Services Management, Maturity and Metrics
Key Points
- services management has defined goals, models for delivery, operations, support, maintenance, retirement
- services delivery process defined
- services operations standards defined as operations service tiers normally
- services measured at runtime based on execution with results captured summarized by tools like Promtheus, Grafana
- services maturity models exist for referemce
- services catalog can be reviewed to assess current maturity levels vs planned service strategies to identify opportunities
References
| Reference_description_with_linked_URLs_______________________ | Notes______________________________________________________________ |
|---|---|
| m Business Process Solution Design Tools | |
| s Blockchain Opportunity Assessment - BOA | |
| m Consulting Process | sth #bdc |
| VCE > Value Chain Economies are virtual economic communities | |
| Design Tools | |
| m REST API design and tools | |
| m REST | |
| m Design Patterns | |
| m Design Engineering Themes | |
| api-service-mgt-v1 gdoc | |
| api-service-mgt-v1.docx | |
| https://itsmacademy.com/content/WHATIS_The_ITIL_Maturity_Model.pdf | |
| https://www.infopulse.com/blog/itsm-maturity-assessment-checklist | |
Architecture Themes
ascrum definitions
Concepts on Service Maturity
https://docs.splunk.com/Documentation/Splunk/latest/RESTREF/RESTmetrics
https://spiresearch.com/psmaturitymodel/service-maturity-levels.html
https://plextrac.com/capability-maturity-model-cmm/
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/cmmi/cmmi-maturity-levels.htm
https://www.megatronicstech.com/maturity-level-of-technology/
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Capability_Maturity_Model
Key Concepts
Key Concepts for Service Maturity
- Correctness: The microservice does what it is intended to do without causing errors.
- Reliability: The microservice can perform its intended function consistently over time.
- Efficiency: The microservice provides value for the resources it consumes (like memory, CPU time, etc.).
- Resilience: The microservice can handle failures gracefully, both within itself and when other services fail.
- Scalability: The microservice can handle increased load by either scaling up (using more resources on a single node) or scaling out (distributing the load across multiple nodes).
- Manageability: The ease with which the microservice can be monitored, managed, and updated.
- Operability: The degree to which the microservice supports the tasks that operators need to do, like deploying new versions, scaling, diagnosing problems, etc.
Reference: The Maturity of Microservices
Importance of Measuring Service Maturity
Measuring service maturity is crucial for several reasons:
- Quality Assurance: Helps to ensure that all microservices meet the organization's standards for performance and reliability.
- Risk Mitigation: Identifies potential issues before they become larger problems.
- Resource Allocation: Informs decisions about where to invest time and resources for improvement.
- Performance Benchmarking: Provides a means of tracking improvement over time.
- Return on Investment: Mature services provide more value for the resources consumed, increasing the return on investment.
Reference: Microservices Maturity Assessment
Ideas for Measuring Service Maturity
- Establish Metrics: Define what constitutes maturity for your microservices, considering aspects like reliability, scalability, resilience, etc.
- Automated Testing and Monitoring: Use automated tools to continuously monitor and test your microservices, providing real-time feedback on their performance and maturity.
- Service-Level Objectives (SLOs) and Service-Level Indicators (SLIs): SLOs define the level of service you aim to provide, and SLIs are the metrics that measure your actual performance against these objectives.
- Incident Response and Postmortem Analysis: When something goes wrong, have a plan to fix it quickly and then conduct a postmortem analysis to learn from it and improve the maturity of the service.
- Regular Reviews: Regularly review the maturity of your services to identify trends, pinpoint areas for improvement, and track progress over time.
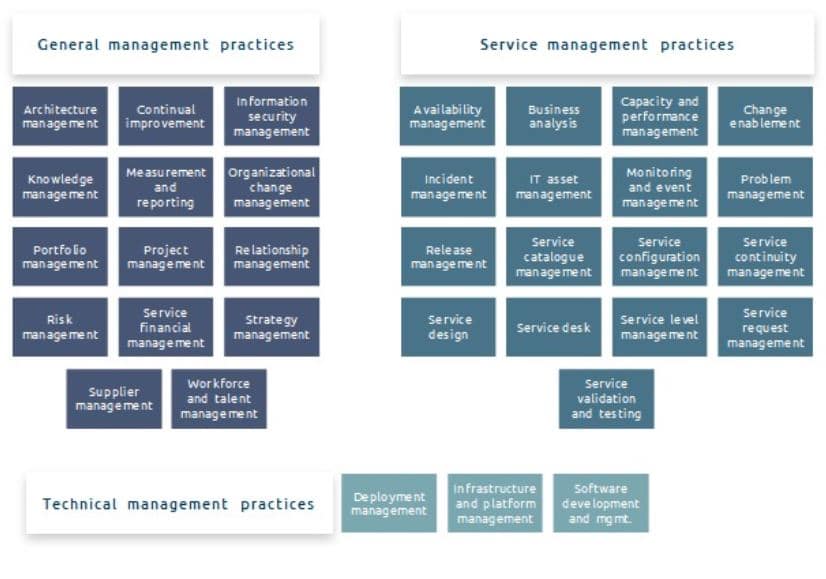
ITIL 4 Summary
ITIL SVS - Service Value System - Foundation for Service Management
https://www.owlpoint.com/itil-4/itil-service-value-system/
Principles
The guiding principles helps an organization’s decision making by ensuring there is a shared understanding and common approach to service management across the organization. Each of the guiding principles can be used to evaluate whether an approach or decision meets the fundamentals of the organizations goals and helps sets the organization’s behaviors and culture.
Governance
Governance ensures that the actions of the organization are aligned properly with the strategic direction and goals established by the sponsor groups or governing bodies. It is governance that ensures that value is actually achieved, not just talked about as a target.
Service Value Chain
The Service Value Chain is an operating model for the creation, delivery, and continual improvement of services. The service value chain represents a set of key activities that leverage various practices to form different value streams. These value streams can be adapted for different types of organizations, including those that have distributed IT versus a centralized IT.
Practices
Practices are the evolution of processes and functions from previous versions of ITIL. They are a set of organizational resources, based on the elements of the four dimensions of service management, designed for performing work or accomplishing an objective.
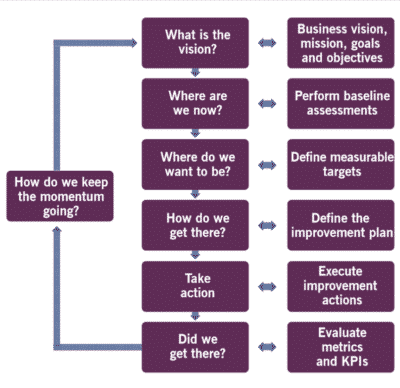
Continual Improvement
Continual Improvement is an ongoing set of organizational activities at all levels that ensure that the organization’s performance continues to meet the evolving objectives of its key stakeholders.
ITIL Maturity Assessments
https://www.owlpoint.com/itil-maturity-model-and-itil-assessment-qa/
Maturity Model vs Maturity Assessment
The ITIL Maturity Model establishes the criteria to achieve each level of maturity of the Service Value System and the capability of each of the 34 ITIL 4 Practices. The ITIL Assessment is a process of evaluating an organization against a specific set of practices and usually the organization’s adoption of a Service Value System using the criteria established by the ITIL Maturity Model.
3 types of Assessments
There are 3 types of assessments that have been defined by AXELOS. They are:
- Comprehensive Assessment – The evaluation of 7 or more practices as well as the components of the ITIL Service Value System
- Capability Assessment – The assessment of selected practices but does not include the SVS components
- Maturity Assessment – The review of the SVS components and up to 6 practices
Capability Maturity Model
CMM Level 1 — Initial
Organizations in the Initial level of the CMM are getting real work done, but often are finishing this work on a delayed timeframe and over their allotted budget
Goal > track work to budget
CMM Level 2 — Managed
Organizational process in the Managed level of the CMM is being managed at least on the project level. This is a huge area of improvement, as the work of the collective is able to be planned, performed, measured, and controlled.
Goal > move to proactive vs reactive projects and solutions
CMM Level 3 — Defined
Organizations in the Defined level of the CMM are on their way to a healthy composition and structure. Processes in level 3 are well characterized and understood, and often are described with standards, procedures, tools, and methods. What really makes the Defined level stand out from the Managed level is the scope of the standards, process descriptions, and overall procedures.
Goal > more usage monitoring and opportunity to expand quantification in all activities along with automation
CMM Level 4 — Quantitatively Managed
Organizations in the Quantitatively Managed level of the CMM are realizing most of their full potential. The big drive in organizations and teams working at level 4 is the inclusions of data and other quantitative information in their processes. The improvement objectives for these individuals are predictable, and all align to meet the expectations of both internal and external stakeholders. These objectives are made based on the needs of the customer, end users, organization, and process implementers.
Goal > automation of service capabilities to fit demand patterns based on quantitative inputs
CMM Level 5 — Optimizing
The ultimate level of maturity for organizations and teams is level 5, Optimizing. The Optimizing level is focused on continuous improvement, and is built to pivot and respond to opportunity and change as it presents itself. This agility is based on the level of stability that the organization has built up over time. This stability allows a baseline of processes that can then be tweaked to better serve the needs of the organization at that present moment. To speak simply: This is an organization firing on all cylinders
Goal > continue optimization and adaptivity as organization grows, changes
CIP - Continuous Improvement Process
BWC defined in. 1985
The purpose of Continual Improvement is to ensure service and products align – and remain aligned – to the Business continuously.
https://www.infopulse.com/blog/itsm-maturity-assessment-checklist
itsm-ebook-modernizing-it-services-with-itsm. link
itsm-ebook-modernizing-it-services-with-itsm.pdf file
https://www.infopulse.com/blog/itsm-maturity-assessment-checklist
4 Signs Your ITSM is Not Mature:
- Your ITSM processes are ad hoc and undocumented.
- Your processes are repeatable but uncoordinated.
- Your ITIL procedures are in place, but not followed.
- You have set practices and SLAs, but not full automation.
How to resolve Level 1 issues:
- Focus on redefining IT service management practices and processes. Each process needs to be aligned with the relevant business context for higher efficiency. Introduce repeatability into all the daily actions and promote the habit of acting according to the set practices.
- Create preliminary Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs). Work with the IT leaders to determine the optimal set of procedures for common tasks and requests. Create the necessary documentation and consider training to build up the lacking IT service management skills.
- Start building a business case for automation. Based on the defined processes and SOPs, start assessing IT service management software vendors that could provide toolkits for automation. JIRA service desk is a basic solution, popular with technical teams. ServiceNow is a more comprehensive, enterprise-grade platform.
How to resolve Level 2 issues:
- Resolve IT isolation. On an inner level, focus on further process formalization, documentation, and automation. Commit to creating a more diverse range of resources and SOPs every individual can refer to. Set clear communication policies to promote a timely escalation of issues and increase collaboration between individuals. Start involving more business stakeholders to reduce the confusion around priorities, requirements, and overall strategic direction.
- Procedure standardization. Continue your efforts of consolidating redundant processes, adding automation, and increasing the levels of standardization across all repeatable procedures. ITSM software offers a wide range of benefits to help standardize your processes. It can be used to centralize and automate repetitive tasks, reduce errors, and improve efficiency.
- Adopt tiered support/service desk. To improve service level consistency, start breaking down your ITSM center into tiers to “filter” different issues by type, priority, and complexity. Introduce automation (self-service) for Tier 0 issue resolution and map out proper escalation procedures for more complex ones. Ensure that each Tier is adequately staffed, and every specialist has sufficient access, knowledge, and tools for resolving their set of tasks. Consider an external IT infrastructure management service provider if you lack in-house resources.
How to resolve Level 3 issues:
- Address cultural resistance. Work further with individuals to encourage the adoption of the set policies. Gather feedback for improvements and promote further knowledge sharing practices to speed up the adoption of new ITIL procedures. Address issues both at the grassroots and at management levels.
- Adopt integrated IT service management solutions. IT service management tools provide real-time visibility into the performance of an organization’s applications and devices. To ensure consistency and higher levels of coordination of all IT management and maintenance activities, address multi-capabilities vendors that provide consolidated visibility into different functions and assets, as well as enable centralized monitoring of tasks execution.
How to resolve Level 4 issues:
- Introduce a greater extent of automation: At this point, your company needs to focus on optimization to improve the team’s performance, reduce execution times, and improve customer services. Robotic process automation (RPA) solutions for ITSM process automation are one option to consider. ML-powered predictive infrastructure monitoring systems and intelligent ticket routing engines are another area of interest for ITSM leaders. In 2022, improving the team's productivity through the use of automation solutions was named a top priority for 57% of organizations.
Potential Value Opportunities
VCE > Value Chain Economies: micro economies for value-chain communities ( VCC )
BWI: Barry Wright BEP - Business Excellence Program
Potential Challenges
ITSM and Service Maturity Assessments
Service Maturity Concepts
Resources
https://itsmacademy.com/content/WHATIS_The_ITIL_Maturity_Model.pdf
https://about.gitlab.com/handbook/engineering/infrastructure/service-maturity-model/
ITSM
ITSM platform functional concepts. - Gartner
ITSM levels
https://www.infopulse.com/blog/itsm-maturity-assessment-checklist
https://www.infotech.com/research/service-management-maturity-assessment-tool
W3school on api / capabilities
Oai
Api design patterns
Api design practices
ETE
Functional, NFR, linting for patterns / reuse
E2M2 for higher reuse
Smarter apps, services using interfaces in xucs to find / gen / apply ABC parts
https://www.ibm.com/garage/method/practices/code/tool_lint/
Topics
Background
ITSM, ITSM levels,
Service criticality
Service SLA, SLOs, SLIs
Environment policies
SDP life cycle
Maturity Dimenions
Management models
Service Dimensions and related Policies
Functional
NFR
Economic
Governance
Operations
Support
Capability Mapping
Service maturity is a general conceptual framework to measure service maturity
If the solution and the environment are measuring KPIs, SLOs, incidents by severity level, automated operations management etc then service maturity isn’t a desk exercise with limited validity but a sustainable reflection of the quality of the managed environment covering the SDP for clients and operators of the environment.
CMM levels applied to Service Maturity
Modes
Definition, delivery, operation, support, improvement
Each mode has operational features / attributes
ascrum NFR can be applied by use case to each mode
Service Assessment Audit
Service 5WH
Definition
Clients
Client survey results
ITSM - SLA, SLO, SLI, incidents, root cause summary
Alignment with IT Strategy, Operations
Environments
Audit Areas > VCRS for each Dimension
Findings
Recommendations by area
Improvement Priorities
Budgeted Projects
Candidate Solutions
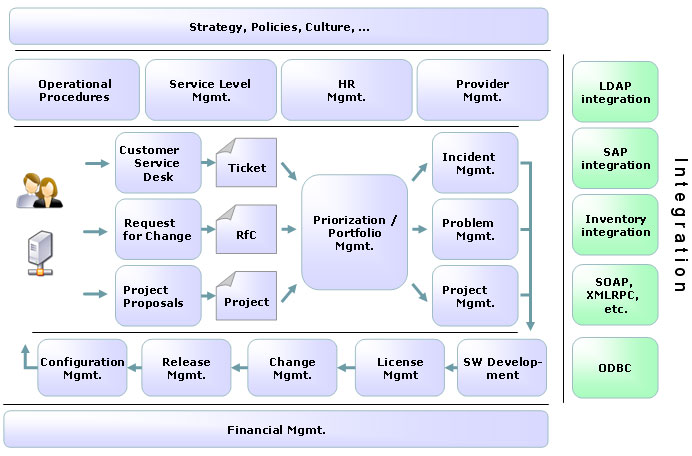
http://www.project-open.com/en/module-itsm
Covers
- Incident Management
- Problem Management
- Change Management
- Configuration Management
- Release Management
- Service Level Management
- Defect Management
- SLA Management
- Configuration Management
http://www.project-open.com/en/process-itsm-service-level-management
Step-by-step guide for Example
sample code block