Key Points
- Needs p2p DER trading system like NSF
- short schedule - lot of work to deliver by 2/2/20
- complex requirements for approver logic ( workflow, tables, services, added UI screens )
- need trading dashboard with tabs for offers, bids on the left, matched trades on the right
- manual trading in MVP, automated trading not needed until production solution
- an acre of good forest can offset 2.5 tons of carbon per year
carbon-offsets-urbanforestrynetwork-Trees Improve Our Air Quality.pdf
References
EBC Project Overview
Industry, Project Name, Organization Name, Description and scope.
Energy Blockchain Consortium
Industry: energy management
Project: EBC - energy management
Peer to Peer energy trading app MVP
- clients can bid, offer and trade energy from residential solar systems over Grid network
- modern trade desk shows bid, offers dynamically to track current market trends visually, manage bids, offers, accept trades
- on ReactJS, NodeJS microservices, Hyperledger Fabric Blockchain and MongoDB
Retail Carbon Management app MVP
- Certified carbon offset provider projects can register on the platform to sell carbon offsets
- Buyers can be retail consumers or businesses trying to offset their carbon footprint
- Carbon calculator and profile show accounts what their net carbon profile is
- Online e-commerce app allows purchasing carbon offsets and other products using payment provider services ( Stripe etc )
- Site designed for multi-currency, testimonials, FAQS, customer blogs
- Integrates Wordpress and plugins as a "headless CMS"
- on ReactJS, NodeJS microservices, Hyperledger Fabric Blockchain, MongoDB and Swift for iPhone
Dev Trading app
https://ebc-dev.sysopsnetwork.com/trade
Fabric Environment v2.2
https://hyperledger-fabric.readthedocs.io/en/release-2.2/
Fabric Node SDK docs
https://hyperledger.github.io/fabric-sdk-node/release-2.2/module-fabric-network.html
Environments
EBC github
08:47:46 From Jim Mason to Everyone : https://github.com/Paramount-Software-Solutions/nsf-blockchain
08:48:00 From Jim Mason to Everyone : https://github.com/Paramount-Software-Solutions/enerblock-master-chaincode/blob/master/common/structs/ebStructs.go
10:09:57 From Thomas Bereczky to Everyone : https://github.com/Paramount-Software-Solutions/ebc-approvers-api/blob/dev/src/services/accounts/accounts.hooks.js
Git vs Github Desktop
EBC DEV environment sites
mongodb compass link
mongodb+srv://dbAdmin:<password>@cluster0.pfjbe.mongodb.net/test
#mongodb compass link
mongodb+srv://dbAdmin:u3KpFTzZBEIEQLzY@cluster0.pfjbe.mongodb.net/test
mongodb+srv://dbAdmin:u3KpFTzZBEIEQLzY@cluster0.pfjbe.mongodb.net/test
use case doc
https://docs.google.com/document/d/1duVmu5pVQZ95aUb9PijtVbbH2dfG1W-B8b2pWboMl-8/edit#
github
https://github.com/Paramount-Software-Solutions/ebc-api
jm9
Syn#
couchdb
http://3.21.101.182:5984/_utils/
admin / adminpw
explorer
http://3.21.101.182:8080/#/
exploreradmin
exploreradminpw
cloud web site links
EBC API Link for dev environment -
https://ebc-dev.sysopsnetwork.com/
EBC API Link for dev approver api
https://ebc-approvers-dev.sysopsnetwork.com
EBC-UI Approver
https://ebc-frontend-dev.sysopsnetwork.com/
EBC-UI Approver
https://ebc-approver-frontend-dev.sysopsnetwork.com/
Explorer
EBC QA environment sites
Frontend: https://ebc-qa.sysopsnetwork.com/
Frontend approvers app:
https://ebc-approver-frontend-qa.sysopsnetwork.com/
EBC API: https://ebc-api-qa.sysopsnetwork.com/
EBC API Link for qa approver api
https://ebc-approvers-qa.sysopsnetwork.com
ChainAPI: http://3.136.68.231:3030
Couch:
http://3.136.68.231:5984/_utils/#
http://3.136.68.231:5984/_utils/#/_all_dbs
api server
ebc-qa.sysopsnetwork.com
EBC
A FeathersJS application
A FeathersJS server
but there is no couch right now
EBC One_app demo now
Check Mongo in DEV
accounts
{"userName": {$in: ["jeff","jody","tim","jim"]}}
jobQ
{ "createdAt": {$gte: ISODate('04-12-2021')}}
Check API server in dev
https://ebc-api-dev.sysopsnetwork.com
Check Fabric in dev
couchdb
http://3.21.101.182:5984/_utils/
admin / adminpw
explorer
http://3.21.101.182:8080/#/
exploreradmin
exploreradminpw
Load, run One_app front-end code locally from one_app branch
old EBC MVP running in dev, qa
To run current one_app:
download latest one_app from github in ebc-frontend folder
npm install
npm start
in Chrome:
http://localhost:3000/device
old dev frontend
https://ebc-dev.sysopsnetwork.com/trade
Key Concepts
EBC Retail P2P Energy Trading Market
Use Case Concept Diagram
Architecture Concept Diagram
Test case:
model a CreateOffer transaction flow from the user browser to completion
High level Flow
Steps
- After login, user on the Web browser goes to the trades menu, offers list and selects Add Offers
- trade API server executes offers.create
- the new offer is written to Mongo
- the new offer is added to the Job Queue
- The chain API server reads the new offer request and sends it to Fabric contract using the SDK
- The Fabric GO smart contract writes the new offer to the ledger and CouchDB
Detail transaction flow
1> User on the trades menu, selects Add Offer action
2> Front-end Web app invokes createOffer request on trade API server
Offers.js
export const callAddOffersApi = (data) => {
return (_dispatch, _getState) => {
return fetchClient.post(`${constants.API.OFFERS.OFFERS}`,
data ...
3> trade API server executes offers.create.before which writes new offer to Mongo
offers.hooks.js
create: [
async context => {
context.data.status = 'open';
await context.app.service('accounts').patch({_id: context.params.account._id }
4> trade API server executes offers.create.after which adds the new offer to the Job Queue
offers.hooks.js
create: [
async (context) => {
await context.app.service('transactions').create(... status: 'created' });
let bc = await context.app.get('blockchain');
await axios.get(bc.url + '/offers/create/' + context.result._id
5> trade API server returns success status to Front-end Web app
offers.hooks.js
feathers returns status to requestor client
6> Front-end Web app returns success message to User
AddOffers.js
.callAddOffersApiAction({ ...initialValues })
.then((res) => {
setIsFlag(true);
CustomerNotification(
"success",
"Offer Added Successfully",
7> chain API server reads jobQ offer, sends to Fabric contract which writes offer to ledger, CouchDB
processOffer.js
let jobs = await ctx.model('jobQueue').find({'jobName': 'CreateOffer', 'status': 'created'}).sort({'createdAt': 1});
await Utils.AsyncForEach(jobs, async (x) => {
try {
await ctx.model('jobQueue').updateOne({_id: x._id}, {status: 'inProgress'});
let entry = await ctx.model('offers').find({'_id': x.entryId});
...
const contract = network.getContract('energy');
let trans = await
contract.submitTransaction('CreateOffer' ...
8> Fabric server smart contract writes offer to ledger, CouchDB
chaincode.go
func (s *SmartContract) CreateOffer(ctx contractapi.TransactionContextInterface, offerid string, accountid string, deviceid string, offerKWH int, rate float64, startTS string, endTS string, status string) (string, error) {
exists, err := s.OfferExists(ctx, offerid)
...
TXID := ctx.GetStub().GetTxID()
ctx.GetStub().PutState(offerid, offerJSON)
return TXID, nil
9> chain API server gets transaction ID, updates offer in Mongo
processOffer.js
await ctx.model('offers').updateOne({ '_id': x.entryId }, { lastTransactionTxId: trans.toString() });
await ctx.model('jobQueue').updateOne({_id: x._id}, { status: 'done' });
jobs = await ctx.model('jobQueue').find({'jobName': 'CreateOffer', 'status': 'created'}).sort({'createdAt': 1});
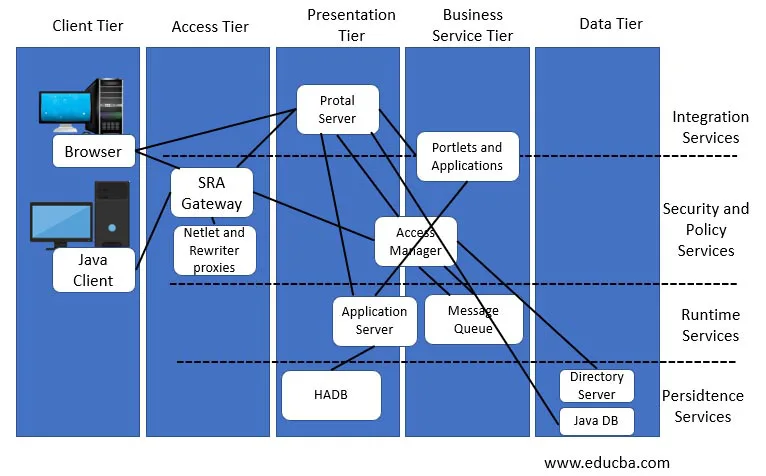
Tiers and Layers Diagram
- Tiers
- N Tier architecture may have an external client tier, multiple service tiers ( representing a complex business services network - Access, Presentation, Services ) and multiple resource tiers ( database, media, messages etc ) as an extension of the basic 3 Tier architecture
- clear separation of roles and responsibilities on a VCN
- Layers
- Modern architecture separates responsibilities into distinct layers where possible. This concept builds on the old OSI comm layer model. With layers, you get
- clean separation of responsibilities and roles for management and governance
- ability to reuse existing services or invoke new services speeding development, delivery and improved modularity
A sample Tiers and Layers diagram from edudba.com
for more see: https://www.educba.com/logical-architecture/
Grids partner with Solar Companies to offer no-cost solar installs
DER, VPP glossary
kva
https://www.generatorsource.com/Generator_Faq.aspx
The primary difference between kW (kilowatt) and kVA (kilovolt-ampere) is the power factor. kW is the unit of real power and kVA is a unit of apparent power (or real power plus re-active power).
inverter
A power inverter, or inverter, is a power electronic device or circuitry that changes direct current to alternating current.
A Power Meter is one of the most useful and simple instruments to measure electrical power when no deeper analysis of the measured data is required. It measures the voltage (V) and current (A) and derives from these the most important power results.
smart power meter
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Smart_meter#:~:text=A%20smart%20meter%20is%20an,system%20monitoring%20and%20customer%20billing.
A smart meter is an electronic device that records information such as consumption of electric energy, voltage levels, current, and power factor. Smart meters communicate the information to the consumer for greater clarity of consumption behavior, and electricity suppliers for system monitoring and customer billing
A distributed energy resources management system (DERMS) is a platform which helps mostly distribution system operators (DSO) manage their grids that are mainly based on distributed energy resources (DER). By lack of a common definition, a DERMS thus – depending on your point of view – is something similar or even identical with a Virtual Power Plant (VPP).
On some key aspects, people seem to agree:
DERMS is a software platform that is used to organize the operation of the aggregated DER within a power grid.
The usual DERMS application is found at the distribution grid level. DERMS typically require a more full-fledged integration of various other systems such as a distribution management system (DSM) for integrating it with a utility. Furthermore, an outage management system (OMS) or a supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) system is usually needed to provide all DERMS functionality.
DERMS provide grid services that especially focus on the location of each aggregated asset. Objectives of a DERMS are:
- Voltage management of the grid
- Optimization of the power flow within the grid
- Local grid load management (e.g. for smart grid projects)
VPPs on the other hand are responsible for active optimizations and control of power production and consumption. The location of the aggregated doesn’t play an important role. The main purposes of a VPP are:
- Grid frequency stabilization
- Energy trading
- Portfolio management
- Peak load/demand management
solar power controller
https://www.altestore.com/store/info/solar-charge-controller/
A solar charge controller manages the power going into the battery bank from the solar array. It ensures that the deep cycle batteries are not overcharged during the day, and that the power doesn't run backwards to the solar panels overnight and drain the batteries.
REC - renewable energy credits
https://www.energysage.com/other-clean-options/renewable-energy-credits-recs/#:~:text=Renewable%20energy%20certificates%20(also%20known,energy%20attributes%20of%20renewable%20electricity.
Renewable energy certificates (also known as renewable energy credits, or RECs) represent the energy generated by renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind power facilities. Buying RECs is not equivalent to buying electricity. Instead, RECs represent the clean energy attributes of renewable electricity.
NE Pool for trading RECs
The New England Power Pool Generation Information System (NEPOOL GIS) issues and tracks certificates for all MWh of generation and load produced in the ISO New England control area, as well as imported MWh from adjacent control areas. In addition to the generation, the NEPOOL GIS provides emissions labeling for the New England load-serving entities by tracking the emissions attributes for generators in the region. In recent years the NEPOOL GIS has adapted to the various state RPS laws to track combined heat and power, demand response and conservation and load management certificates.
https://www.nepoolgis.com/public-reports/
https://www1.nepoolgis.com/mymodule/rpt/CertificateInfo.asp?rhid=2160732&ftType=H2O
Carbon Credits
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Carbon_credit
A carbon credit is a generic term for any tradable certificate or permit representing the right to emit one tonne of carbon dioxide or the equivalent amount of a different greenhouse gas (tCO2e).[1][2][3]
Carbon credits and carbon markets are a component of national and international attempts to mitigate the growth in concentrations of greenhouse gases (GHGs). One carbon credit is equal to one tonne of carbon dioxide, or in some markets, carbon dioxide equivalent gases. Carbon trading is an application of an emissions trading approach. Greenhouse gas emissions are capped and then markets are used to allocate the emissions among the group of regulated sources.
The goal is to allow market mechanisms to drive industrial and commercial processes in the direction of low emissions or less carbon intensive approaches than those used when there is no cost to emitting carbon dioxide and other GHGs into the atmosphere. Since GHG mitigation projects generate credits, this approach can be used to finance carbon reduction schemes between trading partners and around the world.
There are also many companies that sell carbon credits to commercial and individual customers who are interested in lowering their carbon footprint on a voluntary basis. These carbon offsetters purchase the credits from an investment fund or a carbon development company that has aggregated the credits from individual projects. Buyers and sellers can also use an exchange platform to trade, which is like a stock exchange for carbon credits. The quality of the credits is based in part on the validation process and sophistication of the fund or development company that acted as the sponsor to the carbon project. This is reflected in their price; voluntary units typically have less value than the units sold through the rigorously validated Clean Development Mechanism.[4] The European Union's carbon credits traded from $7.78 to $25.19 averaging $16.21 per tonne in 2018.[5] Although it remains in development, it is anticipated that the value and trading of carbon credits will continue to grow particularly as several governments have committed to "green recoveries" following the COVID-19 pandemic recession.[6]
Carbon Offsets
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Carbon_offset
A carbon offset is a reduction in emissions of carbon dioxide or other greenhouse gases made in order to compensate for emissions made elsewhere.[1][2][3] Offsets are measured in tonnes of carbon dioxide-equivalent (CO2e). One tonne of carbon offset represents the reduction of one tonne of carbon dioxide or its equivalent in other greenhouse gases.
There are two types of markets for carbon offsets, compliance and voluntary. In compliance market like the European Union (EU) Emission Trading Scheme companies, governments, or other entities buy carbon offsets in order to comply with mandatory and legally binding caps on the total amount of carbon dioxide they are allowed to emit per year. Failure to comply with these mandatory caps within compliance markets results in fines or legal penalty. According to the World Bank State and Trends 2020 Report 61 carbon pricing initiatives are in place or are scheduled for implementation globally. These include both emission trading schemes (like cap-and-trade systems) as well as carbon taxes and, while these initiatives represent markets for carbon, not all incorporate provisions for carbon offsets, instead placing greater emphasis on achieving emission reductions within the operations of regulated entities. The original compliance carbon market was initiated by the Kyoto Protocol's Clean Development Mechanism (CDM). Signatories to the Kyoto Protocol agreed to mandatory emission reduction targets, enabled (in part) by carbon offset purchases by higher-income countries from low- and middle-income countries, facilitated by the CDM. The Kyoto Protocol was to expire in 2020, to be superseded by the Paris Agreement. The Paris Agreement determinations regarding the role of carbon offsets are still being determined through international negotiation specifying the "Article 6" language.[4] Compliance markets for carbon offsets comprise both international carbon markets developed through the Kyoto Protocol and Paris Agreement, and domestic carbon pricing initiatives that incorporate carbon offset mechanisms.
With the increase of population, more specifically urban population due to densification, there is more of a demand for carbon offset.[5] Within the voluntary market, demand for carbon offset credits is generated by individuals, companies, organizations, and sub-national governments who purchase carbon offsets to mitigate their greenhouse gas emissions to meet carbon neutral, net-zero or other established emission reduction goals. The voluntary carbon market is facilitated by certification programs (e.g., the Verified Carbon Standard, the Gold Standard, and the Climate Action Reserve) which provide standards, guidance, and establish requirements for project developers to follow in order to generate carbon offset credits. These programs generate carbon offset credits provided that an emission reduction activity meets all program requirements, applies an approved project protocol (also called a methodology), and successfully passes third party review (also called verification). Once carbon offset credits are generated, any buyer may purchase them; for example an individual may purchase carbon offsets to compensate for the emissions resulting from air-travel (see more on Air-travel and Climate).
EPA REC concepts
https://www.epa.gov/repowertoolbox/state-solar-renewable-energy-certificate-markets
State Solar Energy Renewable Certificate Markets
A renewable energy certificate (REC) is a market-based instrument that represents the property rights to the environmental, social, and other non-power attributes of renewable electricity generation. Solar RECs (SRECs) are created for each megawatt-hour of electricity generated from solar energy systems. The ultimate owner of the SREC owns the "solar-ness" of the power.
Many states create SREC markets to spur the development of solar by requiring electricity suppliers to purchase SRECs produced by in-state solar systems as part of their obligation under the state’s Renewable Portfolio Standard (RPS). This solar-specific requirement to meet a portion of the RPS with solar resources is often referred to as a “solar carve out.” Through the purchase of the SRECs, electricity suppliers are ensuring that their products meet the RPS-mandated amount of solar power. The monetary value of an SREC in these state markets is determined by supply and demand, with demand largely driven by electricity suppliers needing to meet their solar RPS requirement or pay a compliance premium.
Homeowners and businesses hosting solar systems in states with SREC markets are able to reduce their costs of electricity by selling the SRECs associated with their systems’ output into the SREC market, for ultimate use by utilities. However, by doing so, homeowners and businesses preclude themselves from making solar power “use” claims or claims on reducing their carbon footprint. For more on claims, visit the Solar Power Use Claims Guidance webpage.
Below are resources to help you understand how state SREC markets work, which states have SREC markets, and how SRECs may impact your project development.
The following links exit the site EXIT
Map of State Renewable Portfolio Standards (RPS) with Solar or Distributed Generation Provisions (PDF) (1 pg, 116K)The Database of State Incentives for Renewables & Efficiency (DSIRE), operated by the N.C. Clean Energy Technology Center, is the most comprehensive source of information on incentives and policies that support renewable energy and energy efficiency programs in the United States. DSIRE provides state-specific information on RPSs with solar carve outs or provisions.Database of State SREC ProgramsDSIRE, operated by the N.C. Clean Energy Technology Center, is the most comprehensive source of information on incentives and policies that support renewable energy and energy efficiency programs in the United States. This table provides details on state-specific SREC programs, including which type of entities are eligible for the program, what size and type of solar systems are eligible, and information on the financial incentive offered.Solar Renewable Energy Certificate (SREC) Markets: Status and Trends (PDF) (58 pp, 1.2MB)SREC markets have emerged in U.S. states as a method to meet compliance with solar carve out provisions of RPSs. This report, produced by The National Renewable Energy Laboratory, provides an overview of the SREC market and design, as well as the market trends and key issues facing SREC markets. The report was published in 2011, so some information may not be up-to-date. For more recent information about specific policies in your state, check out DSIRE or contact your state’s energy agency.
REC trading concepts
https://www.epa.gov/greenpower/renewable-energy-certificates-recs
- What is a renewable energy certificate (REC)?
- How do RECs work?
- What is the legal basis of RECs?
- What is REC Arbitrage?
- What is the Difference Between RECs and Offsets?
Greenpoint energy management services
Custom Programs
Fully customizable and white-labeled enterprise solution
RETAIL FUEL REDUCED EMISSIONS PROGRAMS
No fuel additives or new hardware.
FLEET & FINANCIAL PROGRAMS
Go green with every click and transaction.
PACKAGING & CONSUMER PRODUCTS
Reduce your impact to attract new audiences.
RENEWABLE ENERGY PROGRAM
Meet customers’ demand for sustainable energy.
SUSTAINABILITY PROGRAM CONSULTING
Consult with our experts to create your own program.
Branded Products
Turnkey environmental programs for immediate implementation
IMPACT COLLECTIVE
Our turnkey program for consumer-facing products.
GREENERMILES
An eco-friendly fleet mgt
Carbon technology
Carbon life cycle in the ocean: algae, fungus etc
https://phys.org/news/2021-06-fungus-fast-track-carbon.html
carbon-bio-cycle-phys-Fungus creates a fast track for carbon.pdf
Enerblock concepts
from HLR doc v2
Virtual Power Plant framework enabled by blockchain to monitor and trace electricity generated, monitor and transfer electricity from energy storage assets, and produce the requisite tokenization strategy.
Tokenization
Tgen
Power Generation: Tgen tokens created
Kwh
5 minute intervals (beginning)
15 minute intervals (Advanced)
When Charging a Battery: Tgen token is exchanged for the Tstorage token and burned
Operating a Load
Tgen tokens are burned
The operating load would be buying the token at some price, and presumably the asset owner can offer both the Tgen token and the Tstorage token to the operating load (representing the grid) at any given point in time.
Rate
Date/Time
Tstorage
Token Burn Algorithm
Sets tokens aside if it thinks they're not required based upon extrapolations from historical data, but burns them after verifying the capacity has fallen and necessitates the burn using interpolated data at various points.
Must account for different battery burn rates, which is a function of battery discharge and battery lifetime
Other P2P energy trading systems
Tokens in DER systems
Token concepts
- Energy Token -
- Stored Energy can be recorded as an NFT for an expiring asset ( Non-fungible token ).
- The energy token is minted when the energy is created as a unit for an account device
- The energy token is a charge in a battery that decays over time which should be reflected as a standard rate of decay
- The energy token is burned when energy is consumed
- The energy token can be transferred to another party in a trade but there are fees for the trade ( a platform transfer fee and a distribution charge on the grid )
- on the trade, the original energy token is burned, the energy transferred via the grid to the buyer mints a new token
- if the grid "buys" the energy, the original token is burned, the energy transferred to the grid in the purchase but no new token is created
- Rewards Token
- a standard Utility token can be created for the platform to reward specific activities by each party
- Payment Token
- a payment token on the platform can be created to reflect when payment tokens are purchased ( minted ), payments are earned ( minted ), when they are spent ( exchanged ) or redeemed ( burned ) for actual payments to a bank account.
- The payment token can be limited to the platform ( vs a public stable coin like USDT, USDC etc ).
- They payment service can purchase tokens or redeem tokens from a bank account using the ACH connection for a very low fee ( $1.10 )
- The option exists to handle payments using a stable coin ( like Tether USDC etc )
- Those stable coins have higher fees but offer digital custody services etc that our platform would not if we use our own payment tokens
- Concerns for stable coins are actual fees to operate, digital custody and reserve requirements, governance and compliance with banking regulations ( which state ? Wyoming or ? )
- Governance Token
- we have no defined need for a governance token to control how the platform itself operates at this point
The token accounting can be done in our platform directly
The purchase, exchange and redemption of payment tokens can be done directly using our token service to a client bank account on an ACH transfer or using APIs to a stable coin service our clients would be required to register with
EBC Setup - Test Environments - docs
Testing API services locally
Frontend startup
frontend call ...
npm run startLocal
( script )
ebc-api startup
ebc-api call
NODE_ENV=devLocal PORT=3030 npm start
Changes to ebc-api app
added package.json scripts
"scripts": {
"start": "react-scripts start ",
"start-qa": "env-cmd -f .env.qa react-scripts start ",
"startLocal": "env-cmd -f .env.localApi react-scripts start ",
"build": "react-scripts build",
"test": "react-scripts test",
"eject": "react-scripts eject"
},constants.js
API_URL = process.env.REACT_APP_API_URL;
console.log(" process.env", process.env);
.envLocalApi
// REACT_APP_API_URL=https://ebc-api-dev.sysopsnetwork.com/
REACT_APP_API_URL=http://localhost:3030/
Changes to ebc-frontend-app
config folder has json config files for each environment
devLocal.json
{
"blockchain": {
"url": "http://3.21.101.182:3030",
"authkey": "18metreswu0ubrahow9ecuzoyiswldr3drubu57cEpaben2w4achorudrawls9es",
"authsecret": "SpA7At4eyeTab8lchivoyAFra6unEvLjoki1oyogow5owljitro6How3TH7tRltrj+bIs!4Wrl+#+!2uw10IJ#T8iTrihLstuv_T7-!+?2d=chE#tes*9u5lsWum4w&U"
},
"mongodb": "mongodb+srv://dbAdmin:u3KpFTzZBEIEQLzY@cluster0.pfjbe.mongodb.net/ebc_dev?retryWrites=true&w=majority"
}authentication.js
const { AuthenticationService, JWTStrategy } = require('@feathersjs/authentication');
const { LocalStrategy } = require('@feathersjs/authentication-local');
const { expressOauth } = require('@feathersjs/authentication-oauth');
module.exports = app => {
const authentication = new AuthenticationService(app);
authentication.register('jwt', new JWTStrategy());
authentication.register('local', new LocalStrategy());
app.use('/authentication', authentication);
app.configure(expressOauth());
app.service('authentication').hooks({EBC Test Environment Setup Examples
Local NPM builds
npm run build
npm install -g serve
serve -s build
localhost:5000
this url works now - direct call to the active AWS zone
http://ebc-frontend-dev.s3-website.us-east-2.amazonaws.com/
Run apps on Local system
NODE_ENV=devLocal port=3030 npm #dev
Feathers queries on GET requests
https://ebc-api-dev.sysopsnetwork.com/bids?accountId[$ne]=6008f9791404d97cb59bd982&$limit=10&$skip=0
add a starting date query for bids
{{base_url}}/bids/?accountId[$ne]=6008f9791404d97cb59bd982&status=open&createdAt[$gte]=2021-02-22
Key Env Tasks
remote
aws
mongo / mongoose
github
feathers
hlf v2.2 - GO
React / Redux
local or my aws
ubuntu
mysql or mongo / mongoose
git
feathers
hlf v2.2
hlf v2.2 asset xfer samples tests
Key Engineering Tasks
--------------------------------------------
a>> create a production design doc in gdocs
--------------------------------------------
non-functional production requirements
- The 12 SWT solution themes
- 12 Factor app model for services solutions
- OWASP 10 factor security considerations - data in-flight, at-rest, in-process
- identity methods supported - userId-pwd, digital identities for people?
- device ids, credentials with expirations
- digital id, crypto recovery models for accounts, devices
- KMS - key management system - KeyChain software eos ?
- handling key rotations for transactions and queries over time
- additional design, test and user documentation
- support for multiple microservices in feathers or other frameworks
- support for functional authorization by role
- support for data authorization by role
- consider automated testing options for API, database, Fabric, UI
- feathers support for microservices, authorization models, external service integration, extended models based on views with edit rules
- configuration support by environment
- real-time screen updates for selected elements using web sockets
- consider UI options for Web, Mobile interfaces
- persistent messaging services as an option to replace the database transaction tables based on performance tests ( Mongo tables or Kafka ?? )
- rethink what is stored on the ledger
- consider a logical global transaction id linking database and ledger updates ( like the last TXID ) now
- consider IoT integration services ( Nodered or Kafka or MQTT or ?? ) for solar smart controllers
- review IoT device integration standards for solar controllers and test with Elcrow PI
- define analytics module for the home owner, for the grid operator showing consumption and production trends, purchases etc
- consider the automated trader feature based on policies
- consider the trade planner feature
- user accounts need policies
- integrate device data to the user account system
- evaluate a rules framework for feathers or ?
- consider Grails for master table maintenance
- decide on Mongo vs MySQL for JSON data
- review CICD pipeline and related tests
- consider better automated management of crypto artifacts in Fabric and usage by the application for signed transactions etc
- consider better event pub sub services model for streaming events
Key Design Tasks
WP headless CMS
Object Context
Use Case Scenarios
RDD Features
Data Models
Payments with Stripe
Object Context
Use Case Scenarios
RDD Features
Data Models
Account Management
Object Context
Use Case Scenarios
RDD Features
Data Models
Product Management
Object Context
Use Case Scenarios
RDD Features
Data Models
Order Processing
Object Context
Use Case Scenarios
RDD Features
Data Models
Sales Analysis by Account, Product
Object Context
Use Case Scenarios
RDD Features
Data Models
CDD for Non-Functional Features
eg environment items: security, performance, RAS, RTO, RPO, onboarding, authn, authz
Blockchain Concepts
Object Context
Use Case Scenarios
RDD Features
Data Models
Key Dev Tasks
test nsf-api - feathers.js
https://github.com/Paramount-Software-Solutions/nsf-api
data model ok
generate domain classes from jdbc metadata - fields, fk refs
default relation = hasMany
change as needed to belongsTo hasOne
grails ....
create app
create domain classes - gen edit
create controllers
create views
hlf v2.2 nodejs example
Key Test Tasks
Test info
Base URL
https://nsf-api.sysopsnetwork.com/
Documenter
https://documenter.getpostman.com/view/5352743/SzS1SoR6?version=latest
Postman NSF API setup
Postman Testing NSF REST api
Problems with UN SDG s and SDG18
The goals are clearly intentionally poorly defined which logically reduces the opportunity for both consensus and action
Each group believes its interpretation of the goals is the correct one leading to division not consensus
SDG18 is implied - Population growth is a high goal
In a world the other 17 goals are all negatively impacted by population growth and there is no goal to limit the population growth, then SDG18 can be assumed as implicit support for population growth. All the actions on the other 17 also encourage population growth. The behavior of governments and NGOs and many corporations is that population growth must be valuable and good even though none of them directly express that goal.
Potential Value Opportunities
pilot = 2 yrs
prod at national grid after = 2 yrs
3 big goals
- virtualize smeter p2p trading service for nat grid
- create hw package w meters, etc and software for nat grid low income
- other utilities
a> email w docs
a> pilot features, estimates ???
what does a production pilot cost ???
a> how can a smart meter be virtualized here ???
how can we partner w existing energy services companies ???
a> how to package smart meter service to other utilities ???
David King has other energy marketing leads .. Frank
a> see enerblock web site slides
a> new slides on ...
1> dual inverter architecture
2> virtual smart meter
nsf.report>
gsearch - bc poc report
see JIRA, HLR, BOA, bcp folder
diagrams for
use cases
bpm data flows
EBC MVP report model
https://www.hyperledger.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/HL_SolutionsBrief_ReduceCost_V8.pdf
overview
poc goals, value add
poc reqmts map to HLR use cases register user account, create assets, load transactions,
poc environment
poc development
poc testings & findings
poc summary
production architecture
production features
next steps
Candidate Production Requirements
production requirements are driven by functional and non-functional requirements supplied by EBC.
Candidate requirements include:
- The 12 SWT solution themes
- 12 Factor app model for services solutions
- OWASP 10 factor security considerations - data in-flight, at-rest, in-process
- identity methods supported - userId-pwd, digital identities for people?
- device ids, credentials with expirations
- digital id, crypto recovery models for accounts, devices
- KMS - key management system
- handling key rotations for transactions and queries over time
- additional design, test and user documentation
- support for multiple microservices in feathers or other frameworks
- support for functional authorization by role
- support for data authorization by role
- consider automated testing options for API, database, Fabric, UI
- feathers support for microservices, authorization models, external service integration, extended models based on views with edit rules
- configuration support by environment
- real-time screen updates for selected elements using web sockets
- consider UI options for Web, Mobile interfaces
- persistent messaging services as an option to replace the database transaction tables based on performance tests ( Mongo tables or Kafka ?? )
- rethink what is stored on the ledger
- consider a logical global transaction id linking database and ledger updates ( like the last TXID ) now
- consider IoT integration services ( Nodered or Kafka or MQTT or ?? ) for solar smart controllers
- review IoT device integration standards for solar controllers and test with Elcrow PI
- define analytics module for the home owner, for the grid operator showing consumption and production trends, purchases etc
- consider the automated trader feature based on policies
- consider the trade planner feature
- user accounts need policies
- integrate device data to the user account system
- evaluate a rules framework for feathers or ?
- consider Grails for master table maintenance
- decide on Mongo vs MySQL for JSON data
- review CICD pipeline and related tests
- consider better automated management of crypto artifacts in Fabric and usage by the application for signed transactions etc
- consider better event pub sub services model for streaming events
- transaction replay support
References for Production Architecture
Design Node.js Backend architectures
https://afteracademy.com/blog/design-node-js-backend-architecture-like-a-pro
Production Design Concepts - Tony
Development Plan of Release 1.0 is coming But we’ll start with a simple framework
Let’s start with a simple framework with some mock functionality. This is work for only 1-2 weeks and does not need to be very sophisticated. Just functional.
Time Frame: One or two weeks.
Functional Overview: Create a simple framework of an application - Use the existing Version of the product we have developed, and add the following. We can use a template to reduce any design work. Focus should not be on design but just to get the functionality working. Go with the assumption that we will do a UI UX design.
More details will be provided next week (June 11)
- Add couple of fields to registration process;
- Create a simple data structure (in off blockchain) as “carbon inventory”. It needs only a few sample fields.
- Add a few tabs to a user’s dashboard with a simple search function to search the carbon inventory. Show results. Create a mock report that shows where the carbon came from.
- Let user purchase a product. Pay for it via Steller or other. Reduce inventory. Create audit trail of the transaction on Blockchain. The mock carbon report should now say that offset was bought.
- Simple Calculator to calculate carbon offset.
- Do 1-2 day research on an open source NFT (Cardona with PoS, Binance or other) options.
Solution Design
Step 1: Individual or Business User Registration (Do Item 15 above)
Modify the current registration process as follows:
- Add a new field to distinguish a user or a business. Do what people are doing to register uses and businesses. IF there I sno better way then, just add a new field called “ I am “ with possible values of “Individual” or “Business”.
- Add a new value in the “Affiliation” field. It’s called “No Affiliation”
- When a new user registers with Affiliation = “No Affiliation” then we do not need to verify a user by approvers because this user has no affiliation s they are just a simple buyer. If this user needs to add his DER assets then we will deal with that use case later.
- The registration process should send an email to person’s email for verification (This is standard internet practice and should have been implemented in first POC release but it was not). When the user clicks that email, then he/she is considered registered.
- Give the individual user the ability to put personal information and the business user to put business information in addition to personal info.
Step 2: Carbon Offset Inventory (mock) - Create a very simple data structure in offline database to contain carbon offsets inventory.
- Perhaps we can have5-6 simple fields: Certificate Number <Alpha numeric>, Project Name, Project Type, Date Started, End Date, Status= Active, Retired, Withdrawn and then the Units (say we start with 8), Price per Unit = $15 (say), Description.
- Put mock data with 7-8 records with different project types.
- Decrement the counter if the use clicks buy button in next step.
Step 3: User Dashboard (Simple Version): When the new user logs in, who is not affiliated with anyone, then he/she should see a page that has the following tabs:
- Buy Carbon Offsets ß This is default and will provide a search options whose parameters will be provided by Tony. For now just go with a screen that provides 3 fields: Project Type,
- Carbon Packages ß Give three packages or products $10 per month for one year, $20 per month for one year and $50 per year per month. Don’t worry about the exact wording or amount number. Just get basic infrastructure including database access. In the first go, we can wait for tat
- My Carbon Footprint: This is user’s calculated footprint baseline It should stay “Blank” currently.
- Carbon Calculator: We will make this nice but more after one week.
- <Maybe few others TBD later>
- User goes to “Buy Carbon Offset” page, searches per some criteria that is mocked, and it spits out relevant offsets inventory. In front of each line item is a button that says traceability or chain of custody or a some more simpler word. When clicked it displays a very nice report with info relate to the asset: Like who is the project developer, when it started, etc etc. This is dynamically generated. When asset is bought it will say bought etc.
Step 4: Purchase and Pay: User clicks on one product - No matter what they buy , just go to carbon registry and decrement the item purchased and then go to payment processing:
- Let’s add payment gateway to process this payment in US$ or local currency. Thomas was discussing the Steller network. Let’s see if we can use that. I want to make sure that we can use micro payments capability as well.
- Once the payment is processed, let’s keep the transaction info in the history log. Remember for Audit and Traceability purposes we will access this.
- Product is bought
- It goes to user’s transaction history (my orders).
- Reduce inventory once the transaction is successful.
- Offsets should show a link to the transaction we just did.
Step 5: Simple Calculator to calculate carbon offset.
- Assume that an average person has 20 MtCO2e (20 metric tonnes) as their carbon footprint in United States.
- Add a couple of sliding widgets – like num of cars they have (0 to 5), and how often they use public transportation (0% to 100%) and use these numbers to just create some simple new calculated footprint. It does not need to be sophisticated.
Step 6: Do research on open source White Label NFTs and how can we use that to build EBC’s NFT Marketplace. Also do research on “Gas” fees on Ethereum network and the cost. If the cost of NFT minting is say $40 of gas fee etc, and our NFT is $10 then it makes no sense for the NFT owner to pay $40 and g $10. Provide top 2-3 options.
Best
Tony
Recommendations for the Digital Voluntary and Regulated Carbon Markets - 2023 - WE Forum
Recommendations_for_the_Digital_Voluntary_and_Regulated_Carbon_Markets.pdf link
Recommendations_for_the_Digital_Voluntary_and_Regulated_Carbon_Markets.pdf file
1 Challenges facing carbon markets
2 Recommendations for the next generation of digitally native carbon markets
2.1 Improvement of governance
2.2 An accessible marketplace, product definition and clarity
2.3 Applied technology for radical scalability
2.4 Interoperability and transparency across exchanges and platforms
3 The time is now
Carbon Market Challenges
Lack of transparency, integrity and confidence in the monitoring, issuance, sale, retirement and benefits distribution of carbon credits, as well as in third-party certifications
- use of certification standards, Certification bodies, independent - licensed certifier organizations
- online marketplace showing registered parties ( producers, consumers, certifiers, projects, standards orgs ), project status and types, inventory life cycle mgt, order life cycle, delivery life cycle, taxations, my carbon stories, wish lists, private sale lists, histories downloadable
- mobile, web, api access models
- SLT based on trusts, scale
Inaccessibility, inequity and lack of participation in carbon markets by women, local communities, smallholder land stewards, Indigenous people and other vulnerable populations
Insufficient scale to meet climate commitments
Potential Challenges
Improving authentication for EBC MVP applications
To meet an unrealistic MVP deadline from the client, we created 2 separate services: one for users trading, one for approvers
The plan was to only provide a Web UI for user trading, not for approver services.
Approvals of accounts and devices could be done through the database, not a Web UI.
As the client changed the requirements to add a Web UI for approvals, we made the decision to create a second Web app with a matching Web service to cut time and costs.
IF we had more time, funds, a long-term design would use a different model to support different user types and functional authorization
A plan to consolidate the existing MVP solution into a single app and integrated user database
- Consolidate the trade and approver applications into one application
- Change the trade and approver services to use a single authentication token
- Change the account and approver tables to have the SAME identity for any user that is in both tables
Production architecture is out of scope on budget, time now
- Create a new registration solution that incorporates the existing approver table functions
- Create a new authentication service that supports the added approver functions
- Extend the authorization model to support specific RBAC - role based access control - beyond the base roles of user, approver
- Extend the authorization model to support data contexts beyond the limited model in the MVP
MVP2 Challenges
- Client planning gaps for MVP2
- client disappears for 10 weeks to create a "capabilities" specification
- client says it will only take 2 weeks to implement because they are experts on the web technologies used
- client spec is not a design and has many logical, process and data gaps to be filled ( BUT "design not needed" )
- client thinks coding and design can start day 1 not understanding an Agile process has design before coding
- Our team on EBC MVP2
- had 2 people from the prior EBC effort. One was an excellent developer.
- 6 new people added, only 1 from Paramount
- QA person can only manually test UIs, no APIs, no data analysis
- Documentation person didn't have significant role since design had run concurrent to development on the SAME stories
- 2 senior UI developers really are junior level only
- The new UX designer is first class
- HR function is weak
- high pressure, short-term projects are not the place to "train" new teams
- Factory approach to software solutions missing
- Need open standards based platform, technology stacks
- Improve solution value, flexibility, portability avoiding custom cloud services in cloud environments
- Architect solutions as assemblies of common component services ( data services, content services, security services, visualization services, management services, IAM services, JEPL event process services, etc )
- factory pays increasing dividends over time as the services stack value grows to build applications faster, flexibility with better quality over time
- replace large developer teams with fewer, better paid senior developers that can build factory services and deliver solutions on the factory
- compare Feathers, Grails, JHipster on full stack automation
- Carbon Offset Solution Values
- carbon offsets are a payment ( by carbon ton ) from a carbon emitter to a carbon reducer who reduces CO2 output elsewhere ( eg a Tree farm, Solar farm, Wind farm etc)
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Carbon_offset
- https://www.offsetguide.org/understanding-carbon-offsets/what-is-a-carbon-offset/
- https://www.treehugger.com/best-carbon-offset-programs-5076458
- terrapass sells carbon offsets retail at about $10 per ton. Retailers offer monthly subscriptions based on your carbon footprint.
- mm
- more
Carbon accounting concepts and solutions
carbon accounting references
Towards Ontology and Blockchain Based Measurement, Reporting, and Verification For Climate Action - SSRN-id3717389.pdf
https://wiki.hyperledger.org/display/CASIG/Voluntary+Carbon+Offsets+Directory+Research+Project
References
- Securing Climate Benefit: A Guide to Using Carbon Offsets
- Voluntary Ecological Markets Overview by IWA - this document is really about carbon offsets despite its title.
- EDF Trends in Voluntary Carbon Offsets Market
- These Countries have Prices on Carbon. Are they working? (NY Times)
- Taskforce for Scaling Voluntary Carbon Markets Final Report
- Microsoft Carbon Removal - Lessons from an Early Corporate Purchase
- Microsoft Criteria for high-quality carbon dioxide removal
Ratings and Criticisms of Carbon Offsets
A buyer’s guide to soil carbon offsets - Carbon Plan
- BeZero Carbon Ratings Methodology
- The World Needs Better Climate Pledges
- Comments on the Initial Recommendations of the Taskforce on Scaling Voluntary Carbon Markets (TSVCM) from Berkeley Carbon Trading Project and affiliated groups
- Startup That Rates Carbon Offsets Finds Almost Half Fall Short
- Top Airlines’ Promises to Offset Flights Rely on Phantom Credits
- NPR Reporting on Forest Carbon Credits Gets It Wrong in 5 Ways
- Carbon Direct Commentary on Release of the Voluntary Offsets Database
- How Additional is the Clean Development Mechanism
https://wiki.hyperledger.org/display/CASIG/Governance+Research+for+Climate+Action
In a typical climate ecosystem, such as the carbon credits market or climate investing, there are these stakeholders:
- sellers or issuers
- buyers
- intermediaries - transaction services
- gatekeepers - standards organizations, ratings agencies
- other service providers - data services, consultants
Sample carbon accounting app model
https://github.com/opentaps/blockchain-carbon-accounting/blob/main/open-offsets-directory/README.md
The Carbon Offset Marketplace - reference model
Designing, implementing and operating carbon offset projects requires the involvement of a number of parties, stakeholders and authorities. Although the parties involved differ from project to project, some general categories and types of market players can be defined as follows.
Project Owners
The operator and owner of the physical project installation where the emission reduction project takes place. An owner can be any private person, company or other organization.
Project Developers
A person or organization with the intention to develop an emission reduction project. This could be the project owner, a consultant or specialized services provider.
Project Funders
Banks, private equity firms, private investors, non-profit organizations and other organizations may lend or invest equity to fund a project. Some offset program standards have rules as to what kind of funding, aside from offset revenue, is acceptable for an offset project.
Stakeholders
Individuals and organizations that are directly or indirectly affected by the emission reduction project. Stakeholders include the parties interested in developing a specific project (e.g., owner, developer, funder), parties affected by the project (e.g., local population, host community, environmental and human rights advocates) and national and international authorities.
Third Party Auditors – Validators and Verifiers
Almost all offset programs require a third-party auditor to validate and verify a project’s baseline and its projected and achieved emission reductions. Under CDM, the auditors are called Designated Operational Entities (DOEs). To minimize conflicts of interest, the CDM does not allow the validating DOE to also conduct project verification. Most offset programs also have processes for accrediting their third party auditors before they are approved to conduct validation and verification activities.
Standards Organizations
In the absence of national or international legislation, standard organizations define a set of rules and criteria for voluntary emission reduction credits.
Brokers and Exchanges
In the offset credit wholesale market, emission offset buyers and sellers can have transactions facilitated by brokers or exchanges. Exchanges are usually preferred for frequent trades or large volumes of products with standardized contracts or products, while brokers typically arrange transactions for non-standardized products, occasional trades, and small volumes.
Traders
Professional emission reduction traders purchase and sell emission reductions by taking advantage of market price distortions and arbitrage possibilities.
Offset Providers
Offset providers act as aggregators and retailers between project developers and buyers. They provide a convenient way for consumers and businesses to access offset credits from a portfolio of projects.
Final Buyers or End-Users
Individuals and organizations purchase carbon offsets to counter-balance GHG emissions. Therefore, the final buyer has no interest in reselling the offset but will prompt the retirement of the carbon offset credit
Carbon Value of a Tree Farm
How much Co2 do trees absorb?
We had a reader reach out to us with a question I had never really thought about. He asked, “How much CO2 do trees absorb?”. As the answer took some time to research and is a little long-winded, I thought I had better create a post for anyone else wanting to know.
When discussing CO2 absorption by trees, it’s important to remember that elemental carbon locked within the tree differs from carbon dioxide absorbed from the atmosphere. We should note that not all trees absorb the same amount of CO2.
Project Management Challenges
7/13/21 Next Steps
We have wrapped Sprint 1 new features.
We are doing minor support, fixes.
Tony wants a "next sprint" that includes:
Note to Pramod
Sprints for Carbon Mgt App
Sprint 5 Retro
retro.jim>
bad > need better coverage between stories in epics and the actual work getting done
bad > need better job on matching stories to epics every time
bad > need better job of finding the matching story list for an epic when we do customer reviews ( as Amir has been doing )
bad > need better indication of blocked items ( eg a dependency on Word press server environment etc )
bad > need better backlog grooming prior to Sprints ( Jim, Shilpa )
bad > took too long to resolve the blockchain usage model for this app ( vs trading app ) ( Tony, Jim )
good > responsive to customer in our weekly status review meetings
good > work getting done in specific instances by developers
QA environment not setup for Chain API
Frontend and api apps are setup in QA correctly
No AWS environment has been setup for the Chain API in QA
Strategy - minimum work to demo Fabric contracts
Option 1 - test locally to DEV environment on Chain API
create local version of ebc-v2-api that points to Mongo ebc_dev_v2 database
write account and jobQ records there
existing Chain api in DEV will process
view results in Mongo DEV and couchDB DEV
Option 2 - create Fabric environment in QA
Option 3 - reconfigure Fabric DEV environment to be Fabric QA environment
Candidate Solutions
Carbon Offset Production Using Seaweed feed for Cows
https://www.cbsnews.com/news/seaweed-methane-emissions-cows-gas-climate-change/
Managing carbon effectively for ESG
https://www.globalcarbonesg.com/
Learn how we combine carbon sensors, IoT, and Blockchain to help you baseline and manage your carbon footprint.
IBM puts carbon certifications on blockchain
Revolutionizing renewable energy certificate markets with tokenization.pdf
enterprises purchase Renewable Energy Certificates (REC) which represent 1MWh of zero-carbon electricity generated by another entity. The seller of REC could be outside the region or country the enterprise is from. The enterprises then use the RECs to offset their carbon footprint and be compliant with regulations on carbon emissions and green standards.
Companies are looking to newer solutions to capture, analyze and report Environmental Sustainability Goals (ESG) information and reduce their environmental impact. A decentralized and immutable blockchain network, which leverages enhanced characteristics of distributed ledger technology (DLT) can greatly increase the adoption of energy certificates and ensure consumption closely matches the generation.
cumbersome carbon accounting process becomes simplified with significant cost savings, as smart metering and automations are introduced.
exchange of different amounts of energy and granularity of energy certificates. For example, energy certificates can be traded in smaller program time units (PTUs), such as the case of hourly certificates, becoming more in cadence with clearing and settlement
commercial-scale blue hydrogen, derived from natural gas and carbon capture and storage (CCS) and green hydrogen, produced from renewables-based electrolysis processes. This has led to surge in hydrogen project announcements working in conjunction with both the gas and renewable sectors. The energy generation using hydrogen and other mixed sources have some CO2 emission associated and needs to be captured in the certificates.
wide variety of implementations for tokenizing energy certificates, coupled with the fact that they are often at an infancy stage, call out for defining industry standards towards interoperability between networks in different geographical regions across the globe.
self-funding ecosystems are leveraging Ethereum-based (ERC-20) solutions by introducing a dual layer of tokenization. The purpose for public platforms of supporting two layers of tokenization is to provide end-users access to use their platform and contribute to corporate revenues and create exchangeable tokens encapsulating energy certificates.
P2P energy trading
A similar system is being developed by Power Ledger. With its own unique trade matching algorithms, prosumers and consumers can transact available power equitably, without favoring any of the participants. Other characteristics of this platform include pegging of native tokens to a local unit of currency and aggregation of individual meters in a single transaction. The trading group can be configured by either their application host or Power Ledger. WePower also offers an alternative solution on exchanging energy certificates via its native WPR token and auctions. WePower launched a financial derivative product, called Contract for Difference, to mitigate risk in corporate power purchasing agreements (PPAs).
ESG reporting on carbon
As organizations are by now committed to contribute to the Sustainable Development Goals (SDG), there is a need for an elegant solution which enables them to calculate carbon footprint and assist in creating their ESG reporting.
Tokenize energy certificates and reporting
solution (enerT) to tokenize energy certificates using Hyperledger Fabric and Tokens-SDK. Tokenization of energy certificates in a DLT platform can offer an intelligent solution with regards to full disclosure certification of energy. In addition to the amount of energy generated by mixed sources, tokens created in the network could also store other useful characteristic such as CO2 emissions in the energy supply chain.
A tokenized energy marketplace would offer a wide range of trusted certificates in terms of energy types and origin. Such a network would allow suppliers and consumers to trade energy certificates efficiently and inexpensively. A tokenized certification unit would be like what the container did for the shipping industry.
Google Maps GPS API
https://www.businessinsider.com/how-to-find-coordinates-on-google-maps
Currency Codes and Conversion Rates
currencyCodes
currencyConversionRates
https://www.federalreserve.gov/datadownload/Choose.aspx?rel=H10
https://www.bis.org/statistics/xrusd.htm
http://www.portfolioslicer.com/data/file-currency-conversion.html
Meetings
EBC DER trading POC schedule
Jan 5 accounts app works
demo accounts to database again
demo account, device from script to ledger
a> need to move front-end logic to feathers client
Jan 7 approver app works
issue> write account from api to ledger
a> new cd pipeline for approver app
Jan 11 devices in app works
device approvals work
Jan 14 write accounts, devices from api to ledger
a> api wrapper service for ledger accounts, devices
a> demo transactionID on mongo and from Explorer on ledger
i> individual keys for accounts, devices not included now
end Sprint 1
Jan 14 Sprint 2 begins
energy load demo ( Jim )
a> add menu option, api call to load function
Sprint 2 demo
Jan 18 Sprint 3 - offers
review offers UI, api
- create, edit, cancel offer
i> do we need the 19th for this review ??
Jan 25 Sprint 4 - bids
review bids UI, api
- create, edit, cancel bid
i> do we need the 26th for this review ??
Jan 26 Sprint 5 - trades begins
membership certs for accounts
Step-by-step guide for Example
sample code block