Key Points
- Spring saves work but adds work - need to fit to use cases
JHipster is a development platform to generate, develop and deploy Spring Boot + Angular / React / Vue Web applications and Spring microservices.
JHipster is open-source
References
Key Concepts
Spring Training resources
Spring Concepts
Spring Framework
- Spring 5 Tutorials
- Spring Core Tutorials
- Spring Boot Tutorials
- Spring Batch Tutorials
- Spring Cloud Tutorials
- Spring AOP Tutorials
- Spring MVC Tutorials
- Spring Security Tutorials
- Spring ORM Tutorials
- Spring REST Tutorials
- Spring WebFlux Tutorials
Spring Core
Dependency Injection, AOP, beans
- Spring Bean Java Config Example
- Spring Bean XML Config Example
- Spring Bean Eager vs Lazy Initialization
- Spring bean scopes
Spring Boot
https://howtodoinjava.com/spring-5-tutorial/
https://spring.io/blog/2013/08/06/spring-boot-simplifying-spring-for-everyone
We are pleased to announce the first milestone release of a new project called Spring Boot.
Spring Boot aims to make it easy to create Spring-powered, production-grade applications and services with minimum fuss. It takes an opinionated view of the Spring platform so that new and existing users can quickly get to the bits they need. You can use it to create stand-alone Java applications that can be started using ‘java -jar’ or more traditional WAR deployments. We also provide a command line tool that runs ‘spring scripts’.
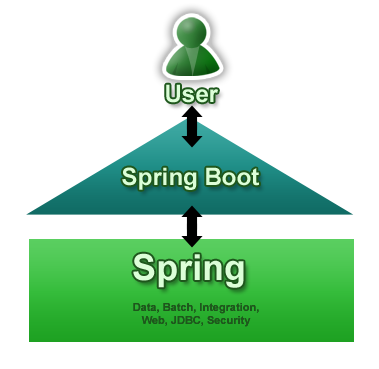
The diagram below shows Spring Boot as a point of focus on the larger Spring ecosystem. It presents a small surface area for users to approach and extract value from the rest of Spring:
The primary goals of Spring Boot are:
- To provide a radically faster and widely accessible ‘getting started’ experience for all Spring development
- To be opinionated out of the box, but get out of the way quickly as requirements start to diverge from the defaults
- To provide a range of non-functional features that are common to large classes of projects (e.g. embedded servers, security, metrics, health checks, externalized configuration)
Spring Boot does not generate code and there is absolutely no requirement for XML configuration.
Tutorial - Spring Boot CRUD with Angular 9
https://developer.okta.com/blog/2020/01/06/crud-angular-9-spring-boot-2
Angular 9’s most prominent new feature is Ivy. Ivy is Angular’s new compiler and renderer. The renderer is the engine that takes your components and templates and translates them into instructions that manipulate the DOM. Ivy is an internal component, so you don’t interact with it directly. However, it can have a significant impact on your code, yielding much smaller JavaScript bundles and increasing performance.
Spring Boot 2.2 was released in September 2019 and focuses on performance improvements and reduced memory usage. It adds Java 13 support, RSocket support, and the ability to group health indicators. Grouping indicators can be useful if you’re deploying to Kubernetes and want different groups for "liveness" and "readiness" probes.
In this post, I’ll show you how to build a CRUD application with Angular 9 and Spring Boot 2.2. Along the way, I’ll do my best to weave in security tips and how to make your apps more secure.
Prerequisites:
- What’s New In Angular 9?
- What’s New in Spring Boot 2.2?
- Create an Angular 9 App
- Add Angular Authentication using OpenID Connect
- Create a Spring Boot 2.2 App
- Add a Notes REST API with Spring Data REST
- Add a Notes CRUD Feature in Angular
- Lock Down Spring Boot with Recommended Security Practices
- Learn More about Angular, Spring Boot, and Kotlin
Angular 9 Spring Boot 2.2 Video Tutorial
Tutorial - Simple CRUD services with React, Spring Boot and JHipster
https://developer.okta.com/blog/2022/06/17/simple-crud-react-and-spring-boot
jhipster-crud-developer.oktacom-Use React and Spring Boot to Build a Simple CRUD App.pdf link
jhipster-crud-developer.okta.com-Use React and Spring Boot to Build a Simple CRUD App.pdf file
React was designed to make it painless to create interactive UIs. Its state management is efficient and only updates components when your data changes. Component logic is written in JavaScript, meaning you can keep state out of the DOM and create encapsulated components.
Developers like CRUD (create, read, update, and delete) apps because they show a lot of the base functionality you need when creating an app. Once you have the basics of CRUD completed in an app, most of the client-server plumbing is finished, and you can move on to implementing the necessary business logic.
Today, I’ll show you how to create a basic CRUD app with Spring Boot and React. In this tutorial, I’ll use the OAuth 2.0 Authorization Code flow and package the React app in the Spring Boot app for production. At the same time, I’ll show you how to keep React’s productive workflow for developing locally.
You will need Java 17 and Node 16 installed to complete this tutorial.
- Create an API app with Spring Boot
- Create a React UI with Create React App
- Call your Spring Boot API and display the results
- Build a React
GroupListcomponent - Add a React
GroupEditcomponent - Add authentication with Okta
- Configure Spring Security for React and user identity
- Modify React to handle CSRF and be identity-aware
- Configure Maven to build and package React with Spring Boot
- Learn more about Spring Boot and React
Spring Cloud
Spring Cloud Webinar notes
Spring Cloud Webinar notes gdoc link
https://docs.google.com/document/d/1t402nm0BzAtweNZBwonuh7j91dzyaeAmT7w7-ZOoNWM/edit?usp=sharing
https://spring.io/projects/spring-cloud
Spring Cloud provides tools for developers to quickly build some of the common patterns in distributed systems (e.g. configuration management, service discovery, circuit breakers, intelligent routing, micro-proxy, control bus, one-time tokens, global locks, leadership election, distributed sessions, cluster state). Coordination of distributed systems leads to boiler plate patterns, and using Spring Cloud developers can quickly stand up services and applications that implement those patterns. They will work well in any distributed environment, including the developer’s own laptop, bare metal data centres, and managed platforms such as Cloud Foundry.
Features
Spring Cloud focuses on providing good out of box experience for typical use cases and extensibility mechanism to cover others.
Distributed/versioned configuration
Service registration and discovery
Routing
Service-to-service calls
Load balancing
Circuit Breakers
Global locks
Leadership election and cluster state
Distributed messaging
Spring Cloud takes a very declarative approach, and often you get a lot of features with just a classpath change and/or an annotation
Spring Cloud projects list
Spring Cloud Config
Centralized external configuration management backed by a git repository. The configuration resources map directly to Spring Environment but could be used by non-Spring applications if desired.
Spring Cloud Netflix
Integration with various Netflix OSS components (Eureka, Hystrix, Zuul, Archaius, etc.).
Spring Cloud Bus
An event bus for linking services and service instances together with distributed messaging. Useful for propagating state changes across a cluster (e.g. config change events).
Spring Cloud Cloudfoundry
Integrates your application with Pivotal Cloud Foundry. Provides a service discovery implementation and also makes it easy to implement SSO and OAuth2 protected resources.
Spring Cloud Open Service Broker
Provides a starting point for building a service broker that implements the Open Service Broker API.
Spring Cloud Cluster
Leadership election and common stateful patterns with an abstraction and implementation for Zookeeper, Redis, Hazelcast, Consul.
Spring Cloud Consul
Service discovery and configuration management with Hashicorp Consul.
Spring Cloud Security
Provides support for load-balanced OAuth2 rest client and authentication header relays in a Zuul proxy.
Spring Cloud Sleuth
Distributed tracing for Spring Cloud applications, compatible with Zipkin, HTrace and log-based (e.g. ELK) tracing.
Spring Cloud Data Flow
A cloud-native orchestration service for composable microservice applications on modern runtimes. Easy-to-use DSL, drag-and-drop GUI, and REST-APIs together simplifies the overall orchestration of microservice based data pipelines.
Spring Cloud Stream
A lightweight event-driven microservices framework to quickly build applications that can connect to external systems. Simple declarative model to send and receive messages using Apache Kafka or RabbitMQ between Spring Boot apps.
Spring Cloud Stream App Starters
Spring Cloud Stream App Starters are Spring Boot based Spring Integration applications that provide integration with external systems.
Spring Cloud Task
A short-lived microservices framework to quickly build applications that perform finite amounts of data processing. Simple declarative for adding both functional and non-functional features to Spring Boot apps.
Spring Cloud Task App Starters
Spring Cloud Task App Starters are Spring Boot applications that may be any process including Spring Batch jobs that do not run forever, and they end/stop after a finite period of data processing.
Spring Cloud Zookeeper
Service discovery and configuration management with Apache Zookeeper.
Spring Cloud Connectors
Makes it easy for PaaS applications in a variety of platforms to connect to backend services like databases and message brokers (the project formerly known as "Spring Cloud").
Spring Cloud Starters
Spring Boot-style starter projects to ease dependency management for consumers of Spring Cloud. (Discontinued as a project and merged with the other projects after Angel.SR2.)
Spring Cloud CLI
Spring Boot CLI plugin for creating Spring Cloud component applications quickly in Groovy
Spring Cloud Contract
Spring Cloud Contract is an umbrella project holding solutions that help users in successfully implementing the Consumer Driven Contracts approach.
Spring Cloud Gateway
Spring Cloud Gateway is an intelligent and programmable router based on Project Reactor.
Spring Cloud OpenFeign
Spring Cloud OpenFeign provides integrations for Spring Boot apps through autoconfiguration and binding to the Spring Environment and other Spring programming model idioms.
Spring Cloud Pipelines
Spring Cloud Pipelines provides an opinionated deployment pipeline with steps to ensure that your application can be deployed in zero downtime fashion and easilly rolled back of something goes wrong.
Spring Cloud Function
Spring Cloud Function promotes the implementation of business logic via functions. It supports a uniform programming model across serverless providers, as well as the ability to run standalone (locally or in a PaaS).
Spring Cloud Message Broker
https://spring.io/projects/spring-cloud-bus
links nodes of a distributed system with a lightweight message broker. This can then be used to broadcast state changes (e.g. configuration changes) or other management instructions. AMQP and Kafka broker implementations are included with the project. Alternatively, any Spring Cloud Stream binder found on the classpath will work out of the box as a transport.
Spring Cloud Data Stream with message, Kafka services
https://developer.okta.com/blog/2020/04/15/spring-cloud-stream
spring-cloud-stream-for-messaging-developer.okta.com-A Quick Guide to Spring Cloud Stream.pdf
JHipster
JHipster Entity CRUD example - books and authors ***
https://www.jhipster.tech/creating-an-entity/
This is a short tutorial on creating two entities (a Author and a Book) which have a one-to-many relationship.
Important if you want to have “live reload” of your JavaScript/TypeScript code, you will need run npm start or yarn start. You can go to the Using JHipster in development page for more information.
Generate the “Author” entity
As we want to have a one-to-many relationship between Authors and Books (one author can write many books), we need to create the Author first. At the database level, JHipster will then be able to add a foreign key on the Book table, linking to the Author table.
jhipster entity author
Answer the next questions concerning the fields of this entity, the author has:
- a “name” of type “String”
- a “birthDate” of type “LocalDate”
Then answer the questions concerning the relationships, the author has:
- A one-to-many relationship with the “book” entity (which doesn’t exist yet)
Generate the “Book” entity
jhipster entity book
Answer the next questions concerning the fields of this entity, the book has:
- a “title”, of type “String”
- a “description”, of type “String”
- a “publicationDate”, of type “LocalDate”
- a “price”, of type “BigDecimal”
Then answer the questions concerning the relationships, the book:
- Has many-to-one relationship with the “author” entity
- And this relationship uses the “name” field (from the Author entity) to be displayed
Check the generated code
Run the generated test suite, with mvn test, which will test the Author entity and the Book entity.
Launch the application (for example with mvn), log in and select the “Author” and “Book” entities in the “entities” menu.
Check the database tables, to see if your data is correctly inserted.
Improve the generated code
The generated files contain all the basic CRUD operations, and don’t need to be modified if you don’t need more than CRUD operations.
If you want to modify the generated code or the database schema, you should follow our development guide
If you want some more complex business behaviors, you might need to add a Spring @Service class, using the service sub-generator.
You’re done!
Your generated CRUD page should look like this:
Create JHipster Native app using Spring Native and Graal VM
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8hPDL9GCD5Q
complete tutorial with source code and testing
done on MACOS or Linux
useful for fast startup on jvm apps especially for serverless functions
https://developer.okta.com/blog/2022/03/03/spring-native-jhipster
https://github.com/oktadev/auth0-full-stack-java-example/tree/spring-native
https://github.com/oktadev/auth0-full-stack-java-example/blob/spring-native/demo-native.adoc
Build Mobile Apps with Angular, Ionic 4, and Spring Boot
https://developer.okta.com/blog/2019/06/24/ionic-4-angular-spring-boot-jhipster
JHipster is an application generator, and platform, for building Java apps with JavaScript frontends.
see Grails Angular profile as an option.
Spring Boot is the only backend framework currently supported, with .NET and Node.js implementations currently in development. On the frontend, Angular, React, Vue, React Native, and Ionic are all supported.
In this brief tutorial, I’ll show you to use Ionic for JHipster v4 with Spring Boot and JHipster 6.
To complete this tutorial, you’ll need to have Java 8+, Node.js 10+, and Docker installed. You’ll also need to create an Okta developer account.
reactive #Java microservices with JHipster
230303
Thanks to everyone who joined and watched my presentation on reactive #Java microservices with JHipster!
📺 Recording: https://lnkd.in/g6VDyAzA
📚 Presentation: https://lnkd.in/gVUkb-ji
⛑️ Demo script: https://lnkd.in/gCa2z9yb
Potential Value Opportunities
Potential Challenges
Candidate Solutions
Okta - Identity Management - Java, Node.js, more
https://dev-896837.okta.com/login/login.htm
dev login
quickstart panel - learn Okta
https://support.okta.com/help/s/
Documentation
Read our reference guides about how to use Okta
Keycloak - an Open Source Identity and Access Management solution
https://github.com/keycloak/keycloak
Step-by-step guide for Example
sample code block