Togaf - Enterprise Architecture Framework
Key Points
- OpenGroup TOGAF v10 digital doc
- OpenGroup TOGAF v9.2 doc
- Wiseman - TOGAF v9.1 overview slides
- https://prod.opengroup.org/togaf
- Leanix Togaf Overview
- CIO.com summary of Togaf value
- Architecture Modernization mbook
References
| Reference_description_with_linked_URLs_______________________ | Notes______________________________________________________________ |
|---|---|
| m Enterprise Architecture | |
| m.Enterprise Architecture and Services | |
| https://prod.opengroup.org/togaf | |
| Leanix Togaf Overview. url. link | |
| Togaf relation to other Enterprise Architecture models | |
| Raj G on TOGAF overview - Linkedin | |
| TOGAF Boundaryless Information Flow concept. |
Key Concepts
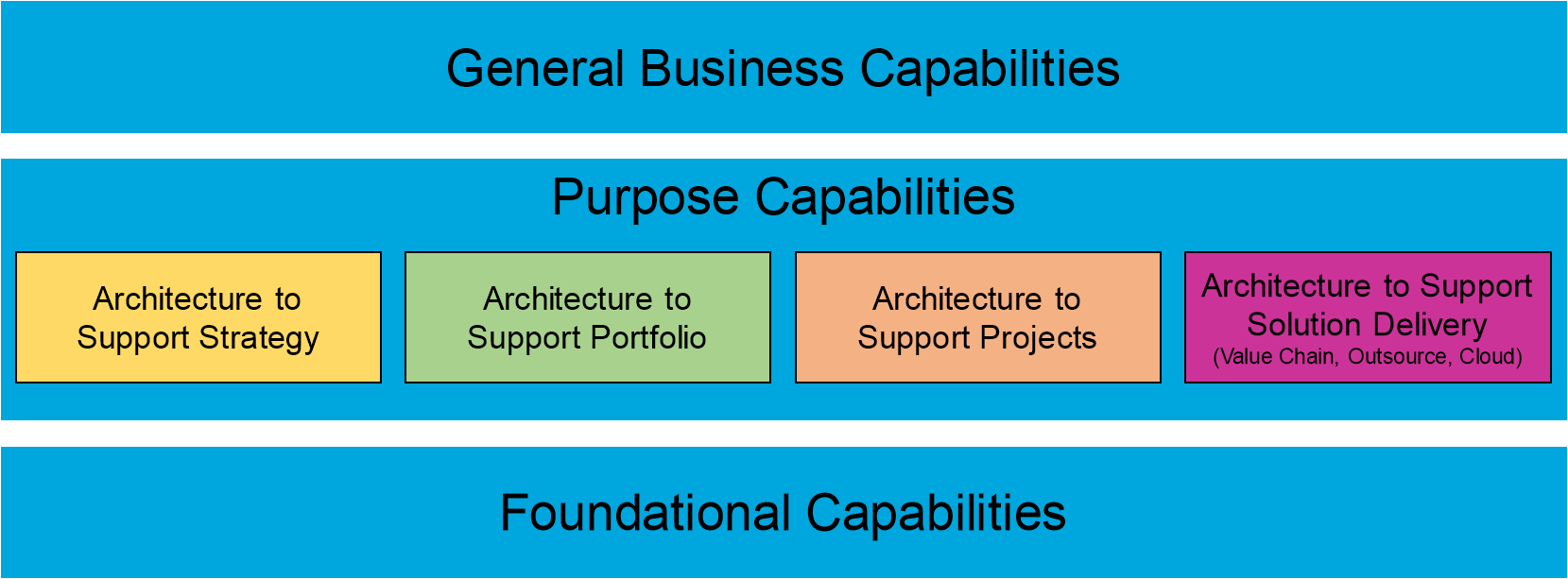
TOGAF Capabilties support Business, IT Services and Infrasrtructure
TOGAF Boundaryless Information Flow concept.
What is Boundaryless Information Flow™?
Boundaryless Information Flow™, a shorthand representation of “access to integrated information to support business process improvements” represents a desired state of an enterprise’s infrastructure and is specific to the business needs of the organization.
An infrastructure that provides Boundaryless Information Flow™ has open standard components that provide services in a customer's extended enterprise that:
- Combine multiple sources of information
- Securely deliver the information whenever and wherever it is needed, in the right context for the people or systems using that information.
The inspiration for Boundaryless Information Flow™ has been captured in the Interoperable Enterprise Business Scenario.
Business Scenario Documents << similar to VCE
Business systems have common needs, capabilities, features as shown in the diagram below
Business Capability Planning
https://pubs.opengroup.org/togaf-standard/business-architecture/business-capabilities.html
TOGAF defines Business Capability Planning but lacks the maturity of the BWI Business Planning Process
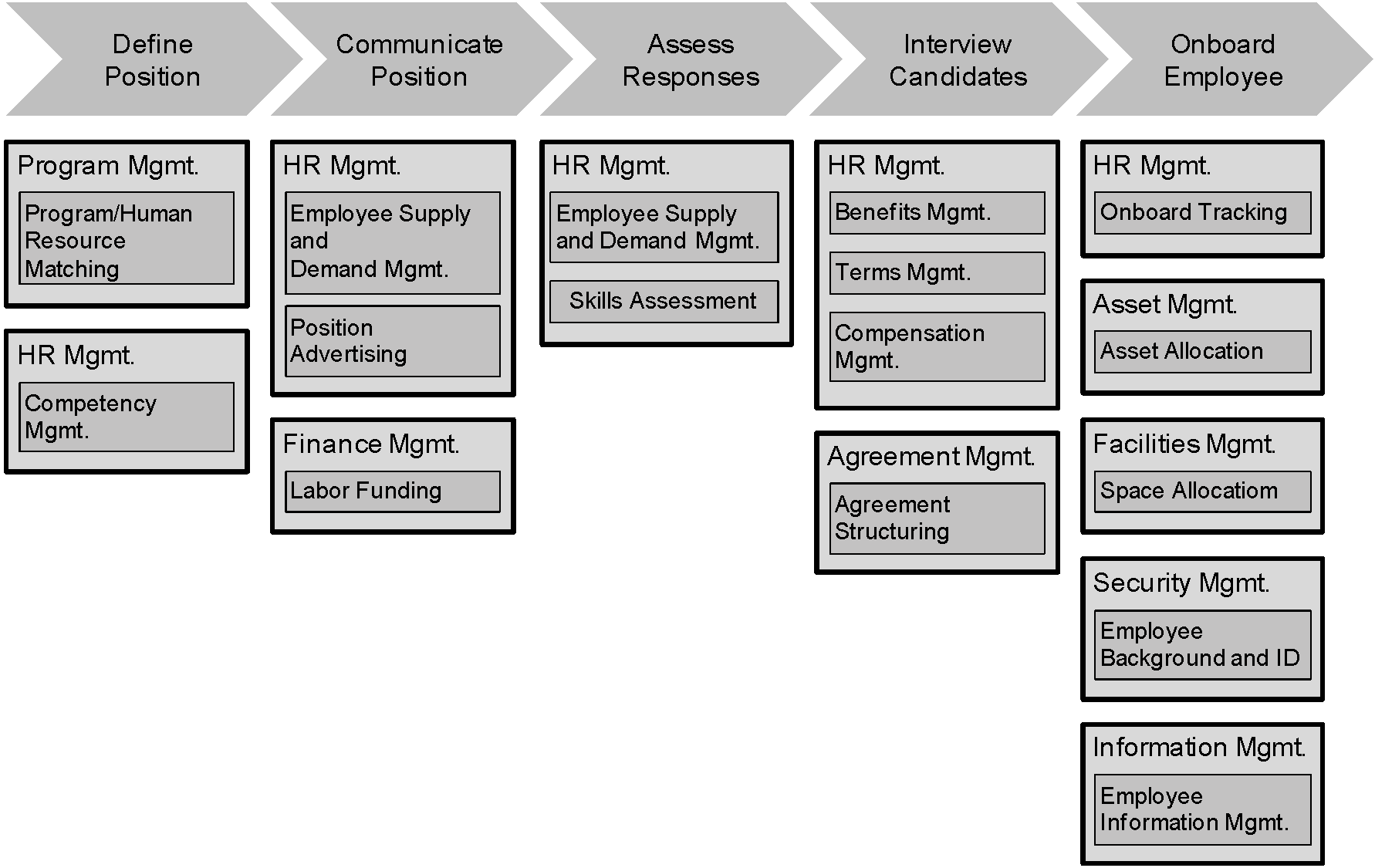
Business Capabilty to Value Stream Mapping
a sample recruit employee value stream and the various value stages mapped to different business capabilities. Each capability enables one or more value stages.
IT Capability Planning
see SWT ISRs, ISPs driven by Business Plans - Strategic and Tactical
IT Infrastructure Planning
Raj G on TOGAF ADM Building Process
The Architecture Development Method (ADM) is a key component of The Open Group Architecture Framework (#TOGAF), which is a widely used framework for developing and managing enterprise architectures. Establishing enterprise architecture capability using ADM involves several key steps. Here's a guide:
1. Understand TOGAF ADM
2. Define Enterprise Architecture Goals
3. Establish #Governance Framework
4. Define Scope and Boundaries
5. Assemble EA Team
6. Training and Awareness
7. Phase-by-Phase Implementation
8. Preliminary Phase
9. Architecture Vision (Phase A)
10. #BusinessArchitecture (Phase B)
11. Information Systems Architecture (Phase C)
12. #TechnologyArchitecture (Phase D)
13. Opportunities and Solutions (Phase E)
14. Migration Planning (Phase F)
15. Implementation Governance (Phase G)
16. Architecture Change Management (Phase H)
17. Continuous Improvement
18. Documentation and Communication
19. Metrics and Measurement
20. Tooling and Technology
21. Feedback Loop
22. Certification and Recognition
23. Community Building
24. #Integration with #IT and #BusinessProcesses
25. Review and Update
By following these steps, organizations can effectively use TOGAF ADM to establish and mature their enterprise architecture capability. The process requires a commitment to continuous improvement, collaboration across departments, and alignment with organizational goals.
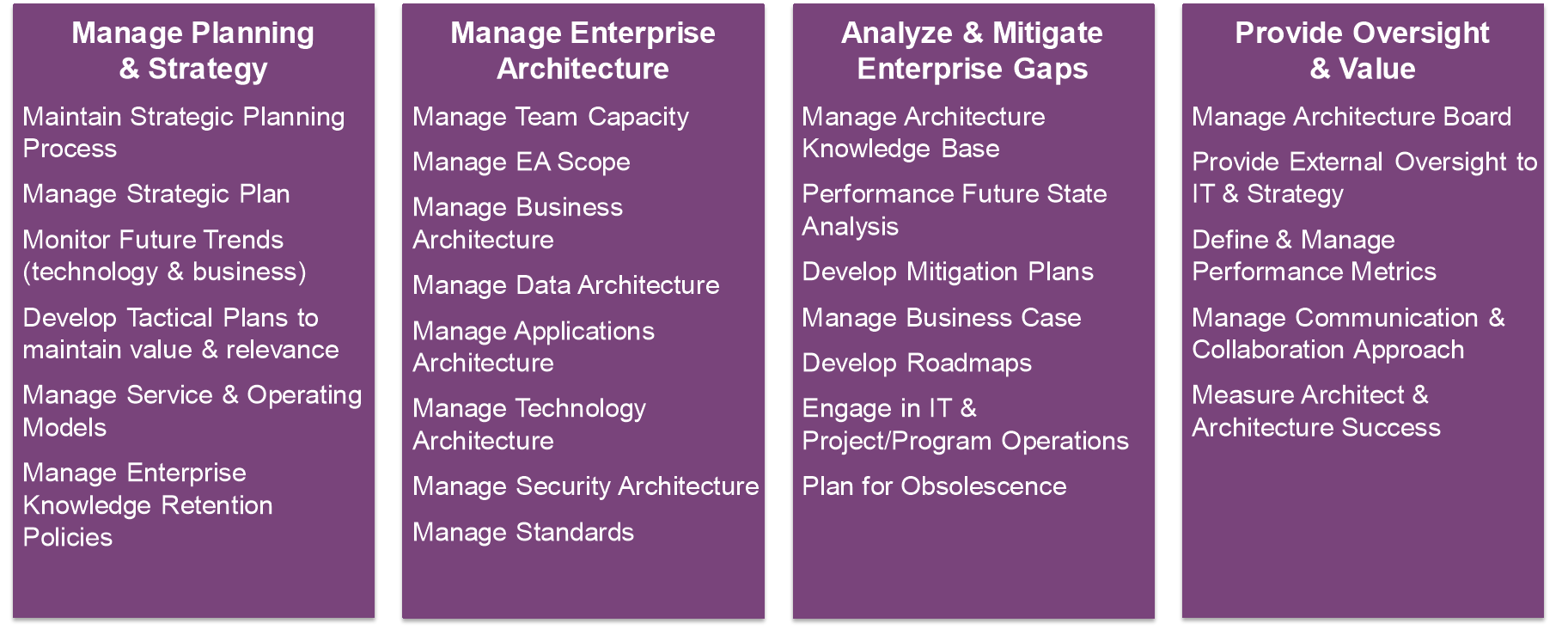
EA Capability Mapping Work
https://pubs.opengroup.org/togaf-standard/togaf-leaders-guide/togaf-leaders-guide_11.html
Define Strategies, Portfolios, Projects, Solutions that Implement Capabilities in the SDP
Enterprise Archtiecture Activities in Support of EA Capabilities
EA Roadmap
Architecture Roadmap task list
https://pubs.opengroup.org/architecture/togaf9-doc/arch/chap32.html#tag_32_02_07
https://pubs.opengroup.org/togaf-standard/togaf-leaders-guide/togaf-leaders-guide_11.html
Raj G on TOGAF ADM overview - Linkedin - part 1
Building Blocks and the ADM (Architecture Development Method)
An architecture is a set of building blocks depicted in an architectural model, and a specification of how those building blocks are connected to meet the overall requirements of the business.
The various building blocks in an architecture specify the scope and approach that will be used to address a specific business problem.
There are some general principles underlying the use of building blocks in the design of specific architectures:
-An architecture need only contain building blocks that are relevant to the business problem that the architecture is attempting to address
-Building blocks may have complex relationships to one another
One building block may support multiple building blocks or may partially support a single building block (for example, the business service of "complaint handling" would be supported by many hashtag#data entities and possibly multiple application components)
-Building blocks should conform to standards relevant to their type, the principles of the enterprise, and the standards of the enterprise
Building Block Design
The process of identifying building blocks includes looking for collections of capabilities or assets that interact with one another and then drawing them together or making them different:
• Consider three classes of building blocks:
• Re-usable building blocks, such as legacy items
• Building blocks to be the subject of development, such as new hashtag#applications
• Building blocks to be the subject of purchase; i.e., Commercial Off-The-Shelf (COTS) applications
• Use the desired level of integration to bind or combine functions into building blocks; for instance, legacy elements could be treated as large building blocks to avoid breaking them apart
Building Block Specification Process in the ADM
The process of building block definition takes place gradually as the ADM is followed, mainly in Phases A, B, C, and D. It is an iterative process because as definition proceeds, detailed information about the functionality required, the constraints imposed on the architecture, and the availability of products may affect the choice and the content of building blocks.
The key parts of the ADM at which building blocks are designed and specified are summarized below.
The major work in these steps consists of identifying the ABBs required to meet the business goals and objectives. The selected set of ABBs is then refined in an iterative process to arrive at a set of SBBs which can either be bought off-the-shelf or custom developed.
The specification of building blocks using the ADM is an evolutionary and iterative process. The key phases and steps of the ADM at which building blocks are evolved and specified are summarized below, and illustrated in figure.
Source: The Open Group
hashtag#TransformPartner – Your hashtag#DigitalTransformation Consultancy
The Journey to Architect
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PLJg1jucpIs
JIM ON ADM >> VCE SDP > better process that has less risk & cost with higher reuse through RDD and Executable Use Cases
VCDP - solutions evolve in a continuous flow through the Value Chain Delivery Process >> see
Like other SDPs, it is circular
TOGAF Overviews
TOGAF Service Guides
https://publications.opengroup.org/guides/togaf/togaf-series-guides
OLAP
BCP 1, 2
MDM
CMDM
Value Streams
Architecture PM
Business Architecture
Architecture Maturity Models
swt>> Capability Maturity Models <<. see VCE SDP
Organization Mapping
ADM Agile
GRM - Government Reference Model
Microservices Architecture
Risk Mgt In Enterprise Architecture
Enterprise Agility Concepts
Digital Transformation Roadmap Development
Business Scenarios
Leaders Guide to Enterprise Architecture
Using TOGAF in Digital Enterprise
TOGAF Digital Business Reference Model
TOGAF 9.2 Guides
How to Develop Enterprise Architecture using ADM
III-RM - TOGAF Integrated Information Infrastructure Reference Model
TRM - TOGAF Reference Model for taxonomy, platform taxonomy
swt>> VCE architecture models for business, solutions, services, information, trust, risk, governance, MDM, data,
TOGAF goverance for SOA
TOGAF Business Models
TOGAF Architecture Skills Map
TOGAF Information Map
TOGAF Details
TOGAF 10 in Action
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0FaU6MHBHBI
- How to develop a TOGAF ADM Architecture Roadmap
- Mapping lifecycle stages, dependencies and impacts using automated views
- Streamlining application portfolios
- Managing legacy systems and technical debt and reducing costs
- Trade-off analysis and cost-benefit analysis to guide decision making and plan future-state business models
- Communicating effectively with the wider business
ABACUS supports cloud-based enterprise architecture, roadmapping & analytics and is certified for TOGAF by the Open Group.
What's New and Different in TOGAF Standard 10th Edition
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pLz3XSSVuNs&t=0s
Togaf 10 Vs Togaf 9 basic difference - 9 mins
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YA38-BOcNQM
experience in leveraging innovation & strategic approach for driving software development with object-oriented techniques and languages in all areas of business, data, application and technology architecture. I am passionate to teach the software professionals on Enterprise Architecture, TOGAF, Cloud migration Architecture, COBIT, Information architecture, Security architecture, Reactive architecture and many more upcoming new technologies.
Compare to TBM
Compare to ITSM
Potential Value Opportunities
Potential Challenges
Candidate Solutions
Step-by-step guide for Example
sample code block