spring Cloud
Spring Cloud Webinar notes
...