m REST
Key Points
- compare to SOAP, messaging, event streams, transaction tables
- event sourcing vs entity state ( see blockchain for event sourcing and current state: ledger is sourcing, couchdb is current state from ledger )
References
| Reference_description_with_linked_URLs____________________ | Notes____________________________________________________________ |
|---|---|
| m REST API design and tools | api and openapi design details |
| https://microservices.io/ | Microservices |
Comparing_Java_REST_API_Frameworks_-_jconf.dev_2020.pdf https://drive.google.com/file/d/1vr5_jae2KghjIOyB6cpix47KB7fwUv5d/ https://developer.okta.com/blog/2021/06/18/native-java-framework-comparison Build Native Java Apps with Micronaut, Quarkus, and Spring Boot pdf rest-compare-Build Native Java Apps with Micronaut Quarkus and Spring Boot.pdf | Raible - compare Java REST Micronaut, Quarkus, Spring Boot work w Grails, JHipster front ends |
| REST tutorials | |
| https://dzone.com/articles/rest-api-your-guide-to-getting-started-quickly | REST tutorial with Swagger and Docker - Dzone |
| models | |
| https://microservices.io/patterns/data/event-sourcing.html | event sourcing vs current state for entities |
| https://microservices.io/ | Microservices patterns |
Key Concepts
REST API: Your Guide to Getting Started Quickly
We’re going to use a simple service and a web browser to learn about the fundamentals of REST.
https://dzone.com/articles/rest-api-your-guide-to-getting-started-quickly
https://drive.google.com/open?id=1l68fa7OE4iYn9RhZFtuXIGnsGm8mo-gz
For this tutorial, you’ll need a system with Docker installed. You can find the instructions for your computer here.
First, follow the instructions and install Docker.
Then, once you’ve completed the installation, you can download and run our sample REST server.
Finally, start the server with this command:
$ docker run -p 8080:8080 -d -–name tutorial ericgoebelbecker/resttutorialMicroservices Event Sourcing pattern tracks state reliably
https://microservices.io/patterns/data/event-sourcing.html
problem
How to reliably/atomically update the database and publish messages/events?
forces
2PC - 2 phase commit not an option
solution
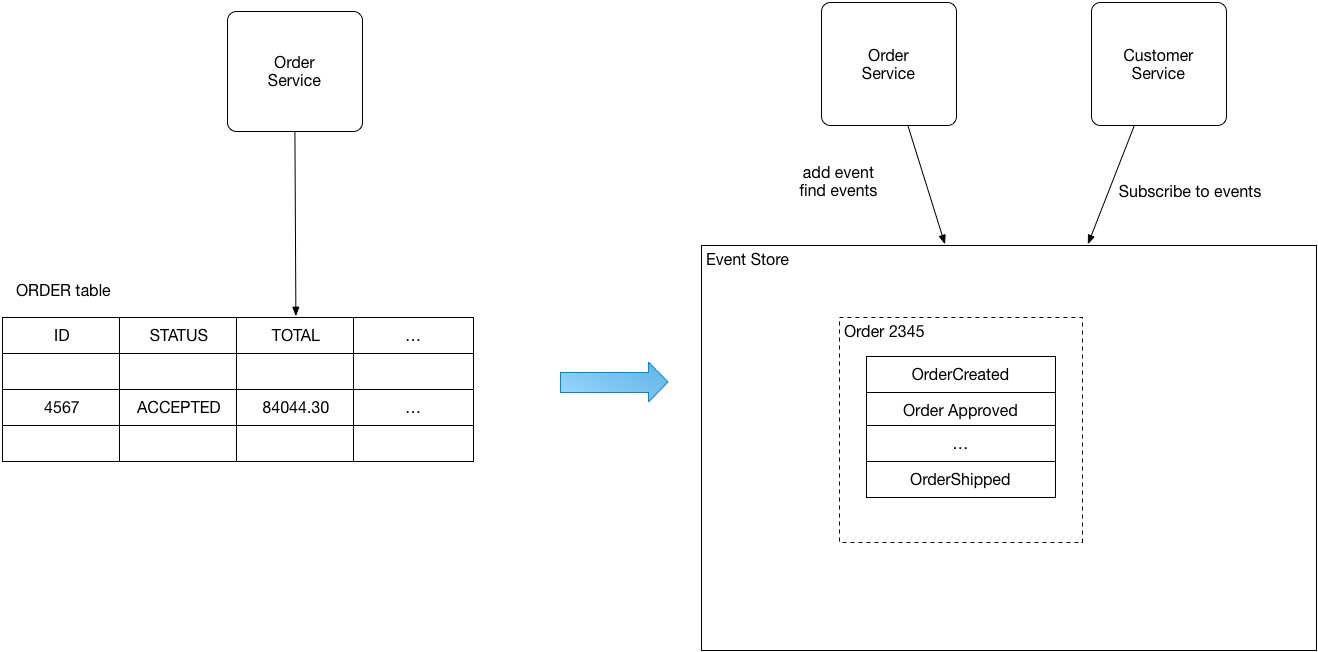
A good solution to this problem is to use event sourcing. Event sourcing persists the state of a business entity such an Order or a Customer as a sequence of state-changing events. Whenever the state of a business entity changes, a new event is appended to the list of events. Since saving an event is a single operation, it is inherently atomic. The application reconstructs an entity’s current state by replaying the events.
Applications persist events in an event store, which is a database of events. The store has an API for adding and retrieving an entity’s events. The event store also behaves like a message broker. It provides an API that enables services to subscribe to events. When a service saves an event in the event store, it is delivered to all interested subscribers.
Some entities, such as a Customer, can have a large number of events. In order to optimize loading, an application can periodically save a snapshot of an entity’s current state. To reconstruct the current state, the application finds the most recent snapshot and the events that have occurred since that snapshot. As a result, there are fewer events to replay.
example
Customers and Orders is an example of an application that is built using Event Sourcing and CQRS. The application is written in Java, and uses Spring Boot. It is built using Eventuate, which is an application platform based on event sourcing and CQRS.
The following diagram shows how it persist orders
Instead of simply storing the current state of each order as a row in an ORDERS table, the application persists each Order as a sequence of events. The CustomerService can subscribe to the order events and update its own state.
Here is the Order aggregate:
Here is an example of an event handler in the CustomerService that subscribes to Order events:
It processes an OrderCreated event by attempting to reserve credit for the orders customer.
There are several example applications that illustrate how to use event sourcing.
Resulting Context
Event sourcing has several benefits:
- It solves one of the key problems in implementing an event-driven architecture and makes it possible to reliably publish events whenever state changes.
- Because it persists events rather than domain objects, it mostly avoids the object‑relational impedance mismatch problem.
- It provides a 100% reliable audit log of the changes made to a business entity
- It makes it possible to implement temporal queries that determine the state of an entity at any point in time.
- Event sourcing-based business logic consists of loosely coupled business entities that exchange events. This makes it a lot easier to migrate from a monolithic application to a microservice architecture.
Event sourcing also has several drawbacks:
- It is a different and unfamiliar style of programming and so there is a learning curve.
- The event store is difficult to query since it requires typical queries to reconstruct the state of the business entities. That is likely to be complex and inefficient. As a result, the application must use Command Query Responsibility Segregation (CQRS) to implement queries. This in turn means that applications must handle eventually consistent data.
Microservices patterns, frameworks
see m Services: SOAP, REST, API
Microservices - also known as the microservice architecture - is an architectural style that structures an application as a collection of services that are
- Highly maintainable and testable
- Loosely coupled
- Independently deployable
- Organized around business capabilities
- Owned by a small team
The microservice architecture enables the rapid, frequent and reliable delivery of large, complex applications. It also enables an organization to evolve its technology stack.
Potential Value Opportunities
Potential Challenges
Candidate Solutions
Step-by-step guide for Example
sample code block